- Organisms and Populations Class 12 Biology MCQs
- Evidence Of Evolution Relationship Among Organisms MCQS
- Evolution Of Man Multiple Choice Questions

Question 1. Match the names of the persons listed under Column A with the contributions given in Column B; choose the choice which gives the correct combination of the alphabet:
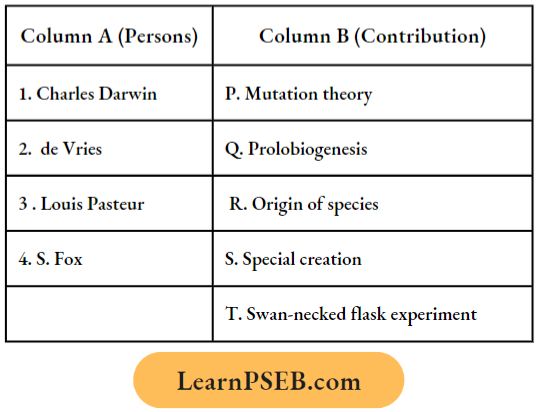
Answer: 4. 1 = r, 2 = p, 3 = t, 4 = q.
Read and Learn More 12th Class Biology MCQs
Question 2. Which one is not vestigial in humans?
Answer: 4. Fingernails.
Question 3. Coal has been mainly formed by:
Answer: 2. Pteridophytes/pteridosperms
PSEB 12th Class Biology Evidence of Evolution MCQs
Question 4. Darwin’s finches provide evidence of evolution from:
Answer: 3. Biogeography
Question 5. The vestigial pelvic girdle and bone remnants of hind limbs are characteristic of:
Answer: 1. Whale

Question 6. Monkeys and some lower groups have certain blood groups which are:
Answer: 1. Identical to those of man
Question 7. The heart is four-chambered in:
Answer: 3. Mammals
Question 8. A living organism with the oldest fossil history is:
Answer: 3. Horse
Question 9. Homologous organs are:
Answer: 3. Hands of Man and wings of Bat
Question 10. The occurrence of endemic species in South America and Australia is due to
Answer: 2. Continental separation
Evidence of Evolution Relationship Among Organisms MCQs PSEB Class 12
Question 11. Similarities in organisms with different genotypes indicates:
Answer: 2. Macroevolution
Question 12. Convergent evolution is illustrated by:
Answer: 1. Dogfish and whale
Question 13. Which one of the following is categorized under living fossils?
Answer: 3. Cycas
Question 14. In which branch do we study about remains of plant life?
Answer: 2. Palaeobotany
Question 15. Flippers of the seal are modified:
Answer: 2. Forelimbs
Question 16. A baby was born with a small tail. It is a case of exhibiting:
Answer: 2. Atavism
Question 17. Which of the following is a living fossil?
Answer: 3. Cycas
Question 18. The age of fossils in the past was determined by the radioactive carbon method and other methods involving radioactive elements found in the rocks. More precise methods, which were used recently and led to the revision of evolutionary periods from different groups of organisms:
Answer: 1. Electron spin resonance and fossil DNA
Class 12 Biology Chapter Evidence of Evolution MCQs
Question 19. Potato and sweet potato have edible parts which are:
Answer: 1. Analogous
Question 20. Which of the following is not a vestigial organ in humans?
Answer: 4. Knee bone.
Question 21. Trilobites evolved during:
Answer: 2. Cambrian
Question 22. Which of the following is not vestigial in humans?
Answer: 2. Nail
Question 23. Which of these pairs is vestigial?
Answer: 1. Cococyx and car pinna muscles
Class 12 Biology Chapter Evidence of Evolution MCQs
Question 24. Which of the following points towards common ancestry?
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 25. The eyes of the octopus and the eyes of the cat show different patterns of structure, yet they perform similar functions. This is an example of:
Answer: 1. Analogous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
Question 26. Which of the following is the relatively most accurate method for dating of fossils?
Answer: 3. Electron-spin resonance method
Question 27. The evolutionary history of an organism is known as:
Answer: 3. Phylogeny
Question 28. Which one of the following is not a living fossil?
Answer: 1. Archaeopteryx
Question 29. An important evidence in favour of organic evolution is the occurrence of:
Answer: 2. Homologous and analogous organs
Question 30. The age of fossils or dating of fossils can be best estimated by:
Answer: 1. Radioactive carbon (C14) dating method
PSEB 12th Class Biology Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 31. The example which best explains the atavism is:
Answer: 4. Long thick and dense hair.
Question 32. Which of the following gives the correct evidence from the connecting link?
Answer: 4. Peripatus — Between Annelida and Arthropoda.
Question 33. Jurassic period of the Mesozoic era is characterised by
Answer: 3. Gymnosperms arc dominant plants and the first birds appear
Question 34. Which one of the following statements is correct?
Answer: 3. Ontogeny repeats phylogeny
Question 35. The Finches of Galapagos islands provide an evidence in favour of:
Answer: 3. Biogeographical Evolution
Question 36. When two species of different genealogy come to resemble each other as a result of adaptation, the phenomenon is termed:
Answer: 3. Convergent evolution
Question 37. Myrmecobius and Myrmecophaga are closely related and have similar adaptations for the same habitat. This phenomenon is
Answer: 2. Parallel evolution
PSEB 12th Class Biology Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 38. Which one of the following options gives one correct example of convergent evolution and divergent evolution?
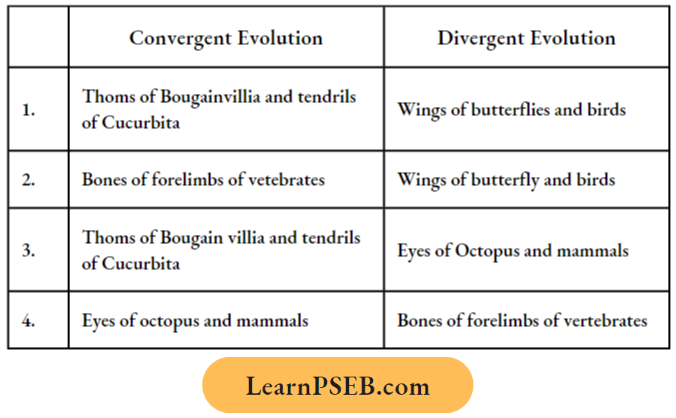
Answer: 4
Question 1. A rapidly growing population experiences increasing genetic variability because:
Answer: 4. Heterozygote superiority is selectively favoured.
