Question 1. If the bond energies of H-H, Br-Br, and H-Br are 433, 192 and 364 kJ mol-1 respectively, the ΔH° for the reaction \(\mathrm{H}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{Br}_{2(g)} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{HBr}_{(g)}\) is
- -261 kJ
- +103kJ
- +261 kJ
- -103 kJ
Answer: 4. -103 kJ
⇒ \(\begin{array}{ccc}
\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{H}+\mathrm{Br}-\mathrm{Br} & \rightarrow & 2 \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{Br} \\
433+192 & & 2 \times 364 \\
=625 & & =728
\end{array}\)
Net energy released = 728 – 625 = 103 kJ
i.e. ΔH° = – 103 kJ
Question 2. For irreversible expansion of an ideal gas under isothermal conditions, the correct option is
- \(\Delta U \neq 0, \Delta S_{\text {total }}=0\)
- \(\Delta U=0 \quad \Delta S_{\text {total }}=0\)
- \(\Delta U \neq 0, \Delta S_{\text {total }} \neq 0\)
- \(\Delta U=0, \Delta S_{\text {total }} \neq 0\)
Answer: 4. \(\Delta U=0, \Delta S_{\text {total }} \neq 0\)
For reversible and irreversible expansion for an ideal gas under isothermal conditions, ΔU = 0, but ΔStotal i.e., \Delta \(S_{\text {sys }}+\Delta S_{\text {Surr }}\), is not zero for an irreversible process.
Read And Learn More Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
Question 3. For the reaction, \(2 \mathrm{Cl}_{(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cl}_{2(g)}\), the correct option is
- \(\Delta_r H>0\) and \(\Delta_r S>0\)
- \(\Delta_r H>0\) and \(\Delta_r S<0\)
- \(\Delta_r H<0\) and \(\Delta_r S>0\)
- \(\Delta_r H<0\) and \(\Delta_r S<0\)
Answer: 4. \(\Delta_r H<0\) and \(\Delta_r S<0\)
In the reaction, \(2 \mathrm{Cl}_{(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cl}_{2(g)}\), the randomness decreases as 2 moles of \(\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{g})}\) are converted to 1 mole of \(\mathrm{Cl}_{2(g)}\), thus, \(\Delta_r S<0\).
This is an exothermic reaction, thus, \(\Delta_r H<0\).
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Question 4. In which case change in entropy is negative?
- \(2 \mathrm{H}_{(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2(g)}\)
- Evaporation of water
- Expansion of a gas at a constant temperature
- Sublimation of solid to gas
Answer: 1. \(2 \mathrm{H}_{(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2(g)}\)
If Δng < 0 then ΔS < 0
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Thermodynamics MCQs
Question 5. For a given reaction, ΔH = 35.5 kJ mol-1 and ΔS = 83.6 J K-1 mol-1. The reaction is spontaneous at (Assume that ΔH and ΔS do not vary with temperature.)
- T > 425 K
- All temperatures
- T > 298 K
- T < 425 K
Answer: 1. T > 425 K
For a spontaneous reaction, ΔG<0 i.e., ΔH – TΔS < 0
T > \(\frac{\Delta H}{\Delta S} ; T>\left(\frac{35.5 \times 1000}{83.6}=424.6\right) \approx 425 \mathrm{~K}\)
∴ T>425K

Question 6. For a sample of perfect gas when its pressure is changed isothermally from pi to pj, the entropy change is given by
- \(\Delta S=n R \ln \left(\frac{p_f}{p_i}\right)\)
- \(\Delta S=n R \ln \left(\frac{p_i}{p_f}\right)\)
- \(\Delta S=n R T \ln \left(\frac{p_f}{p_i}\right)\)
- \(\Delta S=R T \ln \left(\frac{p_i}{p_f}\right)\)
Answer: 2. \(\Delta S=n R \ln \left(\frac{p_i}{p_f}\right)\)
For an ideal gas undergoing reversible expansion, when the temperature changes from Ti to Tf and pressure changes from pi to pf
∴ \(\Delta S=n C_p \ln \frac{T_f}{T_i}+n R \ln \frac{p_i}{p_f}\)
For an isothermal process, \(T_i=T_f\) so, In 1=0
∴ \(\Delta S=n R \ln \frac{p_i}{p_f}\)
Question 7. The correct thermodynamic conditions for the spontaneous reaction at all temperatures is
- ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0
- ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0
- ΔH < 0 and ΔS = 0
- ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
Answer: 1. ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0; and 3. ΔH < 0 and ΔS = 0
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
If ΔH <0 and ΔS>0
ΔG =(-ve)-T(+ve)
then at all temperatures, ΔG = -ve, spontaneous reaction
I fΔH<0 and ΔS=0
ΔG = (-ve) – T(0) = -ve at all temperatures
Question 8. Consider the following liquid-vapour equilibrium. Liquid ⇔ Vapour Which of the following relations is correct?
