PSEB Class 10 Biology Solutions For Chapter 3 Electricity
Electric Current (I)
The amount of electric charge (electrons or ions) flowing through a particular area in a unit time is called electric current. Since in metals, electric charge flows through electrons, therefore, electric current can also be defined as the rate of flow of electrons in a metal (or conductor).
Points To Remember About Electric Current
- In an electric circuit, the direction of flow of electric current is taken as opposite to the direction of flow of electrons. This is because electrons were not discovered when the phenomenon of electricity was first observed. The only sub-atomic particles known at that time were protons (Recall that protons are positively charged particles). So, electric current was considered to be the flow of positive charges, and the direction of flow of positive charges was taken to be the direction of electric current.
- SI unit of electric current is ampere (A). One ampere is the amount of electric current flowing through an electric circuit when an electric charge (Q) of 1 coulomb flows through it in1 second.
- Amount of electric current in an electric circuit is measured using Ammeter.
- Ammeter is always connected in series in an electric circuit.
Electric Charge (Q) – It is the property of matter due to which matter experiences an attractive or a repulsive force when it is placed in an electromagnetic field. SI unit of electric charge is coulomb (C).
- One coulomb is the charge contained in 1.6 x 1018 electrons (Note: Recall that charge on 1 electron = 1.6 x 10-19C)
- Some examples of electric charge in daily life are as follows:
- Chattering sound produced by synthetic clothes – When the clothes made up of nylon are rubbed against some other fabric or against the wearer’s skin, static electricity is formed. This electrostatic force developed between the skin and the clothing particles is accountable for the chattering sound caused while removing such clothes.
- Development of electric charge on a rod – When a metal rod or glass rod is rubbed with a cloth, positive or negative charge develops on it. The type of charge developed depends on the material of the rod, For Example. If a glass rod is rubbed with a cloth, positive charge will develop, whereas if a metal rod is rubbed with a cloth, negative charge will develop.
- Feeling a short-term electric shock on touching some metal surface – When a person randomly touches a metallic surface (For Example, a doorknob), he or she is prone to feel a short-term electric shock. This is due to the existence of an electrostatic force between the doorknob and the person’s hand. Since the doorknob is made up of metal, it is capable of transferring the electrons to every object that comes in contact with it. This leads to the development of electrostatic interaction between the doorknob and the skin.
- Photocopy Machine – In a photocopy machine, the original paper is placed on a glass screen. The image of this original paper is transferred to a drum that is positively charged. The ink powder or the toner used is usually charged with a negative polarity. The drum rolls against the paper on which the impression is required to be created. The ink then gets transferred to the paper due to the electrostatic force of attraction, creating a photocopied image of the original document.
PSEB Class 10 Physics Solutions Chapter 3
Relation Between Electric Current (I) And Electric Charge (Q)
If a charge Q flows through a conductor of any cross-section in time (t), then the electric current (I) through the cross-section is given by the equation
I = Q/t
Potential Difference Or Voltage (V)
It is defined as the work involved or the energy released in the transfer of a unit quantity of electricity (.e, charge) from one point to the other, i.e.,
Potential difference = Work done/ Charge
Or, V = W/Q
- SI unit of potential difference is volt (V).
- One volt is the potential difference between two points in a current-carrying conductor when 1 joule of work is done to move a charge of1 coulomb from one point to another in an electric circuit, i.e.,
- 1 volt = 1 joule/ lcoulomb
- Or, 1V = 1JC-1
- Potential difference in an electric circuit is measured using an instrument called Voltmeter. Voltmeter is always connected in parallel in the circuit.
Cause Of Potential Difference
The generation of potential difference across the terminals of the cell occurs due to the chemical action within a cell or battery.
Important Points About Electric Circuit
- An electric circuit converts electrical energy into other forms of energy, For Example. in a bulb, electrical energy is converted into light energy and thermal energy.
- It has at least two parts – a voltage source (e.g. a cell or a battery) and a conductor (i.e., wires).
- Switches in the electrical circuits control the flow of current. When the switch is turned on, the circuit is closed and current can flow through it. When the switch is turned off, the circuit is open and current cannot flow through it.
