PSEB Class 10 Biology Solutions For Chapter 2: How Do Organisms Reproduce?
Reproduction
The process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves is called reproduction. It can occur in two ways – Asexual and Sexual.
Difference Between Asexual And Sexual Reproduction
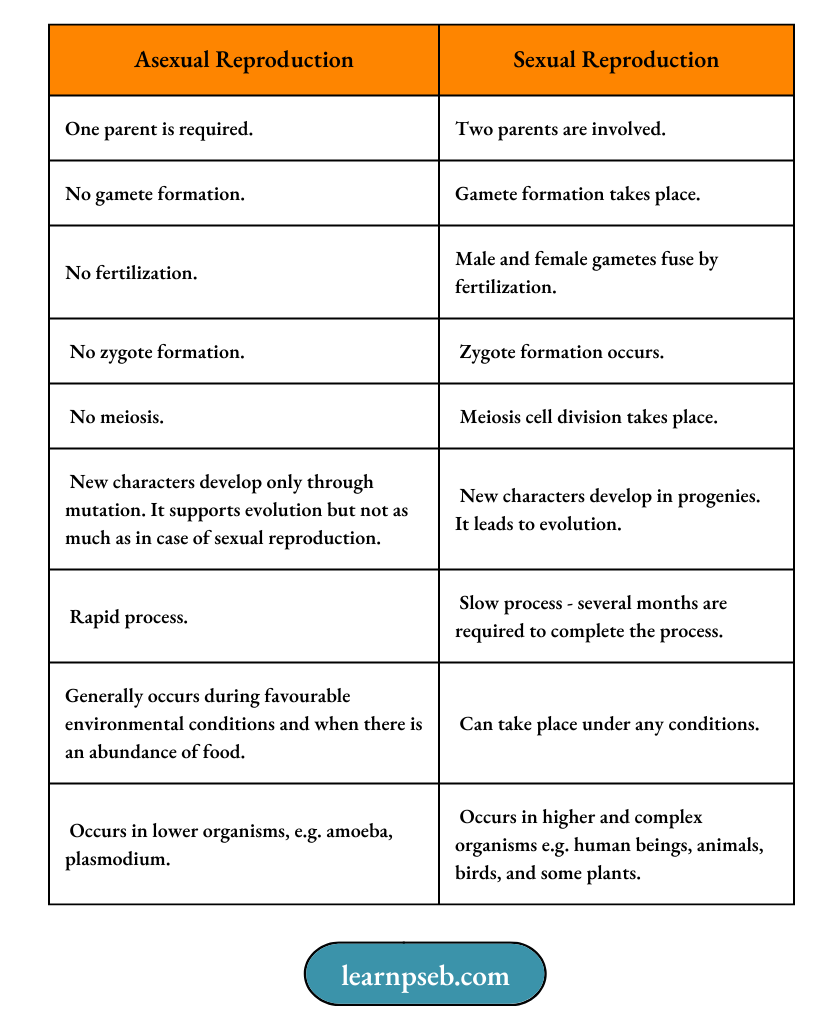
Note:
- Both kind of reproduction, i.e., asexual and sexual, can take place both in unicellular and multicellular organisms.
- Irrespective of the type by which an organism reproduces, the first step in reproduction always involves division of nucleus. This is followed by division of cytoplasm.
Life processes class 10 notes
Advantages Of Sexual Reproduction
- Variations In Characters- Since sexual mode of reproduction allows more variation, and variations ensure survival of species in changing environments, sexual mode of reproduction is beneficial and desirable.
- Ability To Adapt In Changing Environments – More variations means greater ability to adapt in changing environments, which in turn is beneficial for survival.
- Evolution of New Traits – Variations in genetic material (characters) arise due to errors in DNA copying mechanism. In this way, each new variation is made in a DNA copy that already has variations accumulated from previous generations. Combining variations from two or more individuals leads to creation of new combinations leading to evolution of species.
- Suppression of Harmful Traits – During DNA copying, the harmful traits often remain naturally suppressed due to reshuffling of gene pairs that occur during formation and fusion of gametes.
PSEB Class 10 Biology Solutions Chapter 2
Read And Learn More PSEB Class 10 Biology
Limitations Of Sexual Reproduction
- It takes time and energy to find a mate and reproduce.
- Reproduction through sexual means is uncertain as some mates may be infertile or fertilization of gametes may not occur despite numerous attempts.
- Favourable genetics might not be passed to the offspring.
- Fewer offspring are typically produced.