- \(\frac{d \ln P}{d T^2}=\frac{-\Delta H_v}{T^2}\)
- \(\frac{d \ln P}{d T}=\frac{\Delta H_v}{R T^2}\)
- \(\frac{d \ln G}{d T^2}=\frac{\Delta H_v}{R T^2}\)
- \(\frac{d \ln P}{d T}=\frac{-\Delta H_v}{R T}\)
Answer: 2. \(\frac{d \ln P}{d T}=\frac{\Delta H_v}{R T^2}\)
This is Clausius-Clapeyron equation’
Question 9. Which of the following statements is correct for the spontaneous adsorption of a gas?
- ΔS is negative and, therefore ΔH should be highly positive.
- ΔS is negative and therefore, ΔH should be highly negative.
- ΔS is positive and therefore, ΔH should be negative.
- ΔS is positive and therefore, ΔH should also be highly positive.
Answer: 2. ΔS is negative and therefore, ΔH should be highly negative.
Using Gibbs-Helmholtz equation, ΔG = ΔH- TΔS
During the adsorption of a gas, entropy decreases i.e ΔS < 0
For spontaneous adsorption, ΔG should be negative, which is possible when ΔH is highly negative.
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Thermodynamics MCQs
Question 10. For the reaction, \(\mathrm{X}_2 \mathrm{O}_{4(l)} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{XO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}\) ΔU= 2.1 kcal, ΔS = 20 cal K-1 at 300 K Hence, ΔG is
- 2.7 kcal
- -2.7 kcal
- 9.3 kcal
- -9.3 kcal
Answer: 2. -2.7 kcal
⇒ \(\Delta H=\Delta U+\Delta n_g R T\)
Given, \(\Delta U=2.1 \mathrm{kcal}, \Delta n_g=2\)
R \(=2 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{kcal}, T=300 \mathrm{~K}\)
∴ \(\Delta H=2.1+2 \times 2 \times 10^{-3} \times 300=3.3 \mathrm{kcal}\)
Again, \(\Delta G=\Delta H-T \Delta S\)
Given, \(\Delta S=20 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{kcal} \mathrm{K}^{-1}\)
On putting the values of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) in the equation, we get
Δ\(G=3.3-300 \times 20 \times 10^{-3}\)
= \(3.3-6 \times 10^3 \times 10^{-3}=-2.7 \mathrm{kcal}\)
Question 11. A reaction having equal energies of activation for forward and reverse reactions has
- ΔH = 0
- ΔH = ΔG = ΔS = 0
- ΔS = 0
- ΔG = 0
Answer: 1. ΔH = 0
ΔH = \(\left(E_a\right)_f-\left(E_a\right)_b=0\)
Question 12. In which of the following reactions, standard reaction entropy change (ΔS°) is positive and standard Gibbs energy change (ΔG°) decrease sharply with increasing temperature?
- \(\mathrm{C}_{\text {(graphite) }}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{(g)}\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_{(g)}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2(g)}\)
- \(\mathrm{Mg}_{(s)}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{MgO}_{(s)}\)
- \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{C}_{\text {(graphite) }}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CO}_{2(g)}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{C}_{\text {(graphite) }}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{(g)}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_{\text {(graphite) }}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{(g)}\)
⇒ \(\Delta n_g=1-\frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
As the amount of gaseous substance is increasing in the product side thus, \(\Delta S\) is positive for this reaction.
And we know that \(\Delta G=\Delta H-T \Delta S\)
As \(\Delta S\) is positive, thus increase in temperature will make the term \((-T \Delta S)\) more negative and \(\Delta G\) will decrease.