- An electric circuit can function only if it forms a closed loop from the battery and back again as shown:
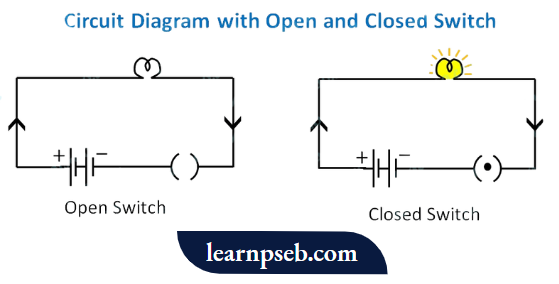
Circuit Diagram
It is a graphical display of an electric circuit using either basic images of parts or industry-standard symbols. A simple circuit diagram consists of multiple parts such as cell or battery, switches, wires, electric components such as an ammeter or a voltmeter, a bulb, etc as shown in the figure below:
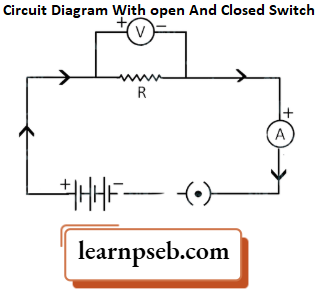
Important Points About Circuit Diagrams
1. In a circuit diagram, the direction of current is always from positive to negative terminal of the battery or cell (Recall that electrons will follow in opposite direction).
2. The longer end of the battery is the positive terminal and the shorter end of the battery is the negative terminal.
3. The positive end of the ammeter or voltmeter is connected to the positive end of the battery or cell and their negative end is connected to the negative end of the battery.
Circuit Diagram Symbols

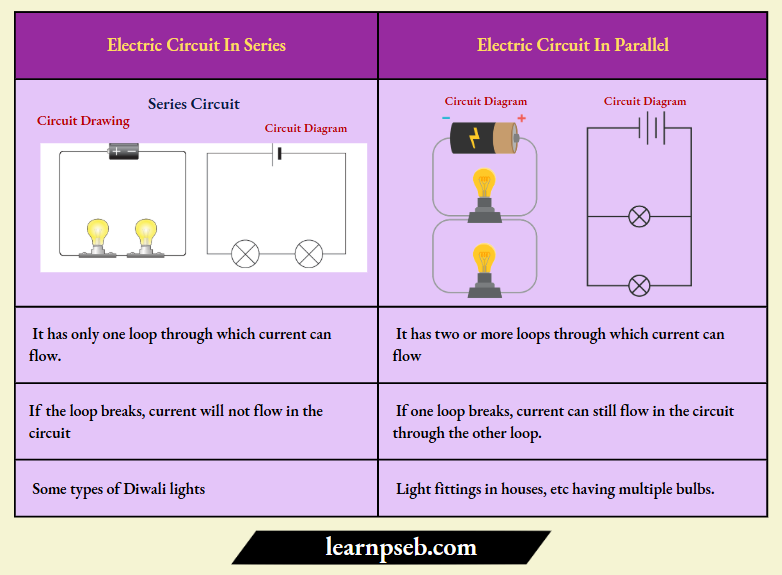
Series And Parallel Electric Circuits
These are the two types of electric circuits. They differ in the number of loops through which current can flow.
Ohm’s Law
It gives the relationship between potential difference (V) and the current (I).
Ohm’s law states that the current (I) through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference (V) across the two points, provided that the temperature remains the same, i.e,
V aI
or, V = IR (1)
where R is constant for the given metallic wire at a given temperature, and is called its resistance.
Resistance (R) – It is the property of a conductor to resist the flow of charge through it.
- SI unit of resistance is ohm (0).
- 1 Ohm is the resistance of a conductor when a potential difference of1 volt is applied across its ends, producing a current of 1 ampere.
- Resistance (R) of a conductor depends on the following factors:
- Length (I) of the conductor, i.e., R oc I
- Area of cross-section or thickness (A) of the conductor, i.e., R oc 1/A, and
- Nature of the material of the conductor.
