PSEB Class 10 Biology Solutions For Chapter 1 Life Processes
Life Processes
These are the processes which together perform the functions of growth, repair, and maintenance of living organisms. These include nutrition, digestion, respiration, transportation, and excretion.
Simple Trick To Remember Life Processes
With the help of the mnemonic “MRS GREN” one can easily tell the life processes which indicate whether an organism is alive or not.
- M: Movement
- R: Respiration
- S: Sensitivity (or Feel)
- G: Growth
- R: Reproduction
- E: Excretion
- N: Nutrition
- Nutrition
Read And Learn More PSEB Class 10 Biology
Nutration
It is the process by which living organisms take in food, utilizes it to get energy for growth, repair and maintenance, and then excretes the waste material from the body.
Life processes class 10 notes
Simple Trick To Remember Modes Of Nutrition, Its Types And Subtypes
Organisms are divided into two categories, viz. Autotrophs and Heterotrophs on the basis of their mode of nutrition.
PSEB Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Life Processes
Autotrophs
Plants are Autotrophs. Autotrophs prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis.
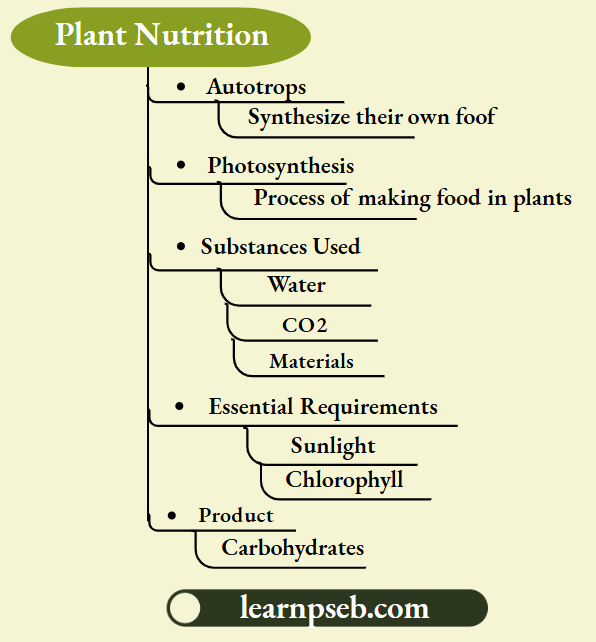
Chemical Equation Of Photosynthesis
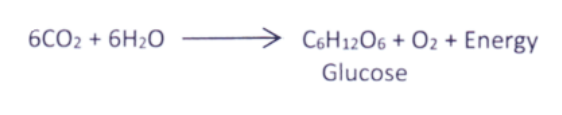
Steps involved in photosynthesis
- Absorption of light energy of sun by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
Heterotrophs
Animals are Heterotrophs. Heterotrophs depend on others for food. They obtain nutrition through process of digestion.

- Digestion is the process of breakdown of complex food molecules into simpler ones.
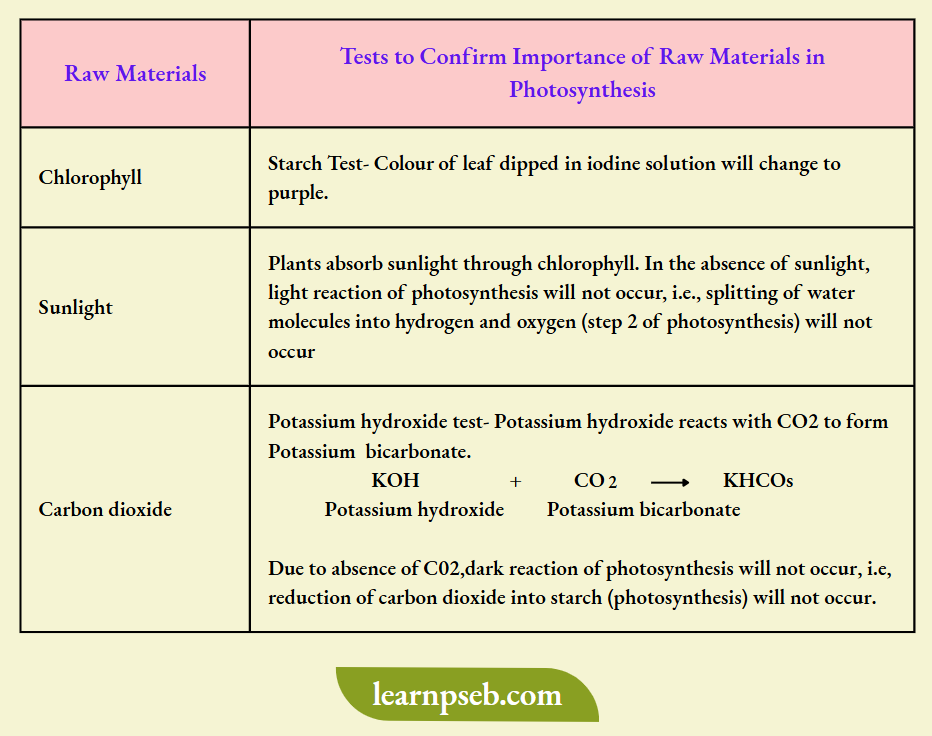
Tests To Confirm Importance Of Various Raw Materials In Photosynthesis
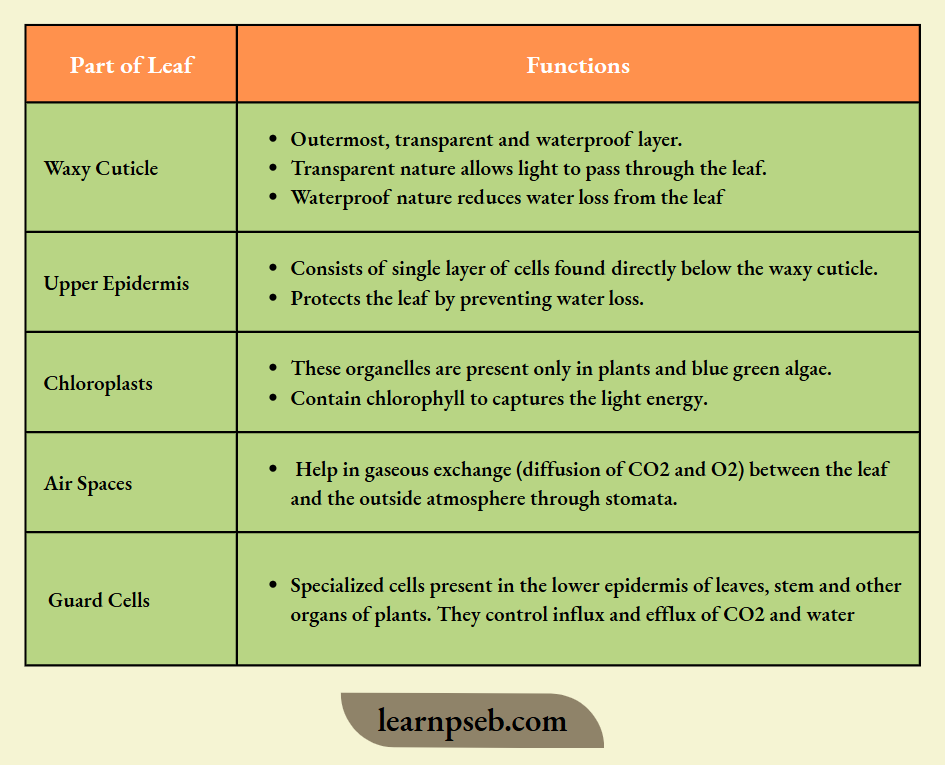
Parts Of Leaf And Their Functions
Summary Of Opening And Closing Of Stomata
Life processes class 10 notes
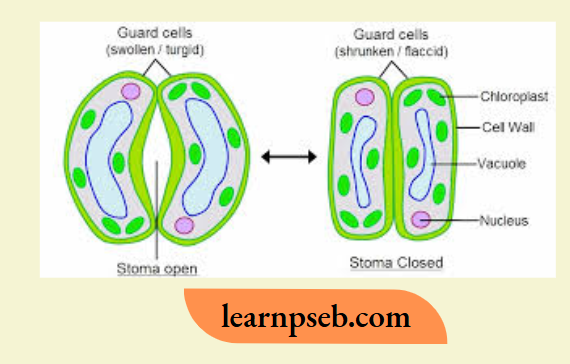
Five main factors that determine the opening and closing of stomata are:
- Light – Stomata open in blue and red light. This is because blue and red light stimulate the production of malic acid by converting starch into sugar. UV light and green light do not result in stomatal opening because aforementioned conversion does not occur.