Question 2. When food is distributed in such a way that an animal must spend a large part of its day wandering from one place to another to find enough to eat, what type of mating system would you expect it to have?
Answer: 3. Polygamy
Question 3. A human male who remains a bachelor is most likely to enhance his evolutionary success by altruistic behaviour towards the children of:
Answer: 3. His mother
Read and Learn More 12th Class Biology MCQs
Question 4. In light of the definition of evolution, which of the following is not capable of evolving?
Answer: 3. Your biology teacher
PSEB Solutions Class 12 Biology Evolution MCQs

Question 5. Which of the following did Kettlewell conclude from his studies on industrial melanism in moths?
Answer: 4. Dark moths are more likely to survive in polluted areas than light moths.
Question 6. Which bird is most evolutionarily successful
Answer: 4. Lays 7 eggs, 5 hatches and 4 reproduce.
Question 7. Suppose that you have a pack of 50 assorted dogs. You select the largest male and the largest female from the group, mate them, and sterilize the other members of the pack. Assuming that food supplies remain adequate, you should expect that, in the next generation of dogs:
Answer: 2. The young dogs will be, on average, larger than the older members of the pack
Question 8. What is petrification?
Answer: 3. A process of fossil formation
Question 9. The main dictates of Lamarck’s theory is/are:
Answer: 1. All the mentioned below
Question 10. For evolutionary success, a mutation occurs in:
Answer: 4. Germplasm DNA.
PSEB Solutions Class 12 Biology Evolution MCQs
Question 11. The idea of natural selection as the fundamental process of evolutionary change was reached by:
Answer: 2. Charles Darwin and A.R. Wallace in 1859
Question 12. Industrial melanism is an example of:
Answer: 2. Natural selection
Question 13. The role of mutation in evolution is:
Answer: 2. Genetic variation
Question 14. One of the following is obtained by artificial selection:
Answer: 1. Kohlrabi
Question 15. The frequency of a mutant gene in a population is expected to increase if the gene is:
Answer: 3. Favourably selected
Question 16. The term isolating mechanism was coined by:
Answer: 3. Dobzhansky (1937)
Question 17. Who is known as the father of evolution?
Answer: 2. Charles Darwin
Class 12 Biology Evolution Multiple Choice Questions PSEB
Question 18. The evolution resulting in the formation of new species is known as:
Answer: 2. Macroevolution
Question 19. Macroevolution operates above species level and results in the establishment of:
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 20. In speciation which of the following is most important:
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 21. Darwin’s finches are:
Answer: 3. Birds of the family Geospizidae
Question 22. Which of the following statements is false?
Answer: 2. The sum total of genes of all the species in an area constitutes the gene pool.
Question 23. Parallelism is:
Answer: 1. Adaptive convergence of closely related species in evolution
Question 24. Two accessory processes which contribute towards the occurrence of evolution are:
Answer: 2. Migration and hybridization
Question 25. _________ was the first person who considered the real meaning of fossils:
Answer: 2. Anaximander
Question 26. Which of the following is a matching set?
Answer: 3. Theory of Pangenesis – Darwin
Question 27. Class Reptilia first appears in the fossils records in:
Answer: 1. Pennsylvanian period
Question 28. The initial appearance of reptiles from amphibian ancestors to completely terrestrial habitat is an example of:
Answer: 1. Microevolution
Class 12 Biology Evolution Multiple Choice Questions PSEB
Question 29. The complete evolution of the horse has taken about:
Answer: 3. 70 million years
Question 30. What is the essence of evolution?
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 31. In the course of evolution:
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 32. The concealing type of protective mimicry is associated with:
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 33. Phyllopteryx equus (Australian sea horse) shows:
Answer: 2. Concealing mimicry
Question 34. Natural selection that favours heterozygotes is called:
Answer: 1. Balancing selection
Question 35. The type of selection that tends to increase the amount of variance within populations is termed:
Answer: 4. Disruptive selection.
Question 36. Condensation of the phylogenetic events and the elimination of others in the embryonic development is referred to as:
Answer: 3. Techygenesis
Question 37. The theory of natural selection of Darwin was based on:
Answer: 3. Prodigality of reproduction, mass production of species, large number of birth rate and survival of the fittest
PSEB Class 12 Biology Chapter Evolution
Question 38. Persons who do hard manual work with their hands are likely to develop:
Answer: 4. Thick epidermis on their palms.
Question 39. Modem synthetic theory of evolution is based on:
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 40. The present giraffe has a long neck as compared to its ancestors. It could be due to:
Answer: 4. Natural Selection.
Question 41. What is important for a species to survive in a changing environment:
Answer: 3. Genetic variability
Question 42. The role of isolation in evolution is:
Answer: 1. Differentiation of species
Question 43. Being all mammals whales, dolphins, bats, and monkeys show important common characteristics but they also show conspicuous differences. This is due to the phenomenon of:
Answer: 4. Divergence.
Question 44. Darwin’s theory gets much recognition because:
Answer: 3. It is a logical sequence of events that should have occurred
Question 45. Birds and mammals in the geological development of earth arose in the period:
Answer: 3. Jurassic
Question 46. “Evolution can be regarded as the effect of natural selection on the continuous appearance of mutant forms.” What reason would you give to it?