Question 13. The enthalpy of fusion of water is 1.435 kcal/mol. The molar entropy change for the melting of ice at 0°C is
- 10.52 cal/(mol K)
- 21.04 cal/(mol K)
- 5.260 cal/(mol K)
- 0.526 cal/(mol K)
Answer: 3. 5.260 cal/(mol K)
⇒ \(\Delta H_{\text {fus }}=1.435 \mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
⇒ \(\Delta S_{f u s}=\frac{\Delta H_{f u s}}{T_{f u s}}=\frac{1.435 \times 10^3}{273}=5.26 \mathrm{cal} /(\mathrm{mol} \mathrm{K})\)
Question 14. If the enthalpy change for the transition of liquid water to steam is 30 kJ mol-1 at 27°C, the entropy change for the process would be
- 10 J mol-1 K-1
- 1.0 J mol-1 K-1
- 0.1 J mol-1 K-1
- 100 J mol-1 K-1
Answer: 4. 100 J mol-1 K-1
We know that ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
0 = ΔH – TΔS ∴ (ΔG = 0 as transition of \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{(t)} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{(v)}\) is at equilibrium)
∴ \(\Delta S=\frac{\Delta H}{T}=\frac{30 \times 10^3}{300}=100 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}\)
Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Questions PSEB Class 11
Question 15. Standard entropies of X2, Y2 and XY3 are 60, 40 and 50 J K-1 mol-1 respectively. For the reaction \(1 / 2 X_2+3 / 2 Y_2 \rightleftharpoons X Y_3, \Delta H=-30 \mathrm{~kJ}\), to be at equilibrium, the temperature should be
- 750 K
- 1000 K
- 1250 K
- 500 K
Answer: 1. 750 K
Given reaction is \(\frac{1}{2} X_2+\frac{3}{2} Y_2 \rightleftharpoons X Y_3\)
We know, \(\Delta S^{\circ}=\Sigma S_{\text {products }}^{\circ}-\Sigma S_{\text {reactants }}^{\circ}\)
= \(50-\left(\frac{1}{2}(60)+\frac{3}{2}(40)\right)\)
= \(50-(30+60)=-40 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~K}^{-1} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\)
At equilibrium \(\Delta G^{\circ}=0\) \(\Delta H^{\circ}=T \Delta S^{\circ}\)
∴ T = \(\frac{\Delta H^{\circ}}{\Delta S^{\circ}}=\frac{-30 \times 10^3 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}{-40 \mathrm{JK}^{-1} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}=750 \mathrm{~K}\)
Question 16. For the vaporization of water at 1 atmospheric pressure, the values of ΔH and ΔS are 40.63 kJ mol-1 and 108.8 J K-1 mol-1 respectively. The temperature when Gibbs’ energy change (ΔG) for this transformation will be zero, is
- 273.4 K
- 393.4 K
- 373.4 K
- 293.4 K
Answer: 3. 373.4 K
According to Gibbs equation, ΔG = ΔH- TΔS
when ΔG=0, ΔH= TΔS
Given, ΔH = 40.63 kJ mol-1 = 40.63 x 10³ J mol-1
ΔS = 108.8 J K-1 mol-1
∴ T = \(\frac{\Delta H}{\Delta S}=\frac{40.63 \times 10^3}{108.8}=373.43 \mathrm{~K}\)
Question 17. The values of ΔH and ΔS for the reaction, \(\mathrm{C}_{\text {(graphite) }}+\mathrm{CO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_{(g)}\) are 170 kJ and 170 J K-1, respectively. This reaction will be spontaneous at
- 910 K
- 1110 K
- 510 K
- 710 K
Answer: 2. 1110 K
For the reaction to be spontaneous, ΔG = -ve
Given : ΔH = 170 kJ = 170 x 10³ J, ΔS = 170 J K-1
Applying, ΔG = ΔH – TΔS, the value of ΔG = -ve only when TΔS > ΔH, which is possible only when T = 1110 K
∴ ΔG = 170 x 10³ – (1110 x 170) = -18700J
Thus, the reaction is spontaneous at T = 1110 K
Question 18. For the gas phase reaction, \(\mathrm{PCl}_{5(\mathrm{~g})} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{PCl}_{3(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}\) which of the following conditions are correct?
- ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0
- ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
- ΔH = 0 and ΔS < 0
- ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
Answer: 4. ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
Gas phase reaction, \(\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{PCl}_{5(g)} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{PCl}_{3(g)}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \\
& \Delta H=\Delta E+\Delta n_g R T
\end{aligned}\)
Δng = Change in number of moles of products and reactants species.
Since Δng = +ve, hence ΔH = +ve also one inole of PCl5 is dissociated into two moles of PCl3 and Cl2 in the same phase.
Therefore, ΔS = SProduct– Sreactants
ΔS = +ve.
Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Questions PSEB Class 11
Question 19. Identify the correct statement for change of Gibbs energy for a system (ΔGsystem) at constant temperature and pressure.
- If ΔGsystem < 0, the process is not spontaneous.
- If AΔGsystem > 0, the process is spontaneous.
- If ΔGsystem = 0, the system has attained equilibrium.
- If ΔGsystem = 0, the system is still moving in a particular direction.
Answer: 3. If ΔGsystem = 0, the system has attained equilibrium.
The criteria for spontaneity of a process in terms of ΔG is as follows:
If ΔG is negative, the process is spontaneous’
If ΔG is positive, the process does not occur in the forward direction. It may occur in the backward direction
If ΔG is zero, the system is in equilibrium
Question 20. The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction: \(\mathrm{Br}_{2(l)}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2(g)} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{BrCl}_{(\mathrm{g})}\) are 30 kJ mol-1 and 105 J K-1 mol-1 respectively. The temperature at which the reaction will be in equilibrium is
- 300 K
- 285.7 K
- 273 K
- 450 K
Answer: 2. 285.7 K
⇒ \(\mathrm{Br}_{2(t)}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{BrCl}_{(\mathrm{g})}\)
Δ\(H=30 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}, \Delta S=105 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~K}^{-1} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\)
Δ\(\mathrm{S}=\frac{\Delta H}{T} \text { i.e. } 105=\frac{30}{T} \times 1000\)
∴ T = \(\frac{30 \times 1000}{105}=285.7 \mathrm{~K}\)
Question 21. Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to result in a spontaneous reaction?
- Exothermic and increasing disorder
- Exothermic and decreasing disorder
- Endothermic and increasing disorder
- Endothermic and decreasing disorder
Answer: 1. Exothermic and increasing disorder
For spontaneous reaction, ΔH= -ve, ΔS = +ve
Spontaneity depends upon both critical minimum energy and maximum randomness disorderness.
Question 22. A reaction occurs spontaneously if
- TΔS < ΔH and both ΔH and ΔS are +ve
- TΔS > ΔH and ΔH is +ve and ΔS is -ve
- TΔS > ΔH and both ΔH and ΔS are +ve
- TΔS = ΔH and both ΔT and ΔS are +ve.
Answer: 3. TΔS > ΔH and both ΔH and ΔS are +ve
ΔG = ΔH-TΔS
ΔG = -ve for spontaneous reaction
When ΔS = +ve, ΔH= +ve and TΔS > ΔH ⇒ ΔG = -ve
Question 23. The standard enthalpy and standard entropy changes for the oxidation of ammonia at 298 K are -382.64 kJ mol-1 and -145.6 J mol-1, respectively. Standard Gibbs’ energy change for the same reaction at 298 K is
- -221.1 kJ mol-1
- -339.3 kJ mol-1
- -439.3 kJ mol-1
- -523.2 kJ mol-1
Answer: 2. -339.3 kJ mol-1
Δ\(G=\Delta H-T \Delta S\)
= \(-382.64-298\left(\frac{-145.6}{1000}\right)\)
= \(-382.64+43.38=-339.3 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\)
Question 24. Considering entropy (S) as a thermodynamic parameter, the criterion for the spontaneity of any process is
- \(\Delta S_{\text {system }}+\Delta S_{\text {surroundings }}>0\)
- \(\Delta S_{\text {system }}-\Delta S_{\text {surroundings }}>0\)
- \(\Delta S_{\text {system }}>0\) only
- \(\Delta S_{\text {surroundings }}>0\) only.
Answer: 1. \(\Delta S_{\text {system }}+\Delta S_{\text {surroundings }}>0\)
For spontaneous process, \(\Delta S_{\text {total }}>0\).