Combining factors (1) and (2), we get
∴ \(R \propto \frac{l}{A} \quad \text { or, } \quad R=\rho \frac{l}{A}\)
where p (rho) is a constant of proportionality and is called the ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY of the material of the conductor. SI unit of resistivity is Q m. Resistivity is a characteristic property of the material.
- Metals and alloys have very low resistivity. They are good conductors of electricity.
- Insulators (For Example, rubber and glass) have intermediate resistivity.
- Resistivity of an alloy is generally higher than that of its constituent metals. Alloys do not oxidise (burn) readily at high temperatures. For this reason, they are commonly used in electrical heating devices, like electric iron, toasters etc.
- Both resistance and resistivity of a material vary with temperature.
Electricity PSEB Class 10 Notes
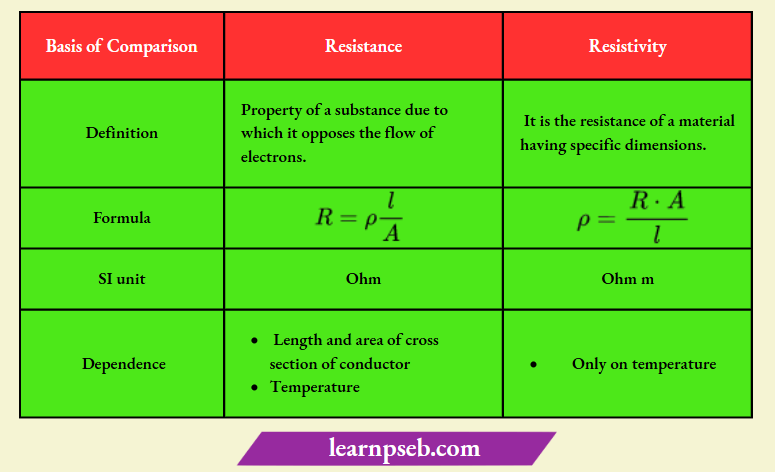
Difference Between Resistance And Resistivity
Effect Of Change In Resistance On Current
Resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to the current (as can be deduced from equation i), i.e. R = V/I
Therefore, if the resistance is doubled, the current gets halved.
Resistor – It is a device having electrical resistance.
- Resistors are used in an electric circuit for protection, operation, or current control.
- Resistors can be connected in a series connection, in a parallel connection or in combinations of both series and parallel.
- Resistors always obey Ohm’s Law irrespective of the combination or complexity of resistor network.
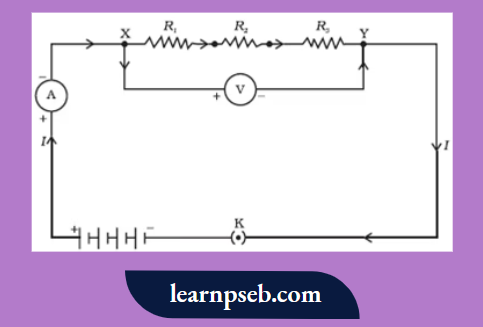
Resistors In Series – Resistors are said to be connected in “Series”, when they are chained together in a single line as shown:
Resistors In Parallel – Resistors are said to be connected together in parallel when both of their terminals are respectively connected to each terminal of the other resistor or resistors, as shown: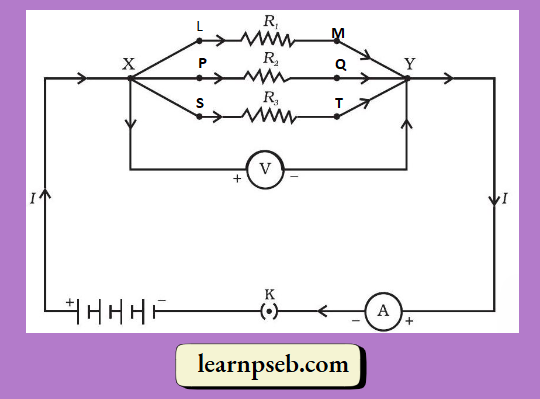
Conductance (G) – The reciprocal of resistance is called conductance, i.e., G = 1/R
SI units of conductance are siemens (S).
Heating Effect Of Electric Current – When an electric current is passed through a conductor, the conductor becomes hot after some time due to the conversion of some electric energy into heat energy.