- Temperature – Stomatal opening is directly proportional to light. Therefore, stomata open in day and close at night.
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration – Stomatal opening is inversely proportional to carbon dioxide concentration. Therefore, stomata open at low CO2 concentration, and close at high CO2 concentration.
- Water Concentration – Swelling of guard cells due to absorption of water increases turgor pressure resulting in opening of stomatal pores, while shrinking of guard cells due to loss of water closes the stomatal pores (cells become flaccid).
- Abscisic Acid (ABA) COncentration – ABA is called the stress hormone of plants. When there is a deficiency of water in leaves. ABA concentration increases leading to closure of stomata. In this way, ABA helps the plant to survive during unfavourable conditions of the environment.
Difference Between Function Of Stomata And Guard Cells
PSEB Class 10 Biology Solutions Chapter 1
Flow Chart And Summary Of Holozoic Nutrition
Life processes class 10 notes

Please Note: See the bracket in above flow chart covers onlyfour steps, i.e., excretion or eaestion is not considered to be a part of nutrition.
- Ingestion means process of taking in food.
- Digestion means breaking down of complex food substances into smaller soluble substances with the help of enzymes.
- Absorption means process by which the products of digestion are absorbed by the blood for supplying to the rest of the body.
- Assimilation means absorbed food is utilized to provide energy and help in growth and development of cells and tissues.
- Excretion means removal of undigested waste from the body.
Life processes class 10 full chapter explanation
Holozoic Nutrition In Unicellular Organisms- Amoeba Vs Paramecium
1. Difference Amoeba Vs Paramecium
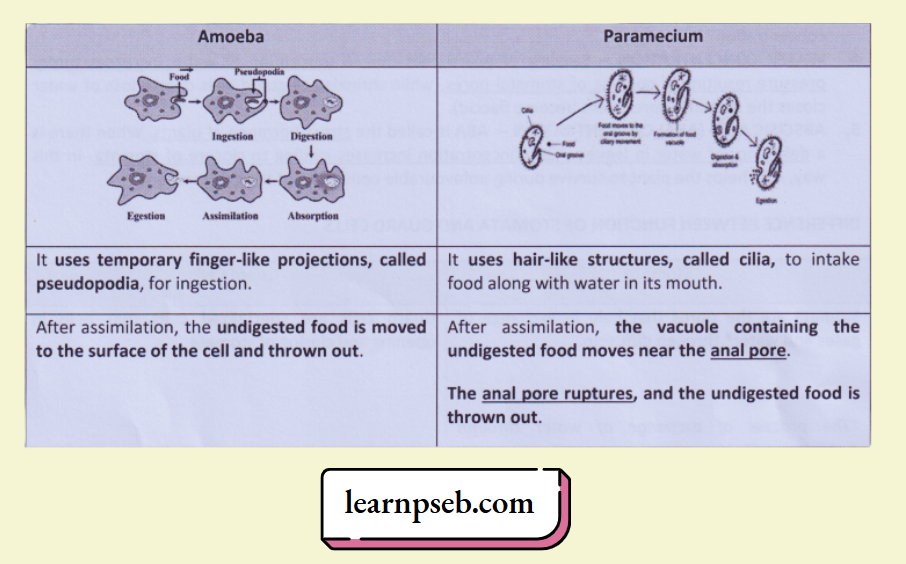
2. Similarity Between Amoeba And Paramecium
- Both follow holozoic mode of nutrition, i.e., in both organisms, the process of nutrition involves ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion.
- Both organisms undergo intracellular digestion.
Life processes class 10 full chapter explanation
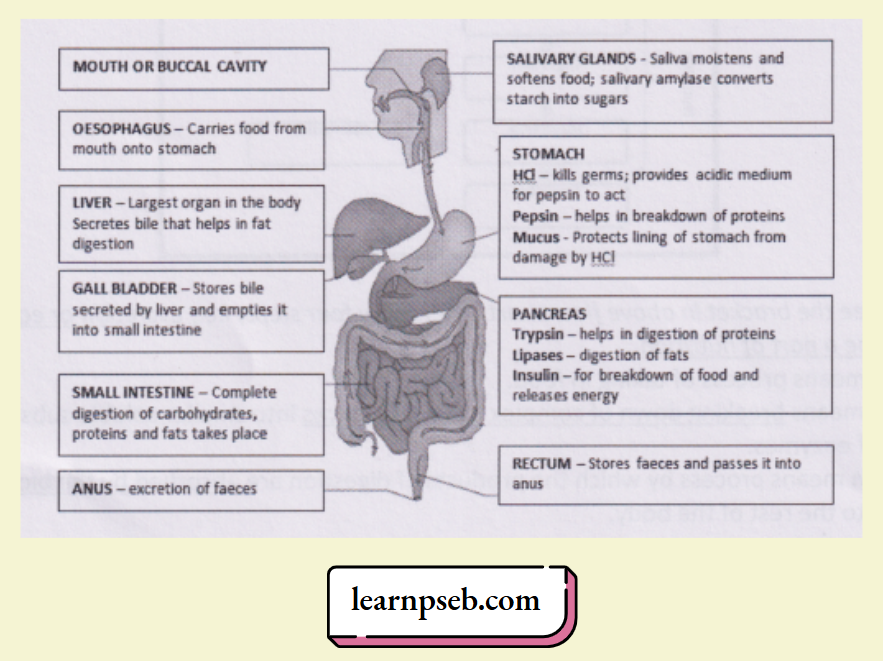
Flow Chart Of Nutrition In Multi-Cellular Organisms- Human Beings
Life Processes PSEB Class 10 Notes
- In human beings, the nutrition is performed by alimentary canal and the associated glands.