Answer: 3. Neo-Darwinism
PSEB Class 12 Biology Chapter Evolution
Question 47. Experimental evidence of the selection of bacteria by using the replica technique was demonstrated by:
Answer: 3. J. Lederberg and E. Ledcrberg
Question 48. Successful adaptation means:
Answer: 2. Producing fertile offspring
Question 49. Regarding evolution. Darwin’s explanation is that:
Answer: 3. Progressive adaptations enable one species to have more offspring
Question 50. Which of the following is not inheritable?
Answer: 4. Somatic mutation.
Question 51. Organic evolution would not have taken place if:
Answer: 1. Individual in a population did not show genetic variation
Question 52. Under which of the following conditions organic evolution could not have taken place:
Answer: 3. Individuals in a population did not exhibit genetic variation
Question 53. Lederberg’s replica plating experiment suggests:
Answer: 2. Natural selection plays an important role in fixing a mutation of survival value
Question 54. Which phenomenon of evolution was best explained by Darwin?
Answer: 3. Natural selection due to the struggle for existence
Question 55. A good example of mechanical isolation in plants is of:
Answer: 2. Calotropis
Question 56. The formation of high milk-yielding cows is an example of the:
Answer: 2. Artificial selection
Question 57. According to Goldschmidt’s classification, evolution of subspecies or geographic races is known as:
Answer: 3. Microevolution
Question 58. A scientist kept 80 generations of Drosophila in darkness, even after that the flies had normal eyes. This disapproves law of:
Answer: 3. Use and disuse
PSEB Class 12 Biology Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 59. Genetic drift:
Answer: 1. Is an orderly change in gene frequencies
Question 60. Who considered that gene is the vehicle of inheritance and discontinuous variations could be inherited through genes?
Answer: 4. Bateson and Morgan.
Question 61. Who proposed the concept of intraspecific and interspecific struggle?
Answer: 4. Darwin
Question 62. Which one of the following is the best example of an evolutionary change in a species of an organism?
Answer: 3. Alteration in the DNA structure by radiation
Question 63. Darwinism is based on:
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 64. The convergent evolution of two species is usually associated with:
Answer: 2. Analogous organ
PSEB Class 12 Biology Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 65. A detailed classification of isolating mechanisms was provided by:
Answer: 2. Dobzhansky
Question 66. The isolation caused by differences in the habits of organisms such as food and physiological requirements is called:
Answer: 1. Ecological isolation
Question 67. A post-mating isolating mechanism in which the development of a hybrid zygote is often irregular and may end at any stage between fertilization and adulthood, is known as:
Answer: 3. Hybrid inviability
Question 68. ______ isolation refers to the barriers to mating among individuals of different species in their courtship behaviour:
Answer: 1. Ethological
Question 69. Mutation, natural selection, genetic drift and emigration are considered to be essential factors of evolution. The statement that best explains genetic drift is:
Answer: 3. The accidental fluctuations in the frequency of an allele in a population.
Question 70. Neo-Darwinism does not appreciate the role in the evolution of:
Answer: 3. Mutations
Question 71. Which of the following statements is false?
Answer: 1. Selection is most effective for recessive mutations
Question 72. The barriers which check the free exchange of genes between populations (subspecies) are called:
Answer: 2. Isolating barriers
Question 73. Galapagos islands in the Pacific Ocean on the west coast of South America is a chain of:
Answer: 2. 14 islands
Question 74. In addition to the other books, Darwin also wrote:
Answer: 3. Descent of man
PSEB Class 12 Biology Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 75. One of the following plants is tolerant to selenium:
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 76. When a hybrid produces sterile or infertile offspring, it is known as:
Answer: 3. Hybrid inviability
Question 77. The distribution of land snails in Hawaiian islands affords an example of:
Answer: 1. Geographical isolation
Question 78. Which of the following is a post-mating isolating mechanism?
Answer: 2. Hybrid sterility
Question 79. Point out the pre-mating isolating mechanism from the following:
Answer: 4. Isolation due to distance.
Question 80. Penguins occur at the south pole while the north pole has polar bears and not penguins. Why?
Answer: 3. These areas are separated geographically from each other
Question 81. Chinese women used to keep their feet enclosed in iron shoes for many years so that their feet remained small in size. Is this character passed on to the next generation?
Answer: 3. No, it is an acquired character
Question 82. A penguin is a bird that lost the use of its wings by not flying. Such a statement would express the views of:
Answer: 3. Lamarck
Question 83. An Indian and a Japanese though differing in physical features resemble each other precisely at the level of:
Answer: 1. Karyotype
Question 84. The mule is a hybrid of:
Answer: 1. Female horse and male ass
PSEB Class 12 Biology Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 85. The hybrid zygotes produced in fishes fail to cleave and develop properly. It is due to:
Answer: 1. Hybrid non-viability
Question 86. Darwinism is based on:
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 87. Who wrote the essay on Population?
Answer: 2. Malthus
Question 88. Who proposed the concept of intraspecific and interspecific struggle?
Answer: 3. Darwin
Question 1. Which of die following Mendel’s law has not been proven to be true in all the cases?
Answer: 3. Law of dominance
Question 2. When the tall red plant is crossed with a dwarf white plant, all the plants of F1 generation are found to be tall red. Which of the following ratios will be available when a test cross is made?
Answer: 1.1: 1 : 1: 1
Question 3. The three important laws of heredity proposed by Mendel relate to :
Answer: 3. Segregation, independent assortment and dominant recessiveness
Read and Learn More 12th Class Biology MCQs
Question 4. Which one of the following statements is true of Mendel’s theory but not of Darwin’s theory of natural selection?
Answer: 3. Clearly defined laws were proposed during the early stages of the theory.
PSEB Class 12 Biology Elements Of Heredity And Variations MCQs
Question 5. Lethal genes are those which cause :
Answer: 1. Die death of the homozygous infant being formed
Question 6. There is a resemblance between parents and offspring but not the exact likeness. This is because of:
Answer: 3. Both the above and the points
Question 7. When one gene pair hides the effect of another pair, this phenomenon is referred to as :
Answer: 2. Epistasis
Question 8. In a dihybrid cross, Fj individuals arc self-crossed, phenotypic ratio comes to be 15: 1. It is due to :
Answer: 1. Duplicate genes
Question 9. An Execution of Mendel’s law is:
Answer: 4. Linkage.