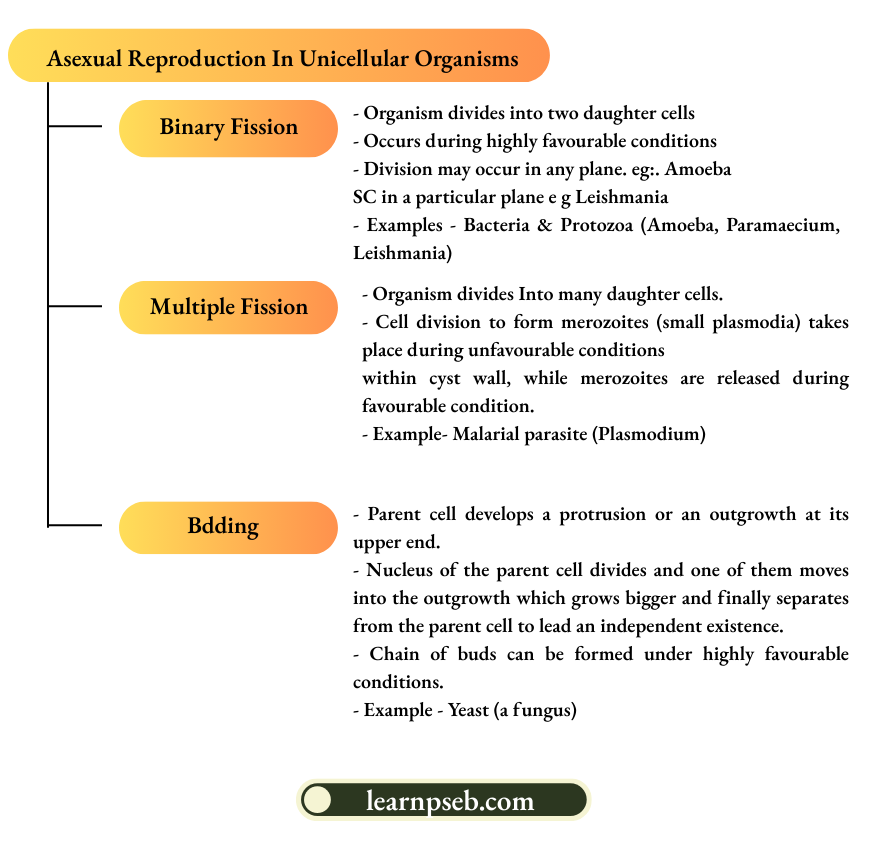
Asexual Reproduction In Unicellular Organisms
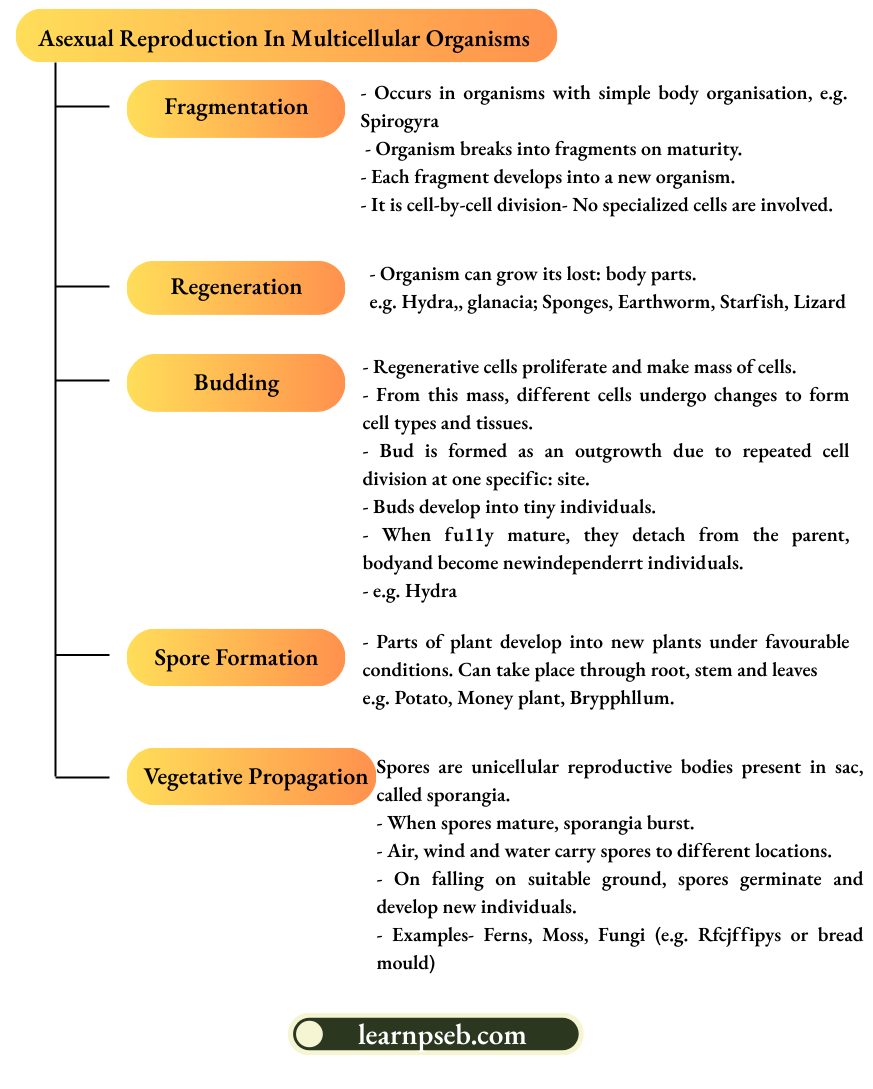
Advantages Of Vegetative Propagation
- Vegetative propagation is used to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, or grapes for agricultural purposes.
- Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- Vegetative propagation is useful for propagation of plants such as banana, orange, rose and jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
- All plants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically similar to the parent plant and have all its characteristics.
Life processes class 10 PSEB solutions
Maintenance Of Number Of Chromosomes In Sexual Reproduction
Maintenance of number of chromosomes in sexual reproduction occurs with the help of meiosis. Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information.
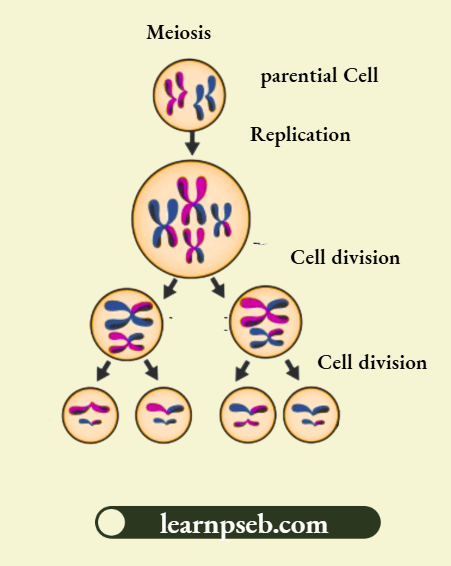
- Sexually reproducing organisms have two kinds of cells, viz. somatic cells (or non-reproductive cells) and reproductive cells.
- Somatic cells have 22 pairs of chromosomes – one member of each pair comes from father and the other comes from mother, i.e., somatic cells are diploid in nature.