- Alimentary canal consists of mouth (or buccal cavity), oesophagus (or food pipe), stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus.
- Four Glands associated with the process of nutrition are salivary glands, gastric glands, liver and pancreas.
Flow Chart Showing Dental Caries Or Tooth Decay
- Dental caries or tooth decay occurs when bacteria acting on sugars produce acids due to which food particles stick to the teeth to form dental plaque.
- When plaque covers the teeth, saliva (which is alkaline in nature) cannot reach the tooth surface to neutralise the acid.
- This may cause gradual softening of enamel and dentine.
- If untreated, microorganisms may invade the pulp, causing inflammation and infection.
- Dental caries can be prevented by regularly brushing the teeth after eating. This removes the plaque before the bacteria produce acids.
Life processes class 10 full chapter explanation

Starch Iodide Test To Check The Presence Of Starch In Saliva- In this test, when a solution of iodine is added to saliva (containing starch), a blue black colour is obtained as shown in figure:

Respiration
It is the process in which oxidation of complex organic substances takes place by taking in oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide to obtain energy in the form of ATP molecules. Respiration is a catabolic process because it involves breakdown of glucose molecules.
Life processes definition and examples
Types Of Respiration
Note: The first step of respiration is same in all the cases, i.e., it involves the break-down of glucose (a 6- carbon molecule) into pyruvate (a 3-carbon molecule). This process takes place in the cytoplasm.
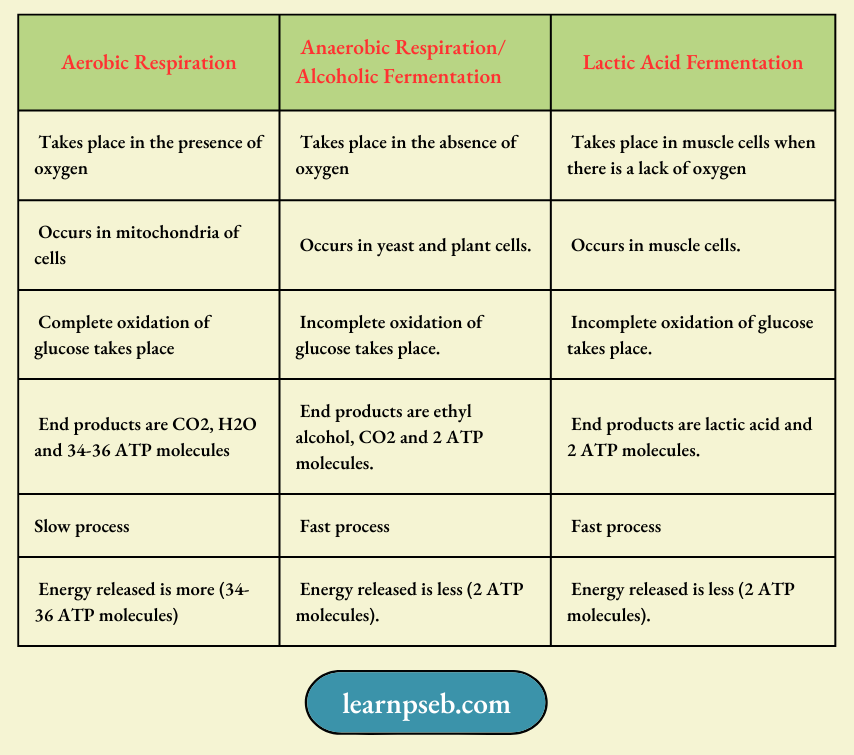
Summary Of Three Types Of Glucose Breakdown Pathways
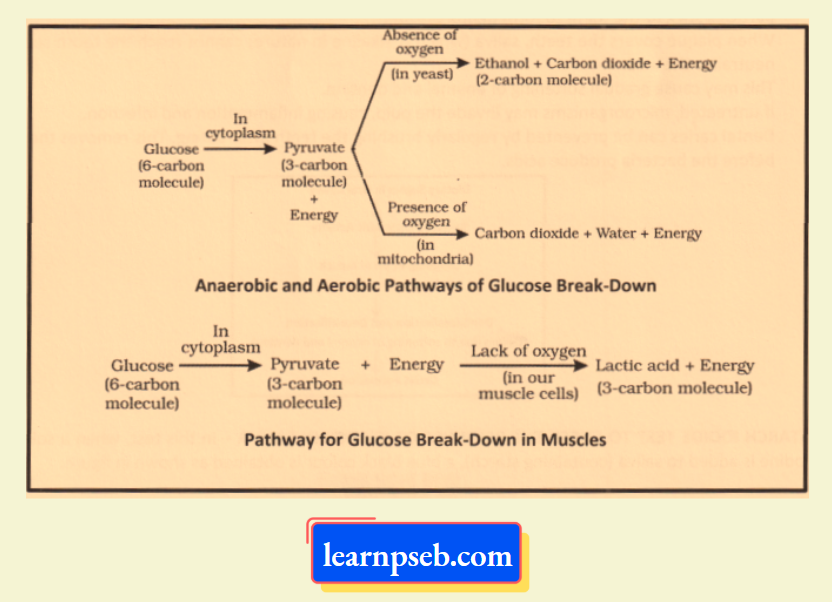
Flow Chart Of Human Respiratory System
Breathing Mechanism In Humans- It is a three-step process.
- Step 1: Inhalation of oxygen through nostrils.
- Step 2: Exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) takes place in alveoli with the help of respiratory pigment, called hemoglobin.
- Step 3: Exhalation of carbon dioxide through nostrils.