Cause Of Heating Effect Of Electric Current – Heating effect of electric current occurs due to collision of electrons in the conductor, as explained below:
- When a potential difference is applied across the ends of a conductor, its free electrons get accelerated in a direction opposite to the applied electric field.
- But the speed of the electrons does not increase beyond a certain speed because during the course of their motion they collide frequently with the positive metal ions.
- During these collisions between the free electrons and the metal ions, the kinetic energy of the moving electrons is transferred to the metal ions. As a result of this, the metal ions begin to vibrate about their mean position.
- Due to the vibrations of the metal ions about their mean positions, the kinetic energy of the metal ions increases. This in turn results in an increase in temperature, i.e., heating of the conductor.
Factors Affecting Heating Effect Of Current – The Heating effect of electric current depends on three factors:
- Resistance Of The Conductor– The Higher the resistance more the heating effect.
- Amount Of Current Flowing Through The Conductor– Higher the amount of current, more will be the heat generated.
- Time For Which The Current Flows Through The Conductor – Longer the time for which current flows through the conductor more will be the heat generated.
Derivation of formula for heat produced by electric current flowing through a conductor
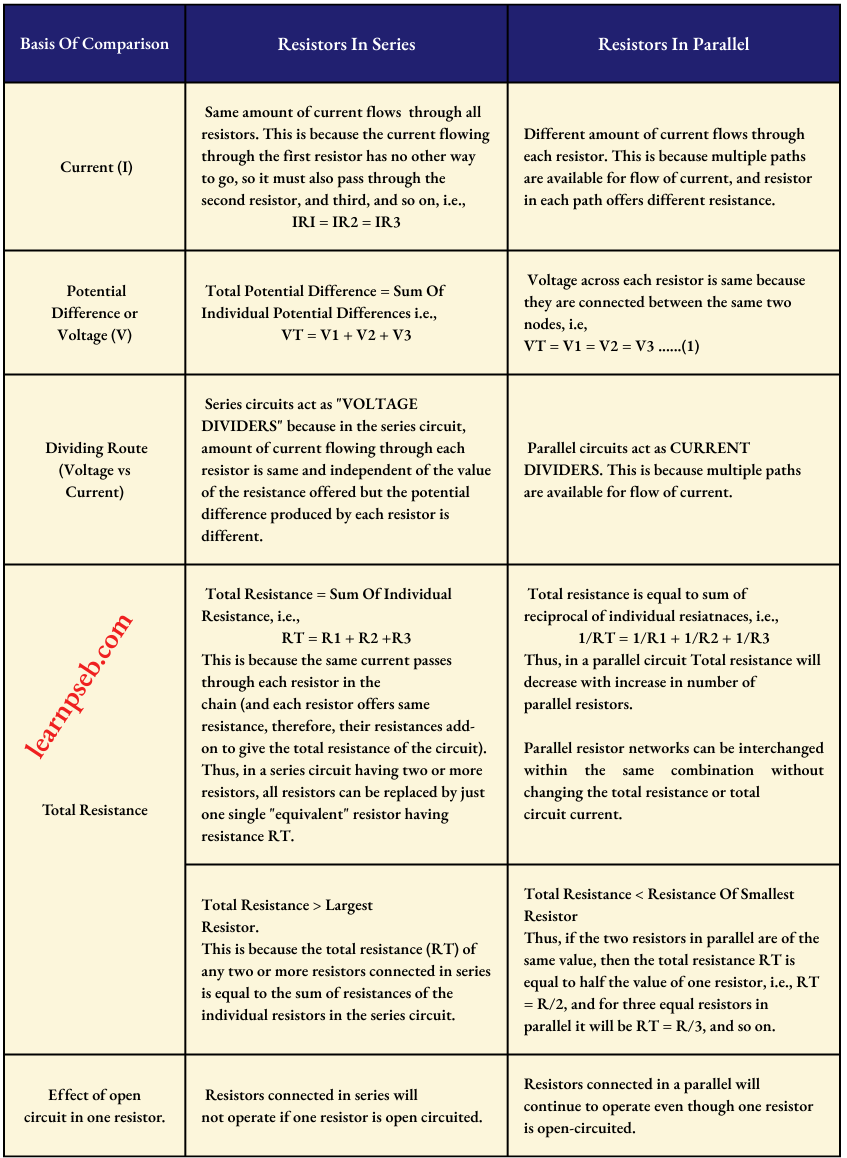
Consider the following circuit diagram:
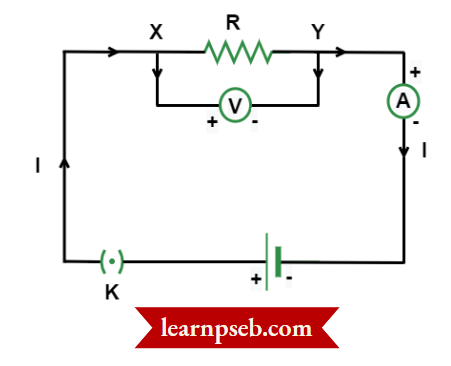
Let I = current flowing through the circuit
R = Resistance of the resistor
V = Potential difference across the two terminals of the resistor
t = Time during which a charge Q flows across the circuit.