Question 10. Complementary genes show a ratio of :
Answer: 3. 9: 7
Elements Of Heredity And Variations Multiple Choice Questions PSEB Class 12
Question 11. If 3n is the number of genotypes where ‘n’ is the number of different chromosome pairs with each carrying one heterozygous allele, what would be the different genotypes produced by garden pea plant?
Answer: 4. 37
Question 12. If a dihybrid for the character is crossed to a homozygous recessive individual for the same character, the phenotypic ratio of the progeny would be :
Answer: 1. 1:1:1:1
Question 13.Genes which have similar phenotypic effects when present separately but interact to produce a new phenotype when present together are known as :
Answer: 2. Complementary genes
Question 14. In a green pod of pea, the seed-coat colour changed from grey to white. This is an example of:
Answer: 2. Spontaneous mutation
Question 15. If the genotype of an individual is AA Bb CC, it is a :
Answer: 2. Monohybrid
Question 16. An individual heterozygous for two alleles (Aa Bb) produces two million sperms; how many of the sperms will have both the recessive alleles :
Answer: 3. 0.5 million
Question 17. If the frequency of a dominant phenotype in a stable population is 75%, the frequency of a dominant allele in the population would be:
Answer: 4. 50%.
Elements Of Heredity And Variations Multiple Choice Questions PSEB Class 12
Question 18. If two hybrids for the same quantitative character are crossed the phenotypic ratio of progeny would be ;
Answer: 1. 1:4 : 6: 4: 1
Question 19.In a cross between a pure tall pea plant with a green pod and a pure short plant with a yellow pod, how many short plants you would expect in F2, generation?
Answer: 1. 4
Question 20. From a single car of com, a far nu’r planted 200 kernels which produced NO tall and 10 short plants. The genotypes of these offspring are most likely :
Answer: 2. IT, Tt and tl
Question 21. An individual with genotype Aa Bb Co will produce ;
Answer: 3. Eight different types of gametes
Question 22. Mendel was successful in formulating the laws of inheritance whereas his predecessors were not because :
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 23. A test cross :
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 3
Class 12 Biology Chapter Elements Of Heredity And Variations MCQs
Question 24. Mendel formulated the laws of heredity considering seven pairs of characters in the pea plant. If he had studied an eighth pair, the law which would have been altered is:
Answer: 2. Law of independent assortment
Question 25. In the F2 generation, genotypic and phenotypic ratios are identical in M case of:
Answer: 3. Incomplete dominance
Question 26. The segregation of paired hereditary factors that Mendel postulated occurs during :
Answer: 2. Anaphase of first meiotic division
Question 27. The independent assortment of two pairs of genes located on non-homologous chromosomes occur as a result of the random orientation of chromosomes during :
Answer: 1. Metaphase of the first meiotic division
Question 28. Appearance of hidden character in some progeny of F2 generation proclaims:
Answer: 3. Law of Fiuily ol gametes
Question 29. Mendelian recombinations are due to :
Answer: 3. Independent assortment of characters
Question 30. Mendel law of segregation is based upon the F2 ratio of:
Answer: 4. 3: 1
Class 12 Biology Chapter Elements Of Heredity And Variations MCQs
Question 31. Which one of the following characters in man is controlled by a recessive gene?
Answer: 3. Colour blindness
Question 32. The constriction on chromosomes where the spindle fibres attach during cell division arc :
Answer: 3. Centromere
Question 32. As a result of linkage and crossing over:
Answer: 4. Exchange of chromosomal material occurs.
Question 33. Gene P and Q are necessary for normal hearing. A deaf man marries a deaf woman and all their children have normal hearing. The genotypes of the parents are :
Answer: 3. PPqq x ppQQ
Question 34.A plant with Aa Bb composition, on self-pollination results in which of the following genetic frequencies among the dominant phenotypes?
AABB : AABb : Aa BB : AaBb
Answer: 1. 1 : 2 : 2 : 4
Question 35. “Like begets like” is an important and universal phenomenon of life, is due to :
Answer: 1. Euthenics
Question 36. The father of genetics G.J. Mendel is famous for propounding :
Answer: 3. Laws of inheritance
PSEB Class 12 Biology Genetics MCQs with Answers
Question 37. The frequency of a mutant gene in a population is expected to increase if the gene is:
Answer: 1. Dominant
Question 38. Genetic information is carried out by a long chain of molecules made up of:
Answer: 2. Nucleotides
Question 39. Mendel studied seven contrasting characters for his breeding experiments: which of the following characters he did not study?
Answer: 4. Leaf shape.
Question 40. A normal plant suddenly started producing Parthenon genetically. the number of chromosomes of the second generation compared to the parent plant will be :
Answer: 2. One half
Question 41. Why were pea plants more suitable than dogs for Mendel’s experiments?
Answer: 2. Pea plants can be self-pollinated
Question 42. Suppose pea plant’s tallness is dominant over dwarfness, to determine whether a tall pea plant is homozygous or heterozygous, it should be crossed with the:
Answer: 2. A homozygous dwarf pea plant
Question 43. The term gene was given by :
Answer: 2. Johannsen
PSEB Class 12 Biology Genetics MCQs with Answers
Question 44. The term back cross refers to :
Answer: 1. A cross between F| hybrid and either of the parents
Question 45. A cross between unlike organisms is called as :
Answer: 1. Hybridisation
Question 46. If Mendel had, by chance, chosen to study two traits determined by linked genes, he would have not been able to derive the :
Answer: 2. Law of independent assortment
Question 47. The character which predominates and is seen in F, generation is said to be :
Answer: 2. Dominant
Question 48. The ratio of recessive epistasis :
Answer: 2.13:3
PSEB Class 12 Biology Genetics MCQs with Answers
Question 49. A pure tall pea plant was reared in soil poor in nutrition and reached the size of the pure dwarf pea plant. If this pea plant is selfed then the phenotype in the F| generation is most likely to be :
Answer: 1. All tall
Question 50. In a monohybrid cross, 2 heterozygous individuals were crossed, phenotype ratio comes to be 2: 1. It is due to :
Answer: 1. Dominant lethal genes in homozygous condition
Question 1. The enzyme which joins with the non-proteinic part to form a functional enzyme is:
Answer: 3. Apoenzyme
Question 2. Enzymes that help in electron transfer are :
Answer: 1. Cytochrome
Question 3. Induced-fit theory of enzyme action was given by:
Answer: 1. Koshland
Read and Learn More 12th Class Biology MCQs
Question 4. The most abundant enzyme among living organisms is:
Answer: 2. Rubisco
PSEB 12th Class Biology Enzymes MCQs

Question 5. Enzymes speed up the rate of reaction by :
Answer: 4. Lowering activation energy.