Life processes definition and examples

Diagram Showing Exchange Of Gases In Humans
PSEB Class 10 Biology Important Questions Chapter 1
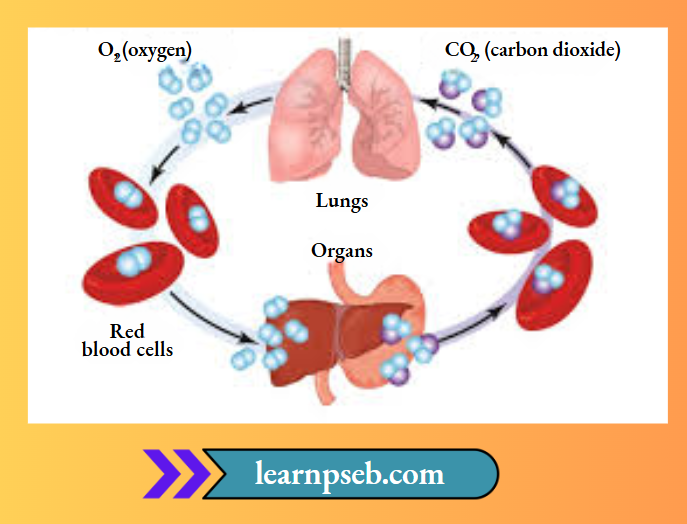
Transportation
- In animals,plants,transportation is carried out through the circulatory system which includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels.
- In plants, it occurs through specialized tissues called xylem(transports water and minerals) and phloem (transports food).
Life processes definition and examples
Blood
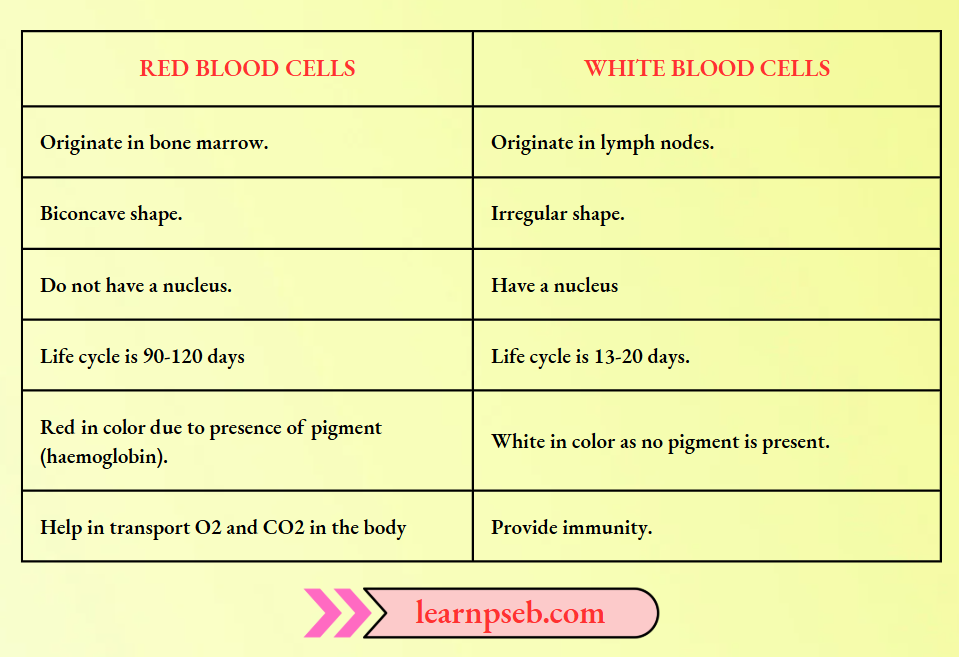
Blood is a connective tissue. It performs the functions of transport of food, oxygen and waste materials in the body. Blood has three main components, viz., plasma, blood cells (red and white blood cells), and platelets.
Functions Of Components Of Blood
- Plasma- Transport of nutrients, waste products, antibodies, clotting proteins and hormones.
- Blood Cells- RBCs (transport of O2 and CO2), WBCs (provide immunity)
- Platelets- help in blood clotting.
Difference Between Red Blood Cells (Rbcs) And White Blood Cells (Wbcs)
Points To Remember About Human Heart And Its Functioning
- Human heart has four chambers – Two upper chambers (called atria) and two lower chambers (called ventricles).
- Atria relax to receive blood from the body whereas ventricles contract to pump blood to different parts/ organs of the body.
- Since ventricles have to pump blood into various organs, walls of ventricles are thicker than those of atria.
- Valves in the heart ensure that blood does not flow backwards when the atria or ventricles contract.
- Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood on the walls of a blood vessel. It is greater in arteries than in veins. Blood pressure of blood inside the artery during ventricular contraction is called systolic pressure and pressure in artery during ventricular relaxation is called diastolic pressure.
- Normal systolic pressure is about 120 mm of He and diastolic pressure is 80 mm of He. It is measured with an instrument called sphygmomanometer.
Life processes class 10 diagram
Flow Chart Of Blood Circulation In Human Beings
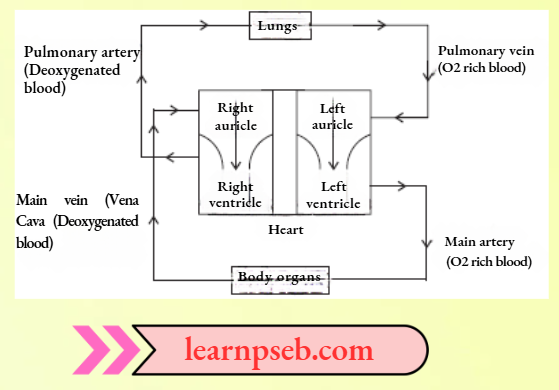
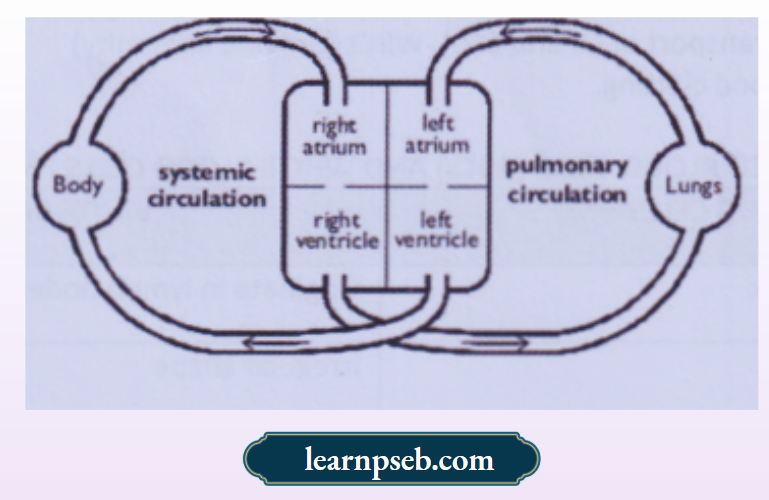
Double Circulation In Humans And Its Advantages
In human beings, blood passes through the heart twice during one cardiac cycle. The deoxygenated blood comes to the heart and goes to the lungs for oxygenation. Simultaneously, the oxygenated blood comes to the heart from lungs and goes to different organs.
