Control And Coordination Questions
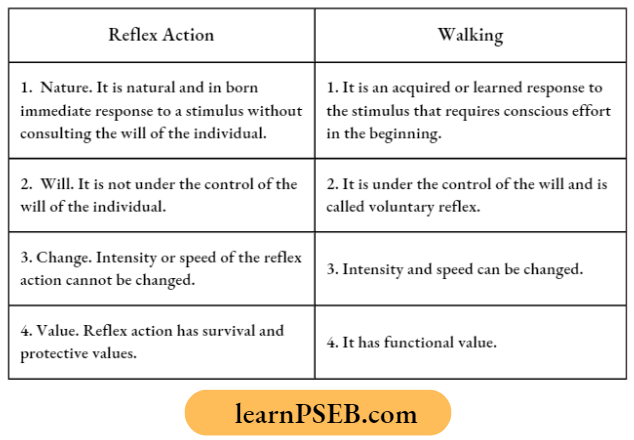
Question 1. What is the difference between reflex action and walking?
Answer:
Question 2. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer:
The synapse between two neurons is a junctional complex that permits an axon end of a neuron to pass its electrical or chemical signal to the dendrite end of another neuron.
- There is a fluid-filled narrow space between the two neurons. It is called synaptic cleft. The presynaptic axon end of the neuron is bulb-like.
- It contains many synaptic vesicles having neurotransmitter chemicals. The postsynaptic dendrite end of the next neuron has a trough-like depression. Its membrane has receptors for the neurotransmitter.
- As the impulse reaches the presynaptic bulb, the synaptic vesicles move to the cleft side and burst open.
- The released neurotransmitter sensitizes the receptors that in turn create the electrical impulse.
- Synapse allows a unidirectional flow of information from the axon end of one neuron to the dendrite end of the next neuron.
Read And Learn More PSEB Class 10 Biology
PSEB Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 Control And Coordination
Question 3. Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer: Cerebellum.
Question 4. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Answer: Burning of agarbatti releases numerous molecules of incense. They enter the nose and come in contact with particular sensory hair of olfactory cells.
An impulse is generated. It passes into the olfactory bulb which relays it to the temporal lobes of the cerebrum for interpretation.
Question 5. What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer: Like the spinal cord, the brain can also play a direct role in certain reflex actions called cerebral reflexes, for example., closing of eyes or flashing of light.
In such cases, brain acts as a relay station in which the impulse of sensory neurons is transferred to motor neurons through an interneuron.
Question 6. What is reflex action? Explain the mechanism of reflex action with a suitable example.
Answer:
Reflex action is a nerve-mediated automatic and spontaneous response to a certain stimulus without consulting the will of the individual.
- The stimulus for reflex action is picked up by its receptor. The receptor is connected to a sensory neuron. An impulse generated in it is passed to the central nervous system.
- The central nervous system acts as a relay or modulator. With the help of an interneuron, it transfers the impulse to a motor neuron. The motor neuron takes the impulse to the effector organ for response.
Question 7. Name the three major regions of the brain. Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer:
Three regions of the brain. Fore brain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Maintenance of posture and equilibrium. Cerebellum.
Question 8.
- Distinguish between voluntary and involuntary actions of our body.
- Choose involuntary actions among the following: reading, beating of heart, salivation in mouth on viewing tasty food, talking.
Answer:
- Voluntary action is under the control of the will and is performed with the help of striated muscles. Involuntary action is performed without instructions from will with the help of smooth muscles.
- The beating of the heart and salivation in the mouth on viewing a tasty food are involuntary actions.
Question 9.
- Name two main regions of our central nervous system,
- Which one of them plays a major role in sending commands to muscles to act without Involving the thinking process,
- Name the phenomenon involved.
Answer:
PSEB Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 Question And Answers
- Brain and spinal cord.
- The spinal cord has a major role in sending instructions to muscles without involving the thinking process.
- Reflex action.
Question 10. Write the function of the following :
- Sensory neuron
- Cranium
- Vertebral column
- Motor neuron.
Answer:
- Sensory Neuron. Conveying impulse or sensation from receptor to central nervous system.
- Cranium. Covering and protection of the brain.