Question 6. The enzyme which fixes CO2 in C4 plants, is :
Answer: 2. Pepcarboxyease
Question 7. Endoenzymes generally act at:
Answer: 1. Neutral ph
Question 8. The nomenclature of the enzyme consists of :
Answer: 1. First name of the product and then reaction name
Question 9. Holoenzyme is :
Answer: 3. Complete enzyme
Enzymes Multiple Choice Questions PSEB Class 12
Question 10. The energy released from enzyme-substrate interaction is known as:
Answer: 2. Binding energy
Question 11. The enzyme involved in the hydrolysis of starch to maltose is called:
Answer: 2. Amylase
Question 12. The hydrolytic enzymes acting at low pH are termed:
Answer: 1. Alpha-amylase
Question 13. The glycogen in a dead or killed animal is disintegrated by the enzymatic action to:
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 15. Enzymes, vitamins, and hormones can be classified into a single category of biological chemicals because all of these:
Answer: 4. Help in regulating metabolism
Question 16. Which of the following statements regarding enzyme inhibition is correct?
Answer: 3. Competitive inhibition is seen when the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the active site on the
Class 12 Biology Chapter Enzymes MCQs
Question 17. The catalytic efficiency of two different enzymes can be compared by the :
Answer: 1. The km value
Question 18. Telomerase is an enzyme that is a :
Answer: 4. Ribonucleoprotein
Question 19. The figure given below shows three velocity-substrate concentration curves for an enzyme reaction. What do the curves a, b, and c depict respectively?
Image-
Answer: 1. A-normal enzyme reaction, b-competitive c-non-competitive inhibition.
Question 21. In which one of the following sets of three items each belong to the category tensioned against them?
Answer: 3. Rennin, helicase, and hyaluronidase….enzymes
Question 21. Assertion: a coenzyme or metal ion that is very tightly bound to an enzyme protein is called a prosthetic.
Reasons: a complete, catalytically active enzyme together with its bound prosthetic group is called an apoenzyme.
Answer: 3. Is a true statement but (r) is false
Question 22. If by radiation all nitrogenase enzymes are inactivated, then there will be no :
Answer: 1. A fixation of nitrogen in legumes
Question 23. Which of the following cell organelles is rich in catabolic enzymes?
Answer: 3. Mitochondria
Question 24. Cytochrome oxidase is a.an :
Answer: 4. Endoenzyme
Question 25. Enzymes found attached to the inner membrane of mitochondria instead of the matrix are :
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2.
PSEB 12th Class Biology Enzymes Questions with Answers
Question 26. A competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase is :
Answer: 2. Maionate
Question 27. An example of feedback inhibition is :
Answer: 3. Allosteric inhibition of hexokinase by glucose 6- phosphate
Question 28. The essential chemical components of many coenzymes
Answer: 3. Vitamins
Question 29. The transition state structure of the substrate formed during an enzymatic reaction is :
Answer: 2. Transient an unstable
Question 1. What evidence suggests that chimpanzees are more closely related to humans than other hominid species?
Answer: 4. DNA of both autosomes and sex chromosomes.
Question 2. The cranial cavity of Australopithecus was:
Answer: 2. 350-450 cm³
Question 3. Tuang baby is:
Answer: 2. Australopithecus
Read and Learn More 12th Class Biology MCQs
Question 4. Which one of the following apes is found in India:
Answer: 1. Gorilla
PSEB 12th Class Biology Evolution Of Man MCQs
Question 5. Most primary hominids that appeared were:
Answer: 3. Late Miocene and early Pliocene

Question 6. There are two opposing views about the origin of modern man. According to one view Homo erectus in Asia were the ancestors of modem man. A study of variations of DNA however suggested the African origin of modern man. What kind of observation of DNA variation could suggest this?
Answer: 1. Greater variation in Africa than in Asia
Question 7. The last common ancestor between the African apes and hominids lived during the epoch:
Answer: 2. Pliocene
Question 8. What was the most significant trend in the evolution of modem (Homo sapiens) from his ancestors?
Answer: 2. Increasing cranial capacity
Question 9. The cranial capacity of Neanderthal man was about:
Answer: 1. 1450 cc
Question 10. What is the correct sequence of human evolution:
Answer: 1. Ramapithecus → Australopithecus → Homo erectus → Neanderthal → Homo sapiens sapiens
Question 11. Among the human ancestors the brain size was more than 1000 cc in:
Answer: 4. Homo neanderthalensis.
Evolution Of Man Multiple Choice Questions PSEB Class 12
Question 12. What was the most significant trend in the evolution of modem man (Homo sapiens) from his ancestors?
Answer: 4. Increasing brain capacity.
Question 13. Which of the following is used as an atmospheric pollution indicator?
Answer: 2. Lichens
Question 14. The theory of spontaneous generation states that:
Answer: 3. Life can arise from non-living things only
Question 15. Animal husbandry and plant breeding programs are examples of:
Answer: 2. Artificial selection
Question 16. Palaeontological evidence for evolution refers to the.