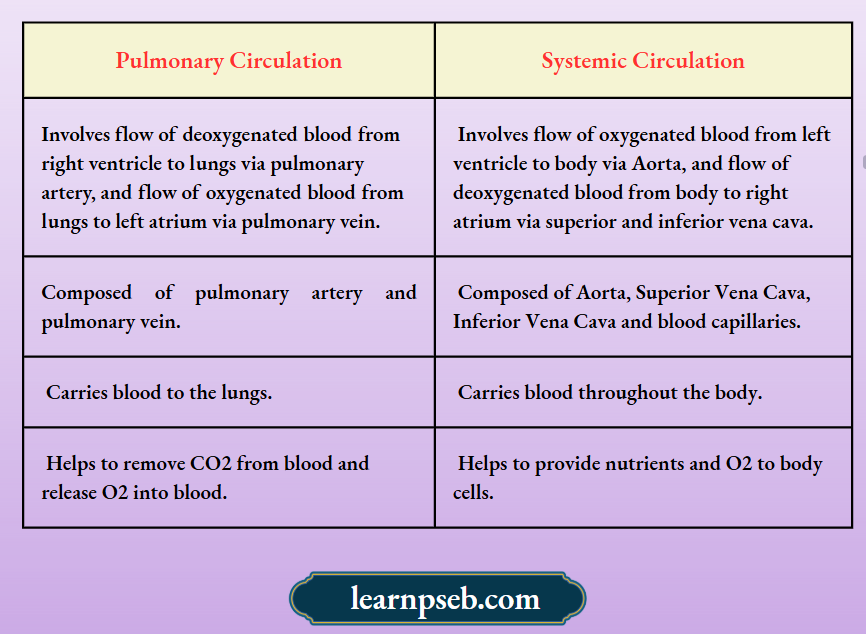
Difference Between Pulmonary Circulation And Systemic Circulation
Life processes class 10 diagram
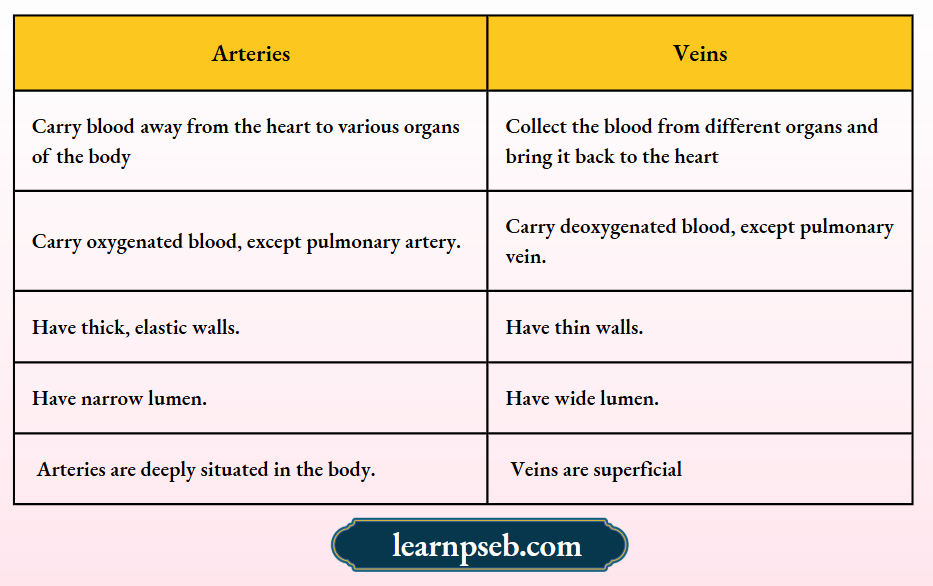
Difference Between Arteries And Veins
Lymph Or Tissue Fluid
It is a colourless fluid that contains a high concentration of white blood cells and plays an important role in the immune response. It is similar to the plasma of blood but it contains less protein compared to plasma.
Life processes class 10 diagram
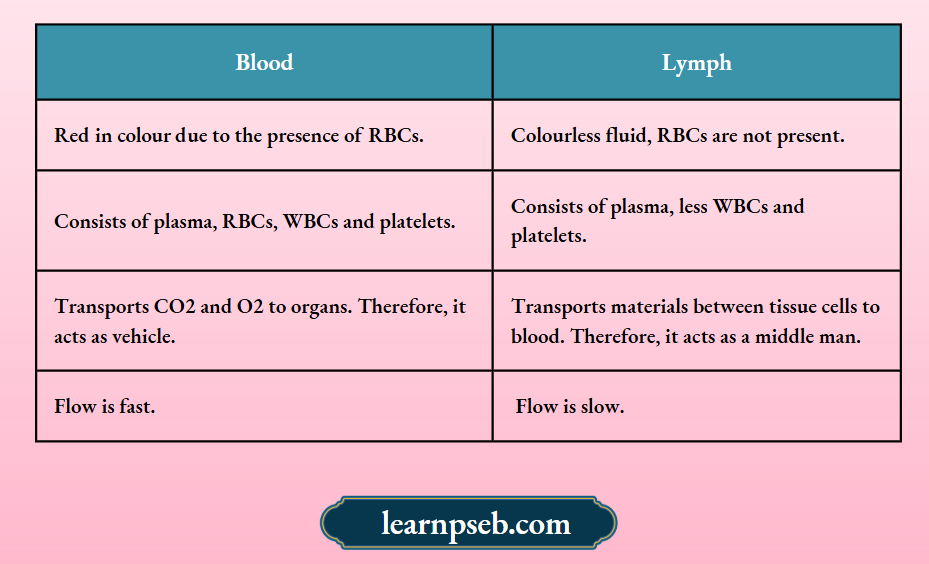
Difference Between Blood And Lymph
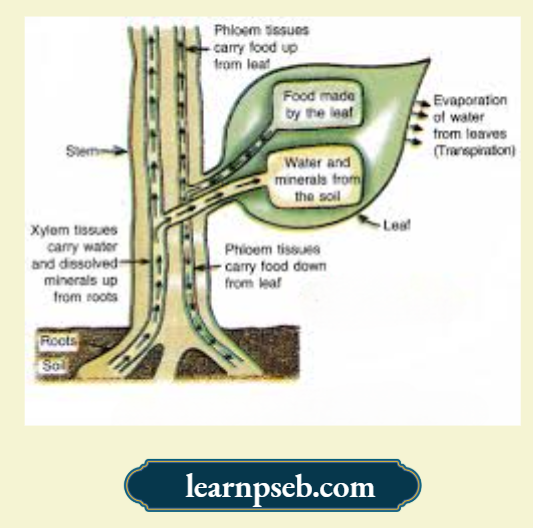
Transportation In Plants
Two types of conducting tissues in plants are:
- Xylem helps in the transport of water and minerals (obtained from the soil).
- Phloem helps in the transport of products of photosynthesis (from leaves to other parts of the plant), respectively.