- Reproductive cells (called gametes) have only half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA as compared to somatic cells, i.e., reproductive cell is haploid in nature.
- Reduction in number of chromosomes in reproductive cells is achieved by meiosis.
- Two different reproductive cells (one male and the other female) unite together (n+n) to form a zygote (2n). In humans, each gamete (egg and sperm) contains 23 chromosomes, and the zygote formed by their union has 23+23 = 46 chromosomes, thereby resulting in re-establishment of the number of chromosomes and the DNA content in the new generation.
Life processes class 10 PSEB solutions
Parts Of A Flower And Their Functions
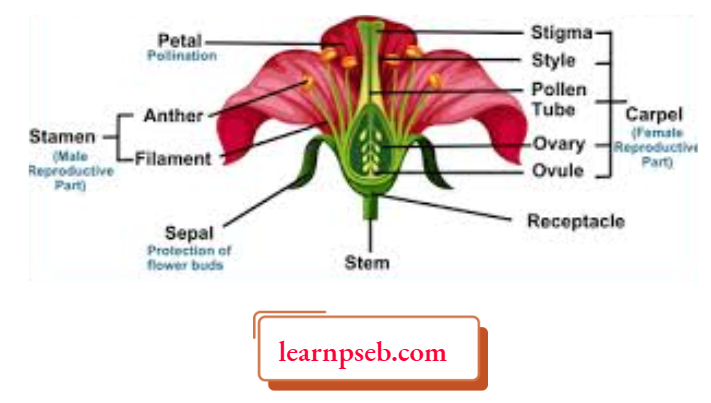
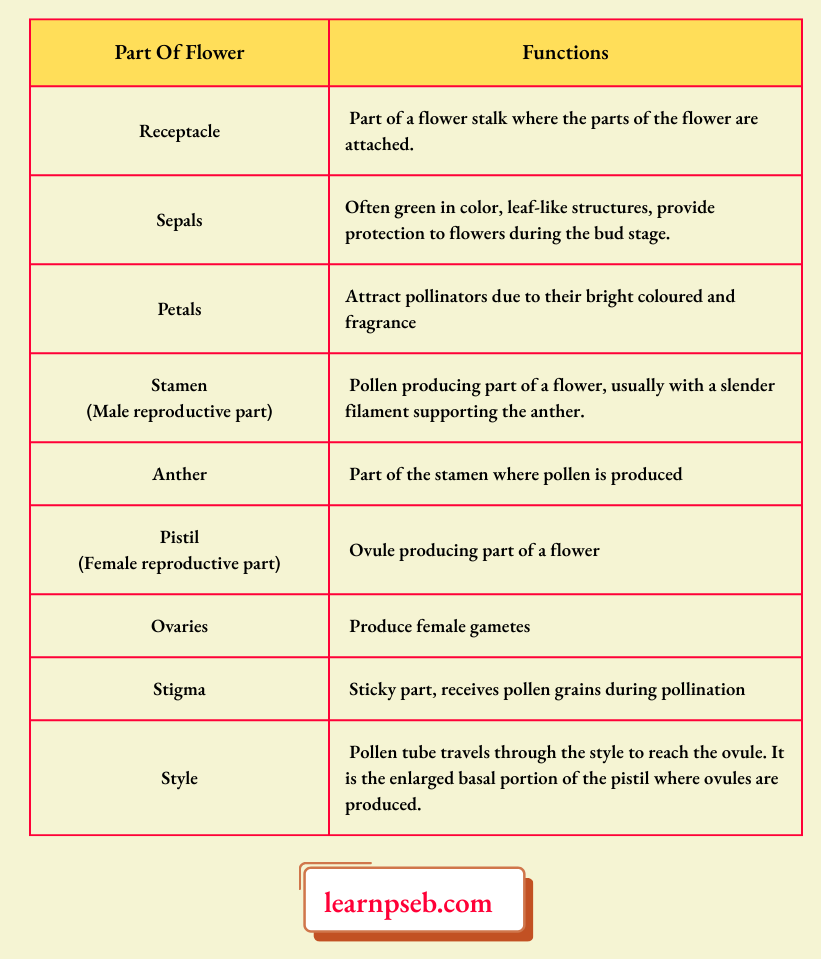
How Do Organisms Reproduce PSEB Class 10 Notes
Steps Involved In Reproduction In Flowering Plants (Angiosperms)
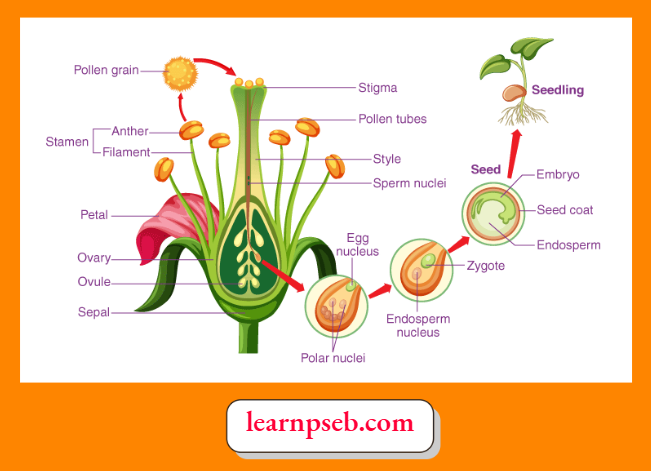
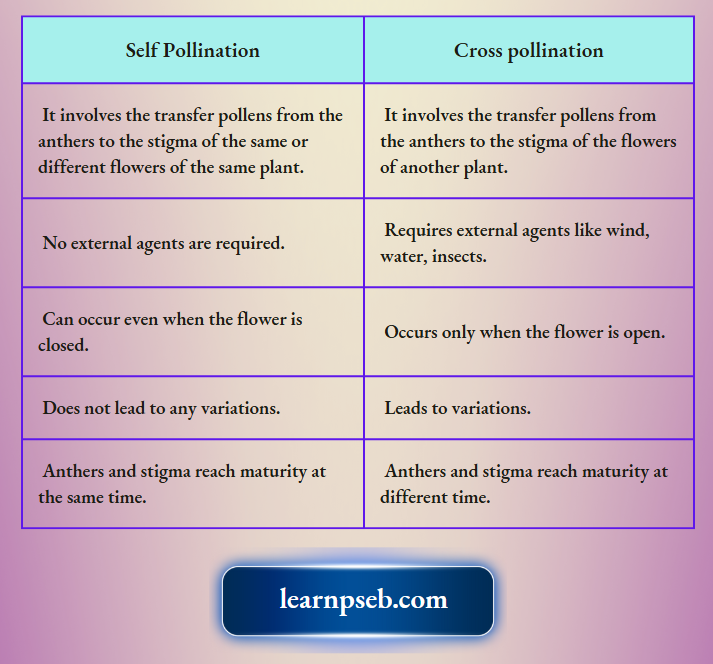
- Reproduction in flowering plants begins with pollination, the transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of the flower.