Answer: 3. Fossils
Question 17. The bones of forelimbs of whales, bats, cheetahs, and man are similar in structure, because:
Answer: 2. They share a common ancestor
Evolution Of Man Multiple Choice Questions PSEB Class 12
Question 18. Analogous organs arise due to:
Answer: 4. Convergent evolution.
Question 19. (p+q)² = p² + 2pq + q² = 1 represents an equation used in:
Answer: 3. Biometrics
Question 20. Appearance of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is an example of:
Answer: 3. Pre-existing variation in the population
Question 21. Evolution of life shows that life forms had a trend of moving from:
Answer: 4. Water to land
Question 22. Viviparity is considered to be more evolved because
Answer: 3. The young ones are protected inside the mother’s body and are looked after they are bom leading to more chances of survival
Question 23. Fossils are generally found in:
Answer: 1. Sedimentary rocks
Question 24. For the MN-blood group system, the frequencies of M and N alleles arc 0.7 and 0.3, respectively. The expected frequency of MN-blood group-bearing organisms is likely to be.
Answer: 1. 42%
Question 25. Which type of selection is industrial melanism observed in moths? Bistort Bulgaria:
Answer: 2. Directional
Question 26. The most accepted line of descent in human evolution is:
Answer: 3. Ramapithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
Question 27. Which of the following is an example of connecting link species?
Answer: 1. Lobe fish
Question 28. Match the scientists listed under column ‘A’ with ideas listed in column ‘B’.
Answer: 2. 1-D; 2-A; 3-B; 4-C
Question 29. In 1953 S.L. Miller created primitive earth conditions in the laboratory and gave experimental evidence for the origin of the first form of life from pre-existing non-living organic molecules. The primitive earth conditions created include:
Answer: 4. High temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere containing CH4, NH3, etc.
Class 12 Biology Chapter Evolution Of Man MCQs
Question 30. Variations during mutations of meiotic recombinations are:
Answer: 1. Random and directionless
Question 31. The essence of Darwinian theory about evolution is:
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2).
Question 32. Darwin’s theory of natural selection was influenced by the work of:
Answer: 2. Thomas Malthus
Question 33. Natural selection is based on certain observations which are factual. They are:
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 34. Key concepts of Darwinian theory are:
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2).
Question 35. The process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and spreading to other areas is called:
Answer: 1. Adaptive radiation
Question 36. Huge clusters of galaxies comprise the universe. This universe is how many years old?
Answer: 4. 20 billion.
Question 37. Big Bang theory explains the origin of the universe. Did life appear on earth about how many years ago?
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2) correct
Class 12 Biology Chapter Evolution Of Man MCQs
Question 38. Analogous structures are a result of:
Answer: 1. Convergent evolution
Question 39. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is affected by
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 40. Dinosaurs became extinct during which period:
Answer: 3. Tertiary
Question 41. The Neanderthal man with a brain size of 1400 cc lived near East and Central Asia between:
Answer: 1. 100,000 – 40,000 years ago
Question 42. The biggest dinosaurs about 20 ft in height were:
Answer: 2. Tyratmosams
Question 43. Which of the following is correct?
Answer: 4. All are correct.
Question 44. A new mutation spreads from one population to another by means of:
Answer: 3. Mutation pressure
Question 45. Genetic drift occurs when a few individuals of a species colonize in land. The particular phenomenon is:
Answer: 2. The founder effect
Question 46. A plant population that reproduces by self-pollination is an extreme example of:
Answer: 4. Assortative mating.
Question 47. Lumpers tend to:
Answer: 2. Combine the population into single species or group
PSEB 12th Class Biology Human Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 48. Reproductive isolation in sympatric speciation develops without a:
Answer: 1. Geographical barrier
Question 49. Which of the following is the most rapid method of speciation?
Answer: 1. Polyploidy
Question 50. Common bread wheat is thought to have arisen through:
Answer: 4. Ecological separation.
Question 51. Which of the following originated during the Miocene epoch in Africa and Asia?
Answer: 2. Dryopithecus
Question 52. Homo habilis, a tool maker having a cranial capacity of? 735 cc and bipedal gait existed during which epoch?
Answer: 1. Pleitostocene
Question 53. The most recent products of animal evolution are:
Answer: 2. Mammal
Question 54. Apes have:
Answer: 2. Arms longer than legs
PSEB 12th Class Biology Human Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 55. Cromagnon man had:
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 56. Which fossil man had a cranial capacity almost equal to modern man?
Answer: 3. Neanderthal man
Question 57. A cranial capacity of about 1200 cc belongs to
Answer: 2. Peking man
Question 58. Who discovered Java man?
Answer: 3. Dubois
Question 59. Handyman is:
Answer: 3. Homo habilis
Question 60. The evolution of man came after Dry epithets
Answer: 1. Ramapithecus
Question 61. Which of the following is closest to man?
Answer: 2. Cromagnon
Question 62. Which of the following is not a feature of apes?
Answer: 4. Occipital condyles lateral in position.
PSEB 12th Class Biology Human Evolution MCQs with Answers
Question 63. Which of the following is not a feature of present-day man?
Answer: 1. More hair
Question 64. Which of the following is not a feature of Australopithecus?
Answer: 1. Simian gap present
Question 65. Homo areas show:
Answer: 1. Upright bipedal locomotion
Question 66. Six races i.e. Negroid, Casusacoid. Mongaloid, Australcoid, Polynesian, and Bushman were recognized by
Answer: 3. Manell (1962)
Question 67. Parapithecus was discovered by:
Answer: 2. Colbert
Question 68. Australopithecus African (African ape man) was discovered by
Answer: 3. Raymon Dart
Question 69. Gregor discovered Homo sapiens fossils during the late Pleistocene period showed the following characters except:
Answer: 4. Cranial capacity 1200-1500 cm³
Question 70. Hominids include:
Answer: 1. Homo sapiens
Question 1. Protobiogenesis occurred:
Answer: 4. More than 3.5 billion years ago.