- Vertebral Column. Covering and protection of the spinal cord.
- Motor Neuron. Conveying impulse for action from the central nervous system to the effector organ.
Question 11. Identify the part of a neuron
- Where information is acquired
- Through which information travels
- Where the impulse must be converted into a chemical signal?
Answer:
- Dendrite
- Axon
- Synapse.
Question 12.
- What is a reflex arc?
- Why have reflex arcs evolved in animals?
Answer:
- A reflex arc is nerve nerve-based pathway performed by an impulse from the receptor of stimulus to the effector organ through the central nervous system without consulting the will of the individual.
- Reflex arcs evolved in animals even before the evolution of intelligence as a survival mechanism because they can provide immediate responses to harmful stimuli.
Question 13. Stale the sequence of events through a reflex arc which occurs when a bright light is focussed on your eyes.
Answer:
- Bright light is sensed by receptors present over the eyes. The sensation is picked up by sensory neurons and taken to the superior quadrigeminal.
- Intemeurons present in the superior corpora quadrigemina transfer the impulse to motor neurons. The motor neurons close the eyelids as well as narrow the pupil.
Question 14.
- Name one gustatory receptor and one olfactory receptor present in human beings.
- Write a and b in the given flow chart of neurons through which information travels as an impulse.
Dendrite a → b → End point of a neuron.
Answer:
- Gustatory Receptor. Taste buds over the tongue.
- Olfactory Receptor. Olfactory epithelium in nasal chambers.
- Dendrite → Cell body → Axon → End point of a neuron.
Question 15. What is a nerve impulse? State the direction followed by a nerve impulse while traveling in the body of an organism.
Answer:
A nerve impulse is a progressive electrical wave or signal that develops in response to a stimulus and travels along a nerve fiber to reach another nerve, muscle, or gland.
Direction Of Nerve Impulse
Dendrite → cell body → Axon → Axon end → Dendrite/gland/muscle.
Control And Coordination PSEB Class 10 Notes
Question 16. List in tabular form two differences between reflex action and walking.
Answer:
Question 17. Which part of the nervous system controls reflex arcs? Trace the sequence of events that occur when we touch a hot object. Mention the part of the neuron that requires information and the form in which information travels.
Answer:
Reflex arcs are controlled by the central nervous system (many in the spinal cord) without analyzing them. CNS functions as a coordinator or relay station for transferring sensory information to motor information.
Events. A hot object is the stimulus. As it is touched, the stimulus is picked up by skin-based receptors. From receptors, the information is taken up as an impulse by sensory neurons.
- Sensory neurons take the impulse to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the impulse is transferred to motor neurons through interneurons.
- The motor neurons take the impulse to the muscles of the hand which pull away the arm. Information travels in neurons in the form of electrochemical impulses.
Question 18. What is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system? Name any two components. Which structure in a neuron helps to conduct a nerve impulse
- Towards the cell body
- Away from the cell body.
Answer:
Structural and Functional Unit. Neuron.
Components of a Neuron. Dendrites, cell body, and axon.
- Dendrite
- Axon
Question 19.
- Which part of the brain controls Involuntary actions?
- Write the function of any two regions of It.
Answer:
Hind brain is a part of the brain that controls involuntary functions. It has three parts—pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata.
- Medulla Oblongata. It regulates blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing. Several reflex actions have centers in the medulla oblongata, viz., swallowing, vomiting, sneezing, coughing, salivation, and peristalsis.
- Cerebellum. It involuntarily co-ordinates muscular activities of the body. The cerebellum maintains equilibrium during different activities or postures of the body.
Question 20.
- If the cerebellum is not functioning properly, state the activities of our body that are affected.
- How do muscle cells move?
Answer:
PSEB Class 10 Biology Important Questions
- Impairment of the cerebellum shall result in non-coordination of body activities and defects in maintaining balance or posture of the body.
- Muscle cells move in response to excitation provided by a neuromuscular junction. The motor impulse passes to the bulb end of the motor end plate of an axon.
- The bulb is in near contact with the sole plate of the muscle cell. As the nerve impulse reaches the bulb, it activates the synaptic vesicles.