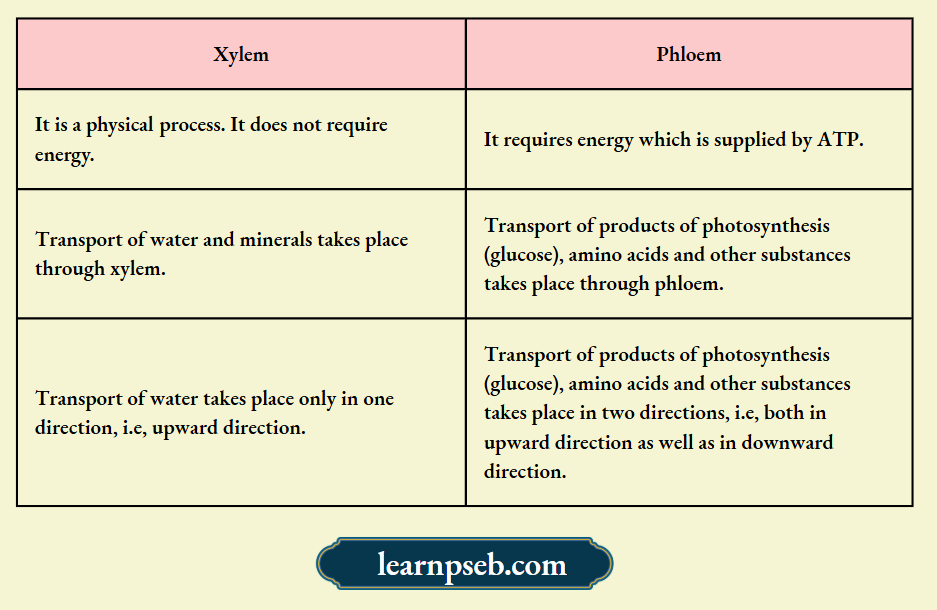
Differences Between Xylem And Phloem
Ascent Of Sap – The upward movement of water and minerals from roots to different plant parts is called ascent of sap.
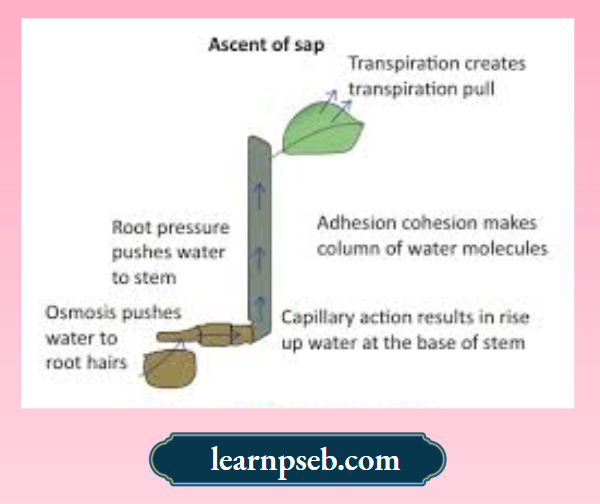
Factors affecting ascent of sap are:
- Osmosis- It pushes water from soil to root hair.
- Root pressure- It pushes water from root hair to base of stem.
- Capillary action- Water rises up to some height of stem due to capillary action.
- Adhesion-cohesion of water molecules – Water molecules make a continuous column in the xylem because of these forces.
- Transpiration- Loss of water vapour through stomata creates vacuum resulting in suction of water, called transpiration pull. The transpiration pull sucks the water column from the xylem tubes, and thus, water is able to rise to great heights in even the tallest plants.
Life processes class 10 NCERT solutions
Excretion
Excretion is the process of removal of gaseous wastes (produced during photosynthesis or respiration) and nitrogeneous wastes (produced during metabolic activities) from the body of an organism.
PSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Solutions
Mode of excretion depends upon the level of structural organization of the organism.
- In Unicellular Organisms, they are removed by simple diffusion.
- In Multicellular Organisms, they are removed by a set of organs which together form the excretory system.
Excretory Organs In Human Beings
Excretory organs in human beings are broadly classified into two categories, viz. main excretory organ (Kidneys) and accessory excretory organs (lungs, liver and skin).
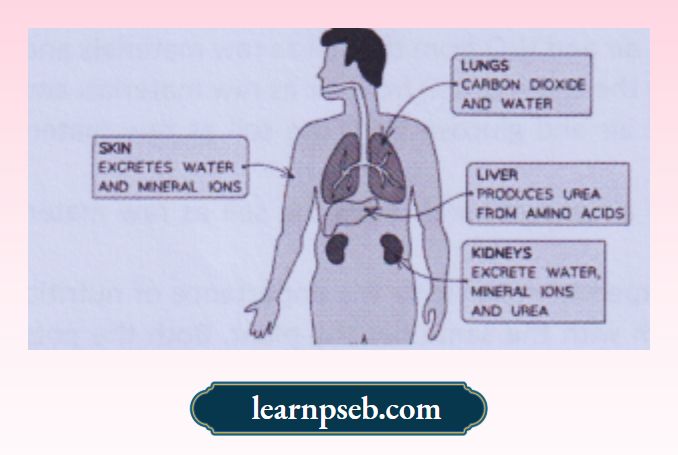
Points To Remember About Human Excretory System
- Nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. It produces urine and cleanses blood by removing waste and excess substances from it. Each kidney has millions of nephrons in it.
- Nephron is composed of a renal corpuscle (glomerulus within Bowman’s capsule), a proximal tubule, an intermediate tubule (loop of Henle), a distal convoluted tubule and connecting ducts.
- If one kidney is damaged or removed, then the other kidney alone can fulfil excretory needs.
- In case of failure of both the kidneys, the function of kidneys needs to be performed artificially with the help of a machine. The process is called hemodialysis.
- Function of hemodialysis is similar to kidneys, except that there is no reabsorption involved.
- Kidney transplantation is the long term solution in case of failure of both the kidneys.
- Kidneys can be donated while the donor is still alive irrespective of his/her age, sex or religion.
Life processes class 10 NCERT solutions
Flow Diagram Of Human Excretory System

Important Points About Excretion In Plants
Plants use the following ways for excretion:
- Gaseous wastes (excess carbon dioxide and oxygen) are excreted through the stomata.
- Excess water is excreted by transpiration through stomata.
- Many plant waste products are stored in cellular vacuoles in leaves that fall off.
- Some waste products are stored as resins and gums, especially in old xylem.
- Aquatic plants excrete metabolic wastes through diffusion. Terrestrial plants excrete metabolic wastes into the soil.
Chapter 1 Life Processes Reason- Assertion Questions And Answers
For question provided below, two statements are given—one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (1), (2), (3) and (4) as given below:
- Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
- A is true, but R is false.
- A is false, but R is true.
Question 1. Assertion: Bile helps in the emulsification of fats.
Reason: Bile makes acidic food coming from the stomach alkaline so that pancreatic enzymes can act on it.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 2. Assertion: Lymph is a light-yellow liquid which flows only in one direction.