We know that
PSEB Class 10 Physics Important Questions Chapter 3
Potential difference (V) between two points = Work done (W)/Charge (Q)
Or, V = W/Q ….(1)
But Q = I x t, and V = I x R …..(2)
Substituting the values of Q and V from equation (2) in equation (1), we get
I x R = W/ I x t
Or, I x R x I x t = W
Or, W = I2Rt
Assuming that all the work done is converted into heat energy we can replace “W” with “H” in the above equation, to get
H = I2Rt
Uses Of the Heating Effect Of Electric Current
- In Heating Devices such as electric iron, electric toaster, electric oven, electric kettle, electric heater, etc.
- Electric heating is used to produce light in an electric bulb. Here, the filament must retain as much of the heat generated as is possible, so that it gets very hot and emits light. It must not melt at such high temperature. A strong metal with high melting point such as tungsten (melting point 3380°C) is used for making bulb filaments.
- Electric fuse used in electric circuits – It protects circuits and appliances by stopping the flow of any unduly high electric current. FUSE IS ALWAYS PLACED IN SERIES WITH THE DEVICE. A fuse consists of a piece of wire made of a metal or an alloy of appropriate melting point, For Example., aluminium, copper, iron, or lead. If a current larger than the specified value flows through the circuit, the temperature of the fuse wire increases. This melts the fuse wire and breaks the circuit. The fuse wire is usually encased in a cartridge of porcelain or similar material with metal ends.
Disadvantages Of Heating Effect Of Electric Current
- Undesirable as it converts useful electrical energy into heat. Thus, some energy gets wasted.
- In electric circuits, the unavoidable heating can increase the temperature of the components and alter their properties.
Electric Power (P) – The rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in an electric circuit is called electric power (P).
The formula for calculating electric power is:
P = V x I …..(1)
But according to Ohm’s law, V = I x R…..(2)
Substituting value of “V” from equation (2) in equation (1), we get
P = I x R x I
Or, P = I2R
But, I = V/R (from Ohm’s law), therefore
P = V2/R
SI unit of electric power is watt (W).
One watt is the power consumed by a device that carries 1 A of current when operated at a potential difference of 1 V.
Thus, 1 W = 1 volt x l ampere = 1 V A
Since, unit ‘watt’ is very small, we use a much larger unit called ‘kilowatt’ (1 kW = 1000 W).
Further, since electrical energy is the product of power and time, the unit of electric energy is, therefore, watt hour (W h).
One watt hour is the energy consumed when 1 watt of power is used for 1 hour.
Commercial Unit Of Electric Energy is Kilowatt hour (kWh), commonly known as ‘unit’.
1 kW h = 1000 watt x 3600 second = 3.6 x 106 watt second = 3.6 x 106 joule (J).
PSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Solutions
Chapter 3 Electricity Reason- Assertion Questions And Answers
The following questions consist of two statements -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- A is true but R is false.
- A is false but R is true.
Question 1. Assertion (A): Tungsten metal is used for making filaments of incandescent lamps.
Reason (R): The melting point of tungsten is very low.
Answer: 3. A is true but R is false.