- The vesicles move to the membrane and burst open to release molecules of neurotransmitters.
- They activate receptors over the end plate and cause activation of muscle interior releasing calcium and causing contraction of muscle cells.
Question 21. Name the part of the brain that controls
- Voluntary actions
- Involuntary actions.
How is the brain protected from injury and shock?
Answer:
- Voluntary Actions. Cerebrum.
- Involuntary Actions. Hindbrain.
Protection of the Brain.
- Covering of brain by cranium,
- Holding of the brain by meninges,
- Presence of shock-resistant fluid medium both inside and outside the brain.
Question 22.
- Name the system which facilitates communication between the central nervous system and other parts of the body.
- Mention two types of nerves it consists of along with their organs of origin.
Answer:
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) facilitates communication between the central nervous system (CNS) and other parts of the body.
- The peripheral nervous system consists of two types of nerves
- Cranial from the brain, 12 pairs
- Spinal from spinal cord, 31 pairs.
Question 23. Trace the sequence of events that occur when a bright light is focused on your eyes.
Answer:
It is an example of a cerebral reflex.
Receptor cells of eyes → Sensory neurons → CNS (Brain) → Motor neurons → Eye muscles → Pupil contracts and eyelids close.
Question 24. List in tabular form three distinguishing features between the cerebrum and cerebellum.
Answer:
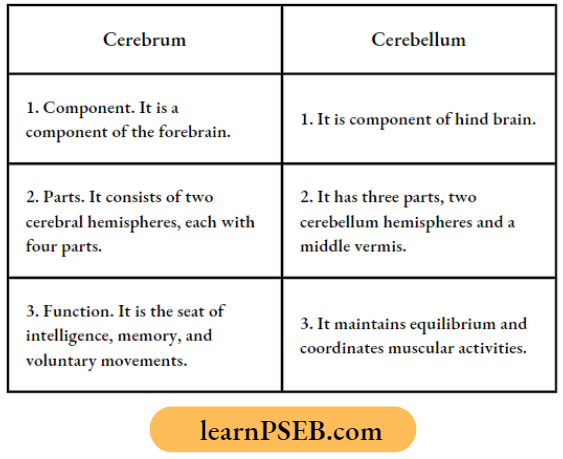
Question 25.
- Name a part of the human brain that controls
- Voluntary actions and
- Involuntary actions.
- Write the function of the peripheral nervous system. Name the components of this system stating their origin.
Answer:
PSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Solutions
- Voluntary actions. Forebrain/cerebrum.
- Involuntary Actions. Hind brain/medulla oblongata.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects different parts of the body with the central nervous system. It consists of nerves. Depending upon their origin, nerves arc of two types, cranial (from the brain) and spinal (from the spinal cord).
Question 26. Name parts in the diagram. What is the term given to the sequence of events occurring in the diagram?
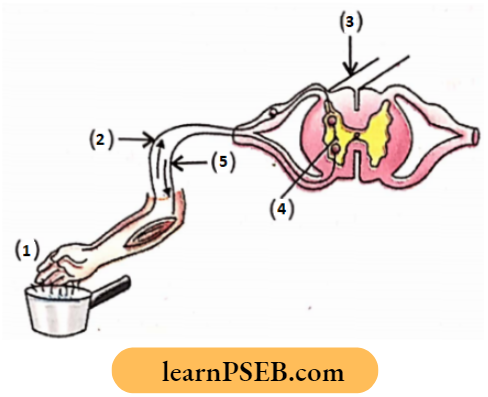
Answer:
- —Receptor (skin)
- —Sensory neuron
- —Spinal cord
- —Relay neuron
- —Motor neuron.
Term. Reflex arc.
Question 27. A cheetah on seeing a prey, moves towards it at a very high speed. What causes the movement of his muscles? How does the chemistry of cellular components of muscles change during the event?
Answer:
- The sight of prey generates a nerve impulse that reaches the muscles. A neurotransmitter is released. It causes the activation of muscles through the release of calcium.
- Calcium brings about a shortening of muscles through the sliding of myosin fibrils over actin fibrils. Shortening and relaxing of muscles allow the cheetah to move at high speed.