Reason: Lymph protects the body by making antibodies.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 3. Assertion: Diffusion does not meet the high energy requirements of multicellular organisms.
Reason: Diffusion is a fast process but only occurs at the surface of the body.
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Question 4. Assertion: Saliva contains an enzyme called amylase.
Reason: Amylase helps to break down simple sugars like glucose into complex molecules like starch.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 5. Assertion: Phloem tissue transports the food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant.
Reason: The movement of food in phloem takes place by diffusion.
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Question 6. Assertion: Arteries are thick walled and elastic in nature.
Reason: Arteries have to transport blood away from the heart.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 7. Assertion (A): Plants lack excretory organs.
Reason (R): Plants usually absorb essential nutrients.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 8. Assertion (A): In anaerobic respiration, one of the end product is alcohol.
Reason (R): There is an incomplete breakdown of glucose.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 9. Assertion (A): In plants there is no need of specialised respiratory organs.
Reason (R): Plants do not have great demands of gaseous exchange.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 10. Assertion (A): Bile is essential for digestion of lipids.
Reason (R): Bile juice contains enzymes.
Life processes class 10 questions and answers
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Question 11. Assertion (A): Carbohydrate digestion mainly takes place in small intestine.
Reason (R): Pancreatic juice contains the enzyme lactase.
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Question 12. Assertion (A): Aerobic respiration requires less energy as compared to anaerobic respiration.
Reason (R): Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell.
Answer: 4. A is false, but R is true.
Question 13. Assertion (A): Human heart is four-chambered.
Reason (R): Vena cava is the only artery that supplies deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Question 14. Assertion (A): Energy is required to carry out different life processes.
Reason (R): Energy is obtained in the form of ATP in the mitochondria.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 15. Assertion (A): Rings of cartilage are present in the throat.
Reason (R): These ensure that the air-passage does not collapse.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 16. Assertion (A): Pyruvate is a six-carbon molecule.
Reason (R): It is prepared in the cytoplasm as the first step to cellular respiration.
Answer: 4. A is false, but R is true.
Life processes class 10 questions and answers
Chapter 1 Life Processes Case Or Source Based Question And Answers
Question 1. The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of population.
1. Which of the following is a common sign of sexual maturation in both boys and girls?
- Development of breasts
- Growth of pubic hair
- Adam’s apple
- Broadening of hips
Answer: 2. Growth of pubic hair
2. Which of the following is an IUCD?
- Copper-T
- Diaphragm
- Oral pill
- Tubectomy
Answer: 1. Copper-T
3. Which among the following is not a sexually transmitted disease?
- Gonorrhoea
- AIDS
- Syphilis
- Cholera
Answer: 4. Cholera
4. A couple wants to space the birth of their second child. Which of the following preventive measure could be taken by the husband?
- Oral pills
- Diaphragms
- Tubectomy
- Condoms
Answer: 4. Condoms
Life processes class 10 questions and answers
5. A pregnant woman visits the doctor to determine the sex of the child. Why is she denied of this testing?
- It is a complicated test.
- It may result in female foeticide.
- It is an expensive test.
- It is harmful test for the developing foetus
Answer: 2. It may result in female foeticide.
Question 2. Blood vessels are the channels or conduits through which blood is distributed to body tissues. The vessels make up two closed systems of tubes that begin and end at the heart. One system, the pulmonary vessels, transports blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left atrium. The other system, the systemic vessels, carries blood from the left ventricle to the tissues in all parts of the body and then returns the blood to the right atrium.
1. Which system carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs?
- Pulmonary
- Systemic
- Hepatic
- Gastric
Answer: 1. Pulmonary
Life processes class 10 important questions
2. Systemic vessels carry blood from:
- Right ventricle to lungs
- Left ventricle to body tissues
- Body tissues to left ventricle
- Lungs to right ventricle
Answer: 2. Left ventricle to body tissues
3. Which blood vessels carry blood away from the heart?
- Veins
- Capillaries
- Arteries
- Venules
Answer: 3. Arteries
4. The exchange of materials between the blood and tissue cells is done by:
- Capillaries
- Veins
- Venules
- Arteries
Answer: 1. Capillaries
5. Which blood vessels carry blood towards the heart?
- Veins
- Capillaries
- Arteries
- Venules
Answer: 1. Veins
Life processes class 10 assertion and reason questions
Question 3. The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in different ways – some use oxygen to breakdown glucose completely into carbon dioxide and water, some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen.
1. Which three carbon molecule is formed during the breakdown of glucose?
- Lactic acid
- Glyceraldehyde
- Acetic acid
- Pyruvate
Answer: 4. Pyruvate
2. The process in which pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide is:
- Germination
- Fermentation
- Cellular respiration
- Oxidation
Answer: 2. Fermentation
3. Breakdown of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the:
- Cytoplasm
- Stroma
- Mitochondria
- Cellular matrix
Answer: 3. Mitochondria
4. The breakdown of pyruvate in the absence of oxygen producing lactic acid occurs primarily in the:
- Muscle cells
- Brain cells
- Cardiac cells
- Nerve cells
Answer: 1. Muscle cells
5. Observe the graph and interpret which of the following is true w.r.t. rate of respiration?
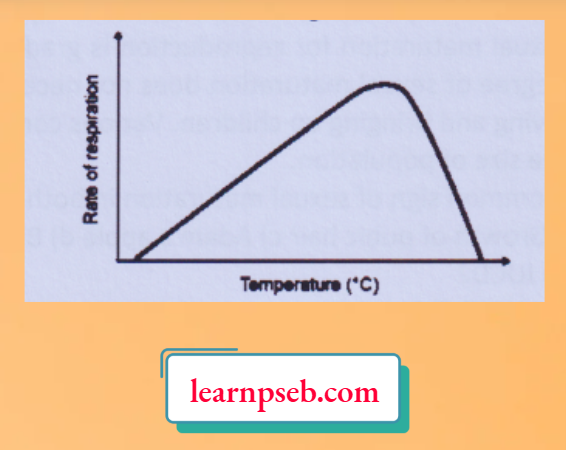
- Increases with an increase in temperature
- Increases first and then decreases with an increase in temperature
- Decreases with an increase in temperature
- Decreases first and then increases with an increase in temperature
Answer: 2. Increases first and then decreases with an increase in temperature
Question 4. The human respiratory system consists of a group of organs and tissues that help us to breathe. Lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system which help in the exchange of gases. The other main parts of this system include a series of airways for air passages, blood vessels and the muscles that facilitate breathing.
Life processes class 10 quick revision
1. Which are the primary organs of respiration in humans?
- Lungs
- Bronchi
- Trachea
- Pharynx
Answer: 1. Lungs
2. Nostrils are divided by a framework of cartilaginous structure termed as:
- Flaps
- Cartilage
- Septum
- Rings
Answer: 3. Septum
3. Respiration in humans is primarily:
- Aerobic
- Anaerobic
- Partially anaerobic
- Partially aerobic
Answer: 1. Aerobic
4. Exchange of gases takes place in the:
- Bronchi
- Alveoli
- Trachea
- Bronchioles
Answer: 2. Alveoli
5. The percentage of nitrogen in exhaled air is:
- 78%
- 0.3%
- 21%
- 0.03%
Answer: 1. 78%
Question 5.