Question 2. Assertion (A): When the resistances are connected end-to-end consecutively, they are said to be in series.
Reason (R): In case the total resistance is to be increased, then the individual resistances are connected in series.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 3. Assertion (A): When the resistances are connected between the same two points, they are said to be connected in parallel.
Reason (R): In case the total resistance is to be decreased, then the individual resistances are connected in parallel.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 4. Assertion (A): The fuse is placed in series with the device.
Reason (R): Fuse consists of a piece of wire made of a metal or an alloy of appropriate melting point.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 5. Assertion (A): The coil of a heater is cut into two equal halves and only one of them is used into heater. The heater will now require half the time to produce the same amount of heat.
Reason (R): The heat produced is directly proportional to square of current.
PSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Solutions
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 6. Assertion (A): A current carrying wire should be charged.
Reason (R): The current in a wire is due to flow of free electrons in a definite direction.
Answer: 4. A is false but R is true.
Question 7. Assertion (A): An Electron has a negative charge.
Reason (R): Electrons move always from a region of higher potential to a region of lower potential.
Answer: 3. A is true but R is false.
Question 8. Assertion (A): Heater wire must have high resistance and high melting point.
Reason (R): If resistance is high, the electric conductivity will be less.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 9. Assertion (A): In a chain of bulbs, 50 bulbs are joined in series. One bulb is removed now and circuit is completed again. If the remaining 49 bulbs are again connected in series across the same supply, then light gets decreased in the room.
Reason (R): Net resistance of 49 bulbs will be less than 50 bulbs.
Answer: 4. A is false but R is true.
Question 10. Assertion (A): The connecting wires are made of copper.
Reason (R): The electrical conductivity of copper is high.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Chapter 3 Electricity Case Or Source-Based Questions And Answers
Question 1. The table shows the current in three electrical appliances when connected to a 240 V main supply.
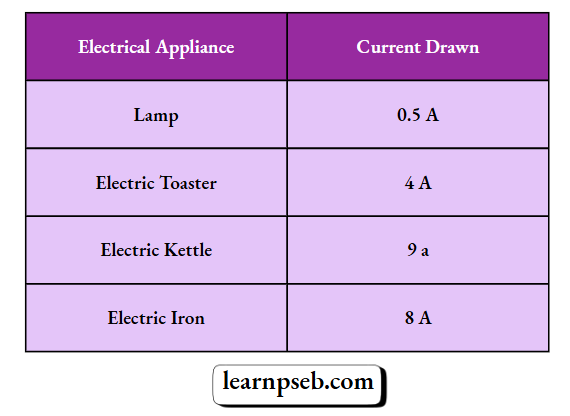
1) Identify the electrical appliance having the highest electrical resistance
- Electric lamp
- Electric toaster
- Electric kettle
- Electric iron
Answer: 1. Electric lamp
2) Calculate the power rating of the kettle when connected to a 240 V main supply.
- 2000 W
- 2160 W
- 3010 W
- 200 W
Answer: 2. 2160 W
3) How much current would be drawn by an electric toaster when it is connected to a 120 V supply?
- 4 A
- 1 A
- 10 A
- 2A
Answer: 4. 2A
4) Calculate the power rating of the lamp when it is connected to a 240 V main supply.
- 300 W
- 120 W
- 200 W
- 240 W
Answer: 2. 120 W
5) 92 Watt = _____ J/S
- 920
- 9.2
- 0.92
- 92
Answer: 4. 92
PSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Solutions
Question 2. In the below circuit, a nichrome wire of length ‘L’ is connected between points X and Y, and note the ammeter reading. The experiment is performed and repeated by inserting another nichrome wire of the same thickness but twice the length i.e., ‘2L’.
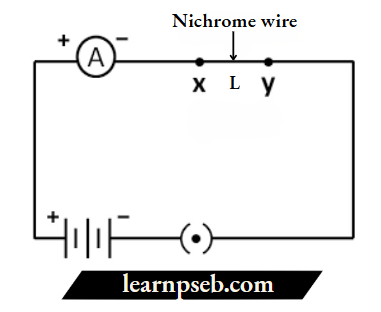
1) What are the changes observed in the ammeter readings?