- If the transfer takes place to the stigma of flower of the same plant, it is called self-pollination.
- If the transfer takes place to the stigma of flower of another plant, it is called cross-pollination.
- Once the pollen grain reaches the stigma, a pollen tube grows from the pollen grain to an ovule.
- Two sperm nuclei develop. One of them unites with the egg nucleus and produces a zygote. The other unites with two polar nuclei to produce an endosperm that stores food for the development of a plant.
- Zygote develops into seed and seedling.
Life processes class 10 PSEB solutions
Male And Female Reproductive Organs Of Flowering Plants (Angiosperms)
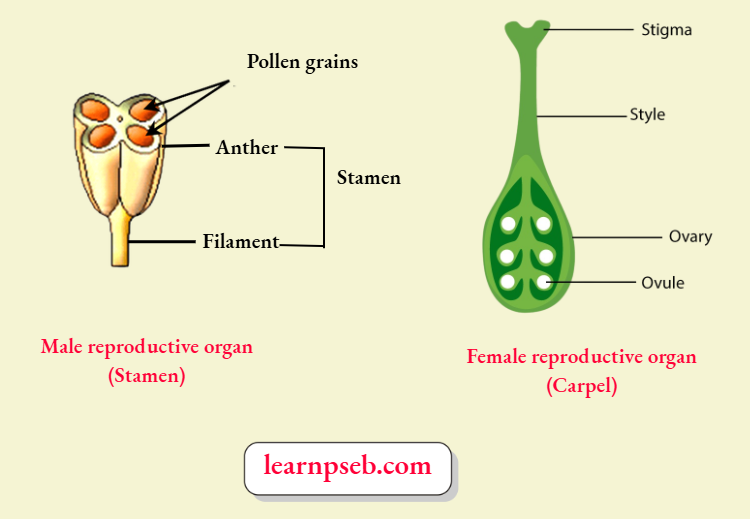
Five Stages In Germination Of Seed
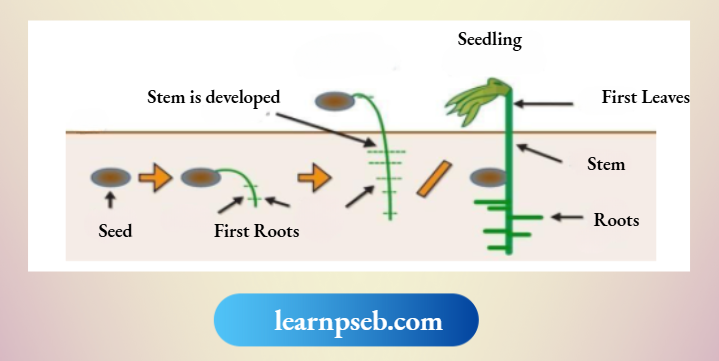
- Water fills the seed. This is called Imbibition.
- Water activates the enzymes that begin the growth of the plant.
- Seed grows a root to access water underground.
- Seed grows shoots that grow towards the sun.
- Shoots grow leaves, etc.
Life processes class 10 extra questions
Difference Between Self-Pollination And Cross-Pollination
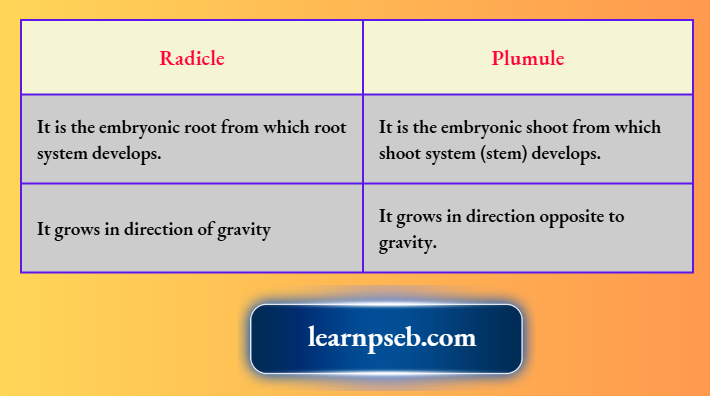
Difference Between Radicle And Plumule
Points To Remember About Sexual Reproduction In Human Beings
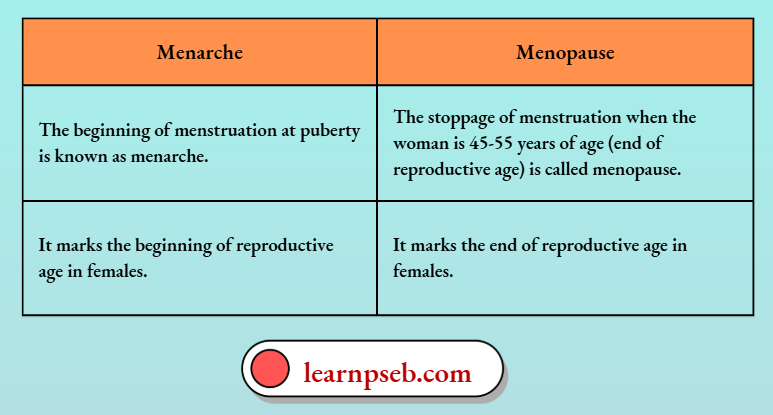
- Human beings become reproductively active from the onset of puberty.