Question 2. Possible early sources of energy were:
Answer: 3. UV radiations and lightning
PSEB 12th Class Biology Origin of Life Questions with Answers
Question 3. One of the greatest advocates of the theory of special creation was:
Answer: 3. Father Saurez
Read and Learn More 12th Class Biology MCQs

Question 4. The theory of spontaneous generation was supported by:
Answer: 1. Van Helmont
PSEB 12th Class Biology Origin of Life MCQs
Question 5. The most advanced theory of the origin of life is that of:
Answer: 2. Haldane and Oparin
Question 6. First life on earth was:
Answer: 2. Chemoheterotrophs
Question 7. There is no life on the moon because of the absence of:
Answer: 1. Water
Question 8. On the primitive earth, polymers such as proteins and nucleic acids in aqueous suspension formed the spherical aggregates, they are called:
Answer: 1. Coacervates
Question 9. Swan-necked flask experiment was done by:
Answer: 3. Louis Pasteur
PSEB 12th Class Biology Origin of Life Questions with Answers
Question 10. The early atmosphere contained methane and other hydrocarbons. They have now been replaced by:
Answer: 3. Carbon dioxide
Question 11. Coacervates were experimentally produced by:
Answer: 2. Oparin and Sydney Fox
Question 12. According to Oparin, which one of the following was not present in the primitive atmosphere of Earth?
Answer: 4. Oxygen.
Origin of Life Multiple Choice Questions PSEB Class 12
Question 13. Which one of the following experiments suggests that the simplest living organisms could not have originated spontaneously from non-living matter?
Answer: 4. Meat was not spoiled when heated and kept sealed in a vessel.
Question 14. One of the following plants has remained unchanged from the time of its origin:
Answer: 2. Ginkgo
Question 15. The theory of special creation was supported by:
Answer: 1. Van Helmont
Question 16. Oparin-Haldane theory of the origin of life states that:
Answer: 1. Life originated as a result of physicochemical changes
Question 17. Miller conducted his experiment in an apparatus containing methane, ammonia and hydrogen in the ratio of:
Answer: 2. 2: 1: 2
Class 12 Biology Chapter Origin of Life
Question 18. Which one of the following amino acids was not found to be synthesized in Miller’s experiment?
Answer: 3. Glutamic acid
Question 1. The keystone species in an ecosystem are those which:
Answer: 4. Contribute to ecosystem properties.
Question 2. The sphere of living matter together with water, air, and soil on the earth is called:
Answer: 4. Biosphere
Question 3. Plants with irreversible and genetically fixed adaptations are known as :
Answer: 1. Ecotypes
Read and Learn More 12th Class Biology MCQs
Question 4. Species which has a restricted distribution is called :
Answer: 1. Endemic
Organisms and Populations Class 12 Biology MCQs
Question 5. The study of communities, especially their environmental relationship, and structure, is known as
Answer: 2. Synecology

Question 6. When the organisms live together in such a manner that one organism is benefited while the other remains unaffected. This type of association is called:
Answer: 1. Commensalism
Question 7. Plants and animals living in a given area form a:
Answer: 3. Biotic community
Question 8. The part of the earth and atmosphere supporting life is:
Answer: 4. Biosphere
Question 9. Which of the following is synecology?
Answer: 2. Study of different species
Question 10. The term ‘biocoenosis’ was coined by:
Answer: 4. E.Haeckel.
Question 11. A number of immigrants is more than emigration and deaths is lower than natality. The growth curve of the population will show:
Answer: 1. Exponential phase
Class 12 Biology Chapter Organisms and Populations MCQs
Question 12. Which one of the following has raised check bone, oblique eyes, and yellowish skin color
Answer: 2. Mongoloids
Question 13. Scent-producing glands arc:
Answer: 1. Anal glands
Question 14. Pheromone is:
Answer: 4. mRNA
Question 15. The percentage ratio of natality over mortality is:
Answer: 2. Vital index
Question 16. The human population shows:
Answer: 3. S-shaped growth curve
Question 17. The process of mating of individuals which are more closely related than the average of the population to which they belong is called :
Answer: 1. Inbreeding
Question 18. Adaptation of a species is its :
Answer: 4. Hereditary Character
Class 12 Biology Chapter Organisms and Populations MCQs
Question 19. The abundance of a species in a population, within its habitat, is called:
Answer: 1. Atniche density
Question 20. Asymptote is a stage when a population is:
Answer: 1. Stabilised
Question 21. Two species cannot occupy the same niche. This law is known as:
Answer: 2. Gause Law
Question 22. In which one of the following habitats, does the diurnal temperature of the soil surface vary most?
Answer: 2. Desert
Question 23. Broad-leaved forest oaks are found in
Answer: 2. Mediterranean evergreen forest
Question 24. Prolonged liberal irrigation of agricultural fields is likely to create the problem of
Answer: 4. Salinity.
Question 25. At which latitude, does heat gain through insolation approximately equals heat loss through terrestrial radiation?
Answer: 3. 42½° North and South
Question 26. Animals have the innate ability to escape from predation. Examples for the same are given below. Select the incorrect example:
Answer: 3. Poison fangs in snakes
Question 27. There exists a close association between the alga and the fungus within lichen. The fungus:
Answer: 2. Provides protection, anchorage, and absorption for the alga
State Board Class 12 Biology Organisms and Populations MCQs
Question 28. Identify the correctly matched pair:
Answer: 2. Kyoto Protocol – Climatic change
Question 29. The ability of the Venus fly trap to capture insects is, due to:
Answer: 4. Rapid turgor pressure changes.
Question 30. Sunderban contains mainly:
Answer: 1. Mangroove plants
Question 31. Pneumatophores are present/common in
Answer: 4. Helopytes
Question 32. Which one of the following correctly represents an organism and its ecological niche?