- Ammeter readings decreases, becomes half
- Ammeter readings increases, becomes two times
- Ammeter readings increases becomes quadrupled
- Ammeter reading decreases becomes one- fourth
Answer: 1. Ammeter readings decreases, becomes half
2) What change is occurred in ammeter reading if instead of changing the length the area of cross- section is doubled?
- Ammeter readings decreases, becomes half
- Ammeter readings increases, becomes two times
- Ammeter readings increases becomes quadrupled
- Ammeter reading decreases becomes one -fourth
Answer: 2. Ammeter readings increases, becomes two times
3) If the resistors of 5 ohms and 10 ohms are connected in series in the above circuit. What is the ratio of the current passing through the two resistors?
- 2:1
- 3:1
- 1:2
- 1:1
Answer: 4. 1:1
4) If the resistors are connected in parallel
- Current across each resistor is same and voltage changes
- Current and voltage across each resistor is same
- Current across each resistor varies and voltage remains same
- Current changes, voltage changes
Answer: 3. Current across each resistor varies and voltage remains same
5) SI unit of current is denoted as
- A
- C
- I
- J
Answer: 1. A
Question 3. Sahil has two wires. Both wires are of the same material but are of different lengths and cross-sections. Sahil has to find the difference in their resistivities for various changes.
1) What is the difference in their resistivity’s for the above-mentioned condition?
- Data given is insufficient to identify the change
- Change in resistivity depends on change in length
- Change in resistivity depends on change in area
- No difference in resistivity’s as both wires are of same material
Answer: 4. No difference in resistivity’s as both wires are of same material
Explanation:
Resistivity’s depends on material of the conductor and not on its dimensions. So, both the wires will have same resistivity’s.
2) If Sahil stretches one of the wires, it becomes double the original length then is there any change in its resistances? If yes, what is the change?
- Area reduces to half and resistance becomes four times the original value
- Area becomes twice and resistance becomes four times the original value
- Area becomes twice and resistance becomes 2 times the original value
- Area decreased by half and resistance becomes 2 times the original value
Answer: 1. Area reduces to half and resistance becomes four times the original value.
3) If he stretches the other wire, it becomes triple its original length then how much is the change?
- Area reduces to one- third and resistance becomes nine times the original value
- Area becomes twice and resistance becomes four times the original value
- Area becomes thrice and resistance becomes 3 times the original value
- Area decreased by one- third and resistance becomes 9 times the original value
Answer: 4. Area decreased by one- third and resistance becomes 9 times the original value.
4) Sahil connect the two wires in series and observe change. What is the change? Why?
- No change
- Area increases
- Area decreased by one- third and resistance becomes 9 times the original value
- Resistance increases as area increases
Answer: 3. Area decreased by one- third and resistance becomes 9 times the original value.
Explanation: When wires are connected in series, there is increase in length. As resistance is directly proportional to length, resistance increases on increasing the length.
PSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Solutions
5) Sahil connected the two wires in parallel and observe the change. What is the change? Give reason.
- Resistance increases as length decreases
- Resistance increases as length increases
- Resistance decreases as area increases
- Resistance increases as area increases
Answer: 3. Resistance decreases as area increases
Explanation: When wires are connected in parallel, the area increases and as we know that resistance is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area, resistance decreases.
Question 4. Sonia has a set of five substances. She has a chart stating resistivities of all the substances.