- Puberty is the period during adolescence when the rate of general body firowth begins to slow down and reproductive tissues begin to mature. A boy or girl becomes sexually mature in puberty.
- Puberty is a slow process spread over months and years. This is because while the body of the individual organism is growing to its adult size, the resources of the body are mainly directed at achieving this growth. While that is happening, the maturation of the reproductive tissue is not likely to be a major priority.
- Onset of puberty in males occurs between 11 to 13 years of age, while in females it occurs between 10 to 12 years of age.
- Puberty is associated with many physical, mental, emotional and psychological changes.
PSEB Class 10 Biology Important Questions Chapter 2
Life processes class 10 MCQ with answers
The physical changes that occur during puberty are called secondary sexual characters.
- Secondary sexual characters common to both boys and girls – Growing of thick dark hair in arm pits and genital area; appearance of thinner hair on legs, arms and face; skin becomes oily and appearance of pimples on face.
- Secondary sexual characters that occur only in boys – Appearance of beard and moustache, voice begins to crack, reproductive organs develop and start producing releasing sperms, penis occasionally begins to become enlarged and erect.
- Secondary sexual characters that occur only in girls – Increase in breast size, darkening of the skin of nipples, and start of menstruation.
Life processes class 10 MCQ with answers
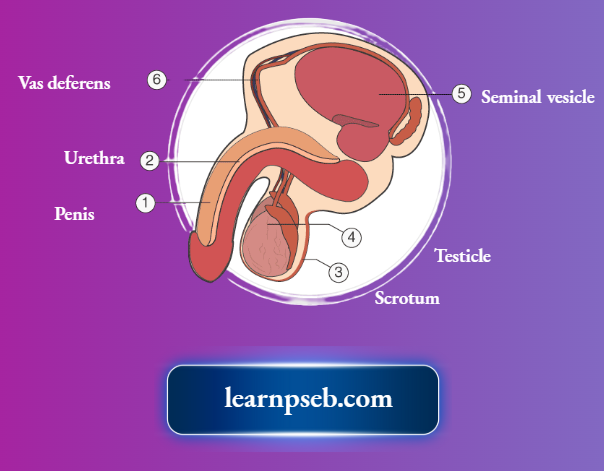
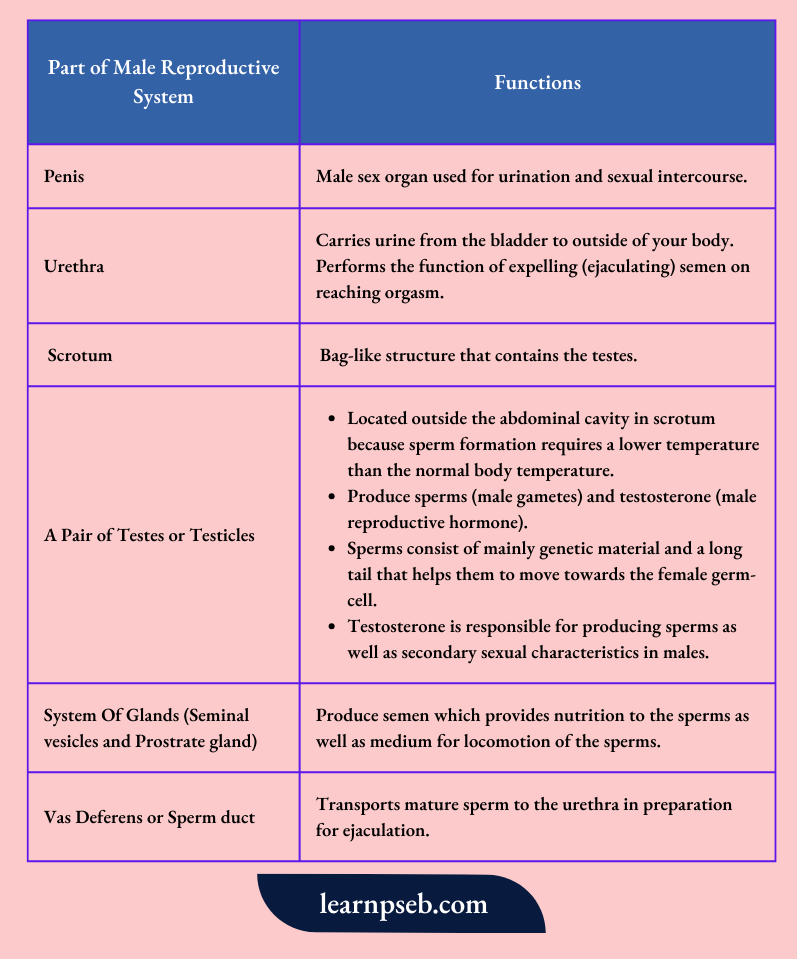
Parts Of The Male Reproductive System And Their Functions
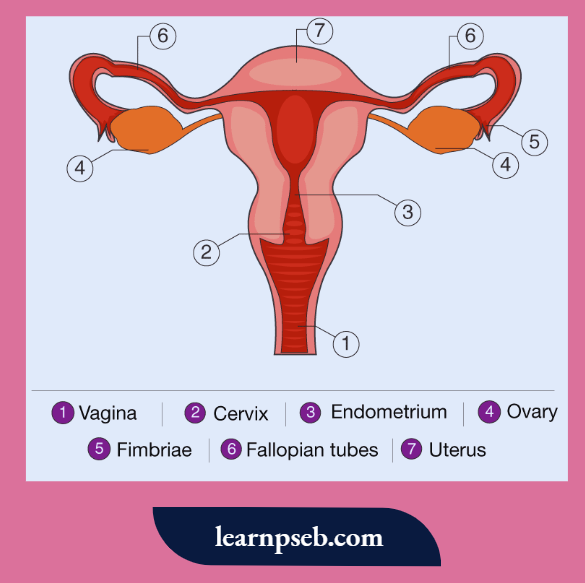
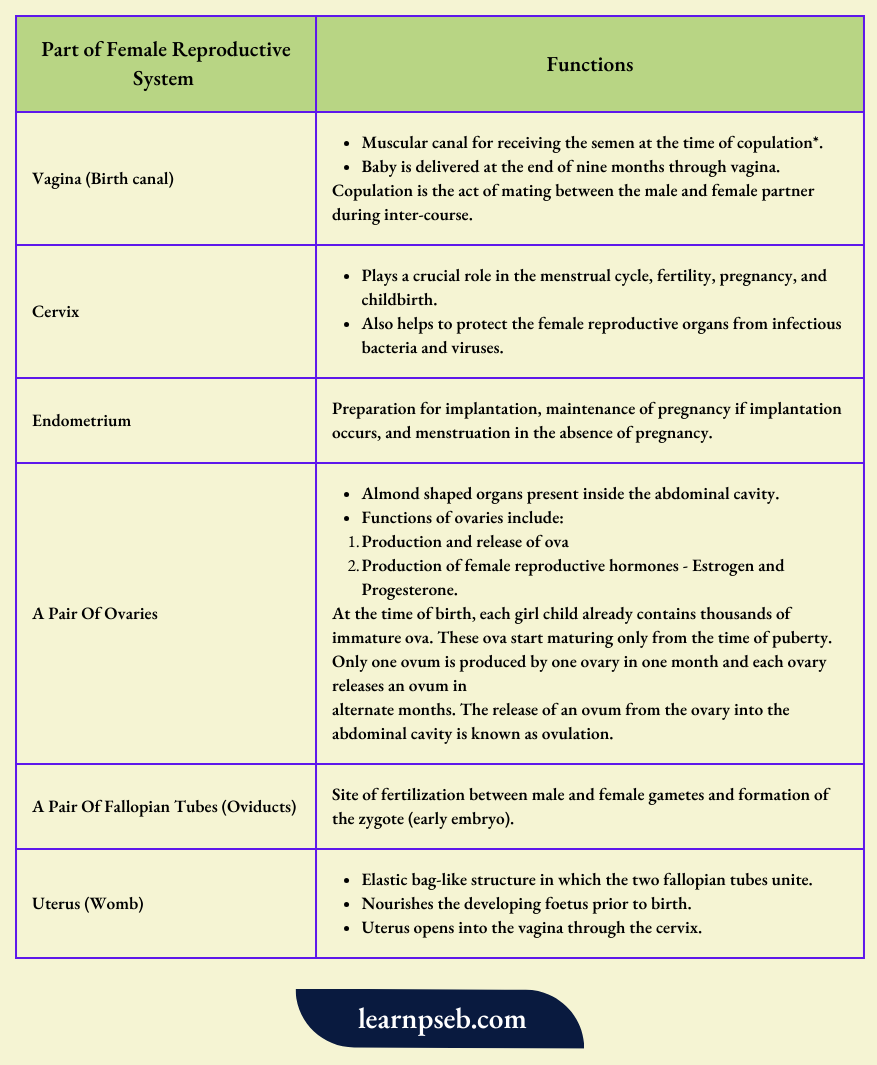
Parts Of The Female Reproductive System And Their Functions
Steps Involved In Reproduction In Human Beings
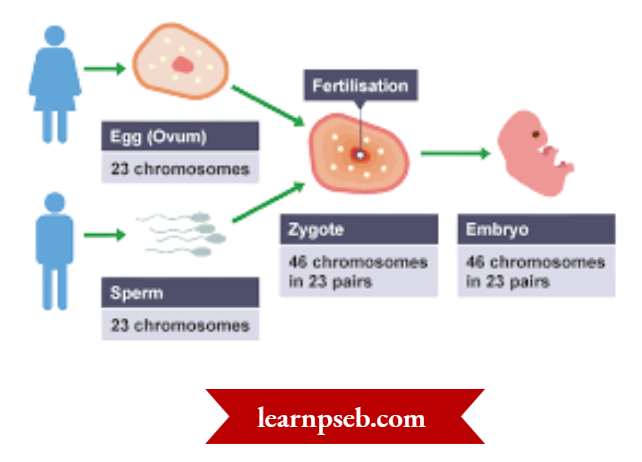
- In Males, testes produce male gametes (sperms).
- In Females, ovaries produce female gametes (ova).
- During sexual intercourse, sperms enter the vaginal passage and travel upwards to reach the oviduct. Here, they may encounter the egg, and fertilization may occur. Fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tube. Fertilization is the process of fusion of nuclei of the sperm and egg.