Answer: 3. Plant lice (aphids) and leaf
Question 33. Humidity in the atmosphere decreases the rate of:
Answer: 1. Transpiration
Question 34. Niche overlap indicates:
Answer: 1. Sharing of one or more resources between the two species
State Board Class 12 Biology Organisms and Populations MCQs
Question 35. Annual migration does not occur in the case of:
Answer: 1. Salamander
Question 36. Choose the correct combination of labeling of the zones in water in a lake.
Answer: 3. a-Littoral zone, b-Limnetic zone, c-Profundal zone, d-Benthic zone
Question 37. Geometric representation of age structure is a characteristic of
Answer: 1. Population
Question 38. The population of an insect species shows an explosive increase in number during rainy season followed by its disappearance at the end of the season. What does this show?
Answer: 2. Its population growth curve is of J-type.
Question 39. Which one of the following is categorized as a parasite in the true sense?
Answer: 3. Head louse living on the human scalp as well as laying eggs on human hair
Question 40. Consider the following four conditions (1 – 4) and select die correct pair of them as adaptation to the environment in desert lizards. The conditions:
Options:
Answer: 2. (1), (3)
State Board Class 12 Biology Organisms and Populations MCQs
Question 41. What type of human population is represented by the following age pyramid?
Answer: 3. Declining population
Question 42. People, who migrated from the planes to an area adjoining Rohtang Pass about six months back:
Answer: 4. Have more RBCs and their hemoglobin has a lower binding affinity to O2
Question 43. The fungal association of roots of higher plants in mycorrhiza is known as :
Answer: 3. Mutualism
Question 44. Hyperparasite is a kind of parasite which:
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 45. Plants obtaining nourishment from other plants by haustoria are:
Answer: 2. Parasites
Question 46. A successful parasite is the one which
Answer: 4. Makes minimum demands from its host.
Question 47. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the two organisms in commensalism?
Organisms and Populations MCQs with Answers Class 12
Question 48. Which is not characteristic of intestinal symbionts?
Answer: 4. Aerobic respiration
Question 49. Ecological succession on sand is:
Answer: 1. Timomere
Question 50. The cause of mimicry is
Answer: 1. Concealment
Question 51. Which of the following insects mimics thin dry branches of the plant on which it lives?
Answer: 2. Mantis religiosa
Question 52. The individual that shows mimicry is called:
Answer: 1. Mimic
Question 53. Heterodon flattens its head and produces frequent hissing and strikes to advertise as if it is dangerous. This is an example of:
Answer: 2. Warning mimicry
Question 54. In conscious mimicry:
Answer: 1. The organisms behave as if they are dead bodies
Question 55. Which of the following resembles a dry leaf?
Answer: 2. Paralectci
Question 56. July 11 is observed as:
Answer: 4. World Environment Day
Organisms and Populations MCQs with Answers Class 12
Question 57. Which among the following is the primary function of mimicry prevalent in some animals?
Answer: 2. Concealment
Question 58. Succession in an ecosystem is the result of:
Answer: 4. Adaptive ability to environmental changes
Question 59. Mycorrhiza is an example of:
Answer: 3. Symbiotic relationship
Question 60. Two opposite forces operate in the growth and development of every population. One of them relates to the ability to reproduce at a given rate. The force opposing it is called :
Answer: 4. Environmental resistance
Question 61. Maximum growth rate occurs in:
Answer: 3. Exponential Phase
Question 62. Lichens are a well-known combination of an alga and a fungus where the fungus has:
Answer: 3. Symbiotic relationship with the alga
Organisms and Populations MCQs with Answers Class 12
Question 63. An ecosystem that can be easily damaged but can recover after some time if the damaging effect stops will have the following:
Answer: 1. High stability and low resistance
Question 64. A terrestrial animal must be able to:
Answer: 4. Conserve water.
Question 65. What is a keystone species?
Answer: 4. A species that makes only a small proportion of the total biomass of a community, yet has a huge impact on a community’s organization and survival.
Question 66. The most thoroughly studied of the known bacteria-plant interaction is the:
Answer: 4. Gall formation on certain angiosperms by Agrobacterium.
Question 67. A term used to describe non-dominant species that dictate community structure is:
Answer: 3. Keystone species
Question 68. In succession, complexities in structure:
Answer: 2. Slowly increase
Question 69. The presence of diversity at the junction of territories of two different habitats is known as
Answer: 2. Edge effect
Question 70. Small fish get stuck near the bottom of a shark and derive its nutrition from it. This kind of association is called as:
Answer: 2. Commensalism
Question 71. A praying mantis is a good example of:
Answer: 2. Camouflage
Question 72. The formula for exponential population growth is:
Answer: 2. dN/dt = rN
Question 73. Match the following with the correct combination:
Answer: 2. 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
Question 74. Find out the correct order of succession levels in xerarch.
Answer: 1. Lichen moss stage, annual herb stage, perennial herb stage, scrub stage, forest
Organisms and Populations MCQs with Answers Class 12
Question 75. The concept of chemical evolution is based on:
Answer: 3. Possible origin of life by a combination of chemicals under suitable environmental conditions
Question 76. If the mean and the median pertaining to a certain character of a population are of the same value, the following is most likely to occur:
Answer: 4. A normal distribution.
Question 77 The equation \(\frac{\Delta N_n}{\Delta N}\) represents which of the following?
Answer: 2. Growth rate
Question 78. The change in population size at a given time interval t, is given by the expression Nt = N0 + I – D – E, I, B, and D stand respectively for
Answer: 5. Rate of immigration, natality rate, mortality rate.
Question 79. Which one of the following is considered as pioneer community in xerarch?
Answer: 5. Lichen
Question 80. Which one of the following statements is correct for secondary succession?
Answer: 2. It occurs on a deforested site
Question 81. A sedentary sea anemone gets attached to the shell lining of a hermit crab. The association is:
Answer: 2. Commensalism
Question 82. A biologist studied the population of rats in a bam. He found that the average natality was 250, average mortality was 240, immigration was 20, and emigration 30. The net increase in population is:
Answer: 3. Zero