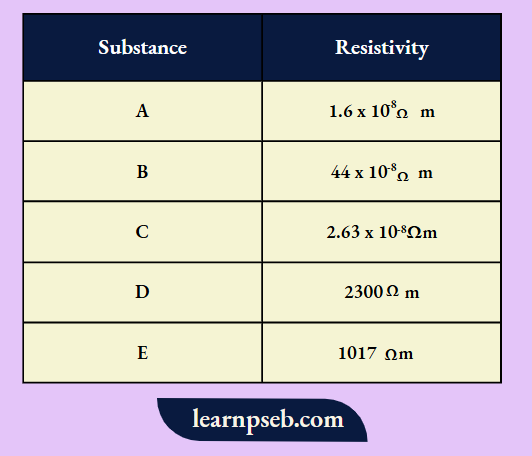
She has to choose an appropriate substance for performing electrical tasks. Which of the above substance according to you
1) Can be used as an insulator
- A
- B
- B as well as C
- E
Answer: 4. E
2) Can be used for domestic wiring
- A
- B
- A as well as C
- D
Answer: 3. A as well as C
3) Can be utilised in making solar cells and transistors
- A
- B
- C
- D
Answer: 4. D
4) Is an alloy
- A
- B
- C
- E
Answer: 2. B
5) Behaves as a semiconductor
- A
- D
- C
- E
Answer: 2. D


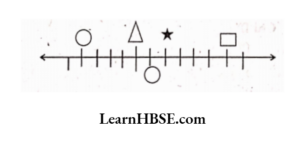
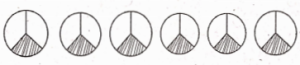 is…….
is…….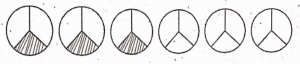

 represents…………..
represents…………..
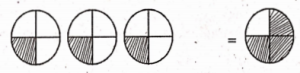

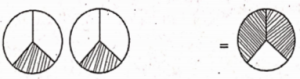
 The value at C is ……….
The value at C is ………. can be represented as
can be represented as
 ( ) a) 0
( ) a) 0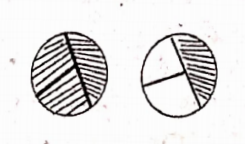 ( ) b) Proper fraction
( ) b) Proper fraction ( ) c) Improper fraction
( ) c) Improper fraction

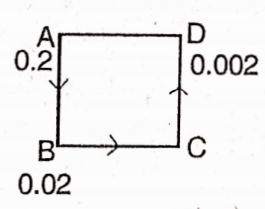
 Find the perimeter of the figure.
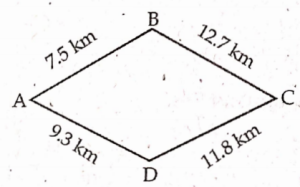
Find the perimeter of the figure.

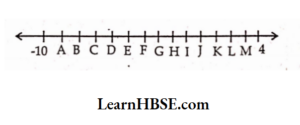
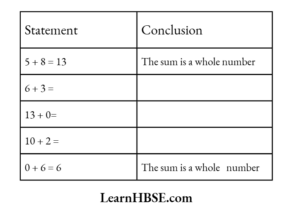
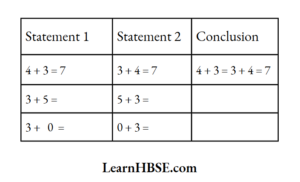
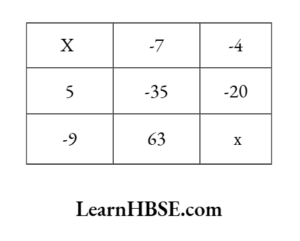
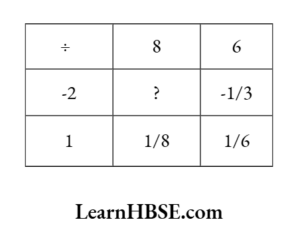
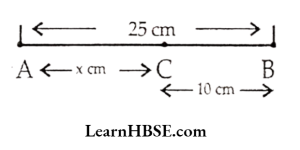
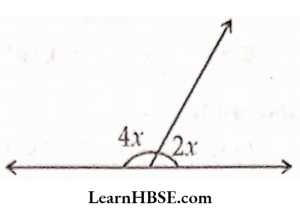
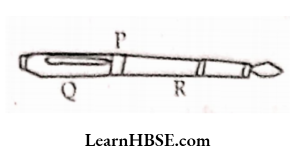 The equation is y + 6 = 12. What are the values of P, Q, R ?
The equation is y + 6 = 12. What are the values of P, Q, R ?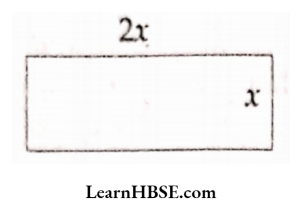 What is the relation between length and beadth of a rectangle?
What is the relation between length and beadth of a rectangle?