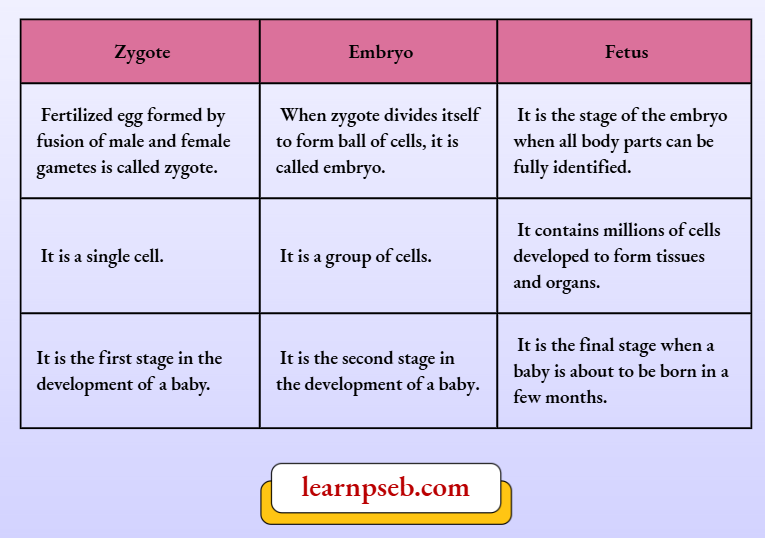
- After fertilization, zygote is formed. A fertilized egg is called a zygote.
- The zygote starts dividing and form a ball of cells and tissues called embryo.
- The embryo is implanted in the inner lining of the uterus (called endometrium; Endometrium is richly supplied with blood vessels and provides nutrients for the growing embryo) where the embryo continues to grow and develop organs to become foetus (When all body parts of the embryo can be fully identified, it called foetus).
- The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. Placenta is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi. This provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo.
- Functions of Placenta include:
- Providing nutrition to the growing embryo from the mother’s blood.
- Removal of waste substances by transferring them into the mother’s blood.
- Functions of Placenta include:
- The development of the child inside the mother’s body takes approximately nine months.
- The child is born as a result of rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus.
Life processes definition and examples
Difference Between Zygote, Embryo And Fetus
Menstruation
It is the monthly process of shedding of the lining of a woman’s uterus as blood and mucus along with the unfertilized ovum and the ruptured cells and tissues of the endometrium through the vagina of the female. Menstruation occurs if fertilization of egg does not occur. It is a 28-dav cycle which occurs in every reproductively active female (from puberty). The flow of blood continues for 2 to 8 days.
PSEB life processes class 10 questions answer
Difference Between Menarche And Menopause
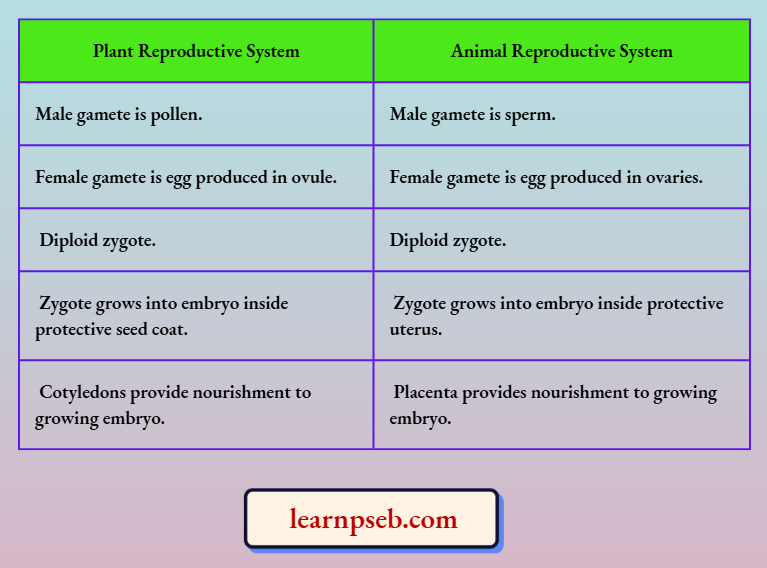
Comparison Between Sexual Reproductive System Of Plants And Animals
Reproductive Health
Reproductive health refers to a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being of males and females during their entire reproductive age. The physical well-being refers to healthy reproductive organs and healthy hormone producing glands.
Reproductive health is important because it protects both the mother and the child from infectious diseases. It also ensures delivery of a healthy baby.
Four pillars of reproductive health are:
- Responsible Parenthood
- Respect for Life
- Birth Spacing
- Informed Choice – Informed choice means giving options to a person to choose from several diagnostic tests or treatments, knowing the details, benefits, risks and expected outcome of each.
PSEB life processes class 10 questions answer
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) – Sexually transmitted diseases can be bacterial or viral.
Bacterial STDs – Gonorrhoea and Syphilis.
Viral STDs – Warts and HIV-AIDS.
Birth Control Measures – Birth control measures means methods to prevent pregnancy. Birth control measures are important for facilitating family planning/spacing of births, reducing unintended pregnancies and abortions. They provide both health and social benefits to mothers and their children.
PSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Solutions
Types Of Birth Control Measures
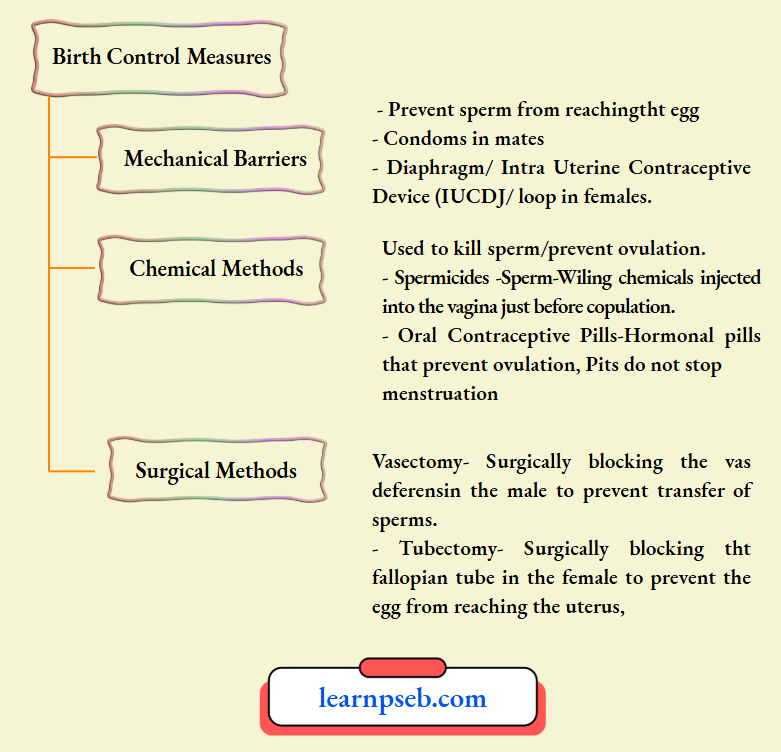
Chapter 2 How Do Organisms Reproduce Reason- Assertion Questions And Answers
For question provided below, two statements are given—one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
- Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
- A is true, but R is false.