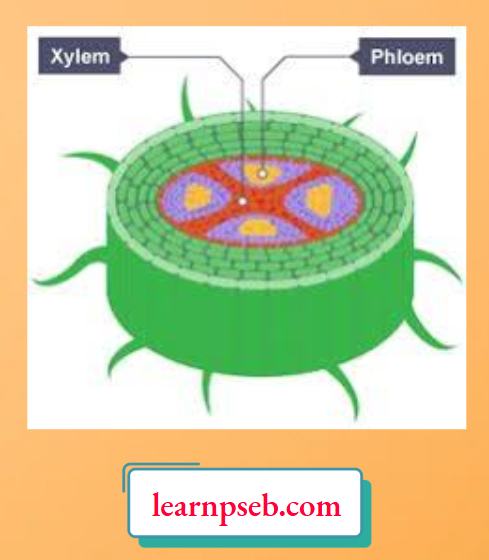
Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant, while phloem transports sucrose and amino acids between the leaves and other parts of the plant.
Life processes class 10 quick revision
1. Which of the following processes will not occur in the absence of xylem?
- Transport of water
- Conduction of food
- Transport of minerals
- Both a) and c)
Answer: 4. Both a) and c)
2. Transport of food by the phloem is called
- Transpiration
- Translocation
- Guttation
- Adhesion
Answer: 1. Transpiration
3. Which of the following is not a characteristic of xylem?
- Living cells
- Lack of cytoplasm
- Impermeable to water
- Presence of lignin
Answer: 2. Lack of cytoplasm
4. In phloem, transport occurs between where the substances are made, i.e. ______ and where they are used or stored, i.e. ______
- Sink, source
- Source, sink
- Origin, destination
- Destination, origin
Answer: 2. Source, sink
5. ___________ is the process which involves transport of water and minerals.
- Transpiration
- Translocation
- Guttation
- Adhesion
Answer: 1. Transpiration
Question 6. The carbon and energy requirements of the autotrophic organism are fulfilled by photosynthesis. It is the process by which autotrophs take in substances from the outside and convert them into stored forms of energy.
1. Which of the following acts as an internal energy reserve in plants?
- Starch
- Glycogen
- Chitin
- Cellulose
Answer: 1. Starch
2. Which of the following processes are not a part of the process of photosynthesis?
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules
- Oxidation of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
Answer: 3. Oxidation of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
Life processes class 10 quick revision
3. Which of the following structures is absolutely essential for the process of photosynthesis?
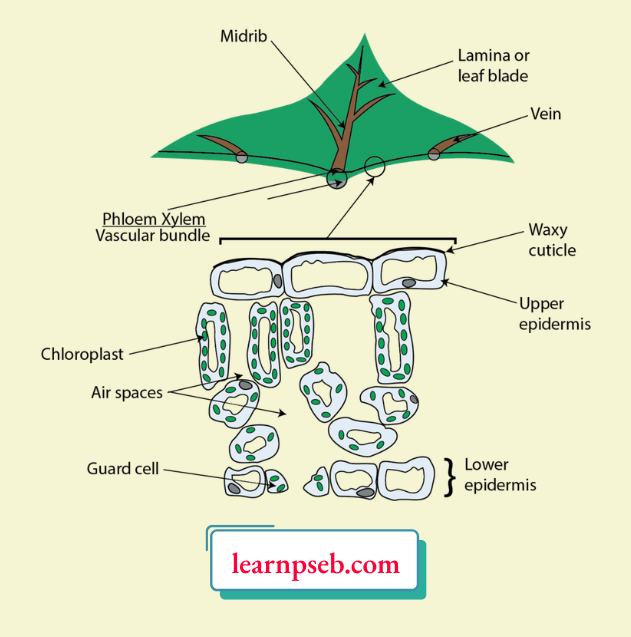
- Lower epidermis
- Chloroplasts
- Phloem
- Waxy cuticle
Answer: 2. Chloroplasts
4. What is the role of stomata in process of photosynthesis?
- Gaseous exchange
- Absorption of light
- Transfer of nutrients
- Emission of light
Answer: 1. Gaseous exchange
Question 7. Tooth decay starts when the pH of the mouth is lower than 5.5. Tooth enamel, made up of calcium phosphate is the hardest substance in the body. It does not dissolve in water, but is corroded when the pH in the mouth is below 5.5. Bacteria present in the mouth produce acids by degradation of sugar and food particles remaining in the mouth after eating. The best way to prevent this is to clean the mouth after eating food. Using toothpastes, which are generally basic, for cleaning the teeth can neutralise the excess acid and prevent tooth decay.
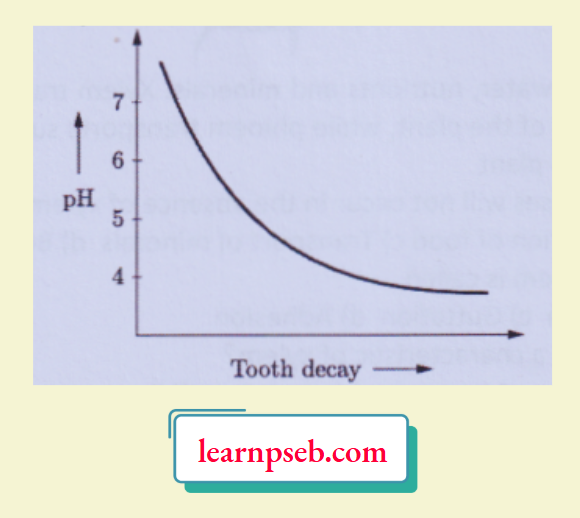
1. The tooth decay be prevented:
- By rinsing mouth with excess of water after eating.
- By using basic toothpaste.
- Both (a) and (b)
- Preventing use of acidic substances like lemon, etc.
Answer: 3. Both (a) and (b)
2. Teeth enamel is made of a substance called:
- Aluminium
- Calcium phosphate
- Iron
- Diamond
Answer: 2. Calcium phosphate
3. Tooth decay in the mouth starts when:
- pH of mouth is below 5.5
- pH of mouth is 7.6
- pH of mouth is 7.5
- pH of mouth is 7.52.
Answer: 1. pH of mouth is below 5.5
4. The acidity in the mouth is due to:
- Undigestion of food.
- Degradation of sugar and food particles remaining in the mouth by bacteria.
- Drinking of Mosambi juice.
- Eating of acidic substances like tomatoes, oranges etc.
Answer: 2. Degradation of sugar and food particles remaining in the mouth by bacteria.