- A is false, but R is true.
Question 1. Assertion: Sexual reproduction generates recombination.
Reason: Sexual reproduction involves crossing over.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 2. Assertion: Reproduction enables the continuity of life for generations.
Reason: Reproduction is a biological process in which an organism gives rise to young ones similar to itself.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 3. Assertion: Sexual reproduction generates recombination.
Reason: Sexual reproduction involves crossing over
PSEB life processes class 10 questions answer.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 4. Assertion: Asexual reproduction requires only female animals.
Reason: Male animals are not capable for asexual reproduction.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 5. Assertion: The zygote developed from sexual reproduction is diploid.
Reason: In sexual reproduction, haploid gametes fuse and form zygote.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 6. Assertion (A): Spores are unicellular bodies.
Reason (R): The parent body simply breaks up into smaller pieces on maturation.
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Question 7. Assertion (A) : The offspring produced by sexual reproduction is likely to adjust better in environmental fluctuation.
Reason (R): During the fusion of gametes there is mixing of genetic material from two parents.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 8. Assertion (A): Testes lie in penis outside the body.
Reason (R): Sperms require temperature lower than the body temperature for development.
Answer: 4. A is false, but R is true.
Question 9. Assertion (A): Amoeba reproduces by fission.
Reason (R): All unicellular organisms reproduce by asexual reproduction.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Chapter 2 How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Or Source-Based Questions
Question 1. Contraception is an artificial method or other techniques, mainly used to prevent pregnancy as a consequence of sexual intercourse. When a sperm reaches the ova in women, she may become pregnant. Contraception is a method that prevents this phenomenon by stopping the egg production or by keeping the egg distinct from the sperm or by stopping the fertilized egg attaching to the lining of the womb.
- What happens if an egg is not fertilized?
- How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
- Why do we need to adopt contraceptive measures?
- How does contraception work?
Answer:
- If an egg is not fertilized by a sperm then blood along with cellular debris comes out through the vagina and this process is called menstruation.
- The embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body with the help of placenta
- We need to adopt contraceptive measures:
- To prevent unwanted pregnancies,
- To prevent sexually transmitted diseases,
- Spacing between children
- Contraception is a method that prevents unwanted pregnancies by stopping the egg production or by keeping the egg distinct from the sperm or by stopping the fertilized egg attaching to the lining of the womb.
Question 2. Different organisms reproduce in a different manner. The modes by which various organisms reproduce depend on the body design of the organisms.
Life processes class 10 MCQ with answers
1. Splitting up of a single cell into exactly two daughter cells occurs in:
- Multiple fission
- Binary fission
- Regeneration
- Segmentation
Answer: 2. Binary fission
2. Multiple fission occurs in:
- Paramoecium
- Euglena
- Leishmania
- Plasmodium
Answer: 4. Plasmodium
3. Spirogyra reproduces by:
- Fragmentation
- Fission
- Budding
- Regeneration
Answer: 1. Fragmentation
4. Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells called
- Bud cells
- Regenerative cells
Stem cells - Proliferative cells
Answer: 3. Stem cells
5. Which mode of reproduction is seen in the given picture?
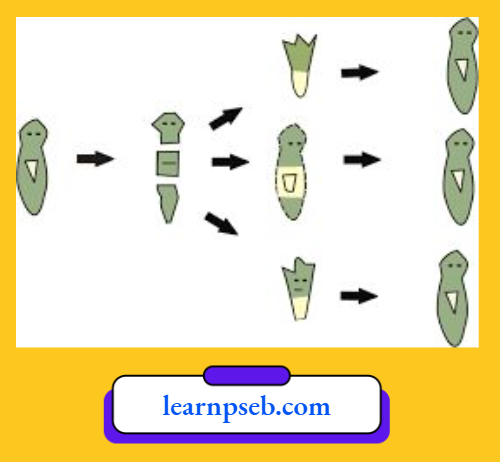
- Budding
- Regeneration
- Fission
- Segmentation
Answer: 2. Regeneration
Question 3. The most obvious outcome of the reproductive process still remains the generation of individuals of similar design. The rules of heredity determine the process by which traits and characteristics are reliably inherited.
1. Which type of reproduction would give rise to exact copies of parents?
Answer: Asexual Reproduction
2. The visible characteristic in an organism is known as:
- Prototype
- Stereotype
- Phenotype
- Genotype
Answer: 3. Phenotype
Life processes class 10 MCQ with answers
3. A plant with two ‘small’ genes breeds with a plant with two ‘tali’ genes to produce:
- Small plants and tall plants in the ratio 1:3
- All small plants
- All tall plants
- Tall plants and small plants in the ratio 3:1 17
Answer: 3. All tall plants
4. What are the “Factors” that Mendel talked about in his experiment?
- RNA Fragments
- Protein chains
- Similar forms of single gene
- Contrasting forms of single gene
Answer: 4. Contrasting forms of single gene
5. Offspring formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because
- Sexual reproduction is a lengthy process
- Genetic material comes from a single parent
- Genetic material comes from two parents of different species
- Genetic material comes from many parents
Answer: 3. Genetic material comes from two parents of different species