∴ \(\Delta S_{\text {sys }}+\Delta S_{\text {surt }}>0\)
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 MCQs with Answers
Question 25. What is the entropy change (in J K-1 mol-1) when one mole of ice is converted into water at 0°C? (The enthalpy change for the conversion of ice to liquid water is 6.0 kJ mol-1 at 0°C.)
- 20.13
- 2.013
- 2.198
- 21.98
Answer: 4. 21.98
S = \(\frac{q_{\text {rev }}}{T}=\frac{6000}{273}=21.978 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~K}^{-1} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\)
Question 26. The densities of graphite and diamond at 298 K are 2.25 and 3.31 g cm-3, respectively. If the standard free energy difference (ΔG°) is equal to 1895 J mol-1, the pressure at which graphite will be transformed into diamond at 298 K is
- 9.92 x 108 Pa
- 9.92 x 107 Pa
- 9.92 x 106 Pa
- 9.92 x 105 Pa
Answer: 1. 9.92 x 108 Pa
ΔG° = – PΔV = Work done
ΔV \(=\left(\frac{12}{3.31}-\frac{12}{2.25}\right) \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~L}=-1.71 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~L} \)
Δ\(G^{\circ}=\text { Work done }=-\left(-1.71 \times 10^{-3}\right) \times P \times 101.3 \mathrm{~J}\)
P = \(\frac{1895}{1.71 \times 10^{-3} \times 101.3}=10.93 \times 10^3 \mathrm{~atm}\)
=11.08 x 108 Pa= 9.92 x 108 pa (1 atm = 101325 pa)
Question 27. The unit of entropy is
- J K-1 mol-1
- J mol-1
- J-1 K-1 mol-1
- J K mol-1
Answer: 1. J K-1 mol-1
Entropy change \((\Delta S)\) is given by \(\Delta S=\frac{q_{r e v}}{T}\)
∴ Unit of entropy \(=\mathrm{J} \mathrm{K}^{-1} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\)
Question 28. 2 moles of ideal gas at 27°C temperature is expanded reversibly from 2 lit. to 20 lit. Find entropy change. (R = 2 cal/mol K)
- 92.1
- 0
- 4
- 9.2
Answer: 4. 9.2
The change of entropy dS = \(\frac{q_{\text {rev }}}{T}\)
From the first law of thermodynamics, \(d q=d U+P d V=C_V d T+P d V\)
⇒ \(\frac{d q}{T}=C_V \frac{d T}{T}+\frac{P}{T} d V\)
⇒ \(\frac{d q}{T}=C_V \frac{d T}{T}+\frac{R d V}{V}\) (For 1mole of a gas \(\frac{P}{T}=\frac{R}{V}\))
dS = \(C_V \frac{d T}{T}+R \frac{d V}{V}\)
⇒ \(\Delta S=C_V \ln \frac{T_2}{T_1}+R \ln \frac{V_2}{V_1}\) for one mole of ideal gas
Here \(T_2=T_1=27^{\circ} \mathrm{C}=300 \mathrm{~K}\)
ln \(\frac{T_2}{T_1}=0\)
∴ \(\Delta S=R \ln \frac{V_2}{V_1}=2 \ln \frac{20}{2}=2 \ln 10=4.605\)
∴ ΔS=4.605 cal/mol K
Entropy change for 2 moles of gas = 2 x 4.605 cal/K = 9.2 cal/K
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 MCQs with Answers
Question 29. \(\mathrm{PbO}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{PbO}; \Delta G_{298}<0\) \(\mathrm{SnO}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{SnO}; \Delta G_{298}>0\) The most probable oxidation state of Pb and Sn will be
- Pb4+, Sn4+
- Pb4+, Sn2+
- Pb2+, Sn2+
- Pb2+, Sn4+
Answer: 4. Pb2+, Sn4+
The sign and magnitude of Gibbs free energy is a criterion of spontaneity for a process.
When ΔG > 0 or +ve, it means Gproducts >Greactants
as ΔG = Gproducts – Greactants
the reaction will not take place spontaneously, i.e. the reaction should be spontaneous in the reverse direction.
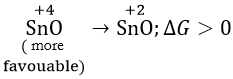
ΔG < 0 or -ve, the reaction or change occurs spontaneously.
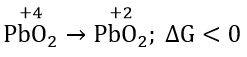
Question 30. Cell reaction is spontaneous when
- ΔG° is negative
- ΔG° is positive
- ΔE°red is positive
- ΔE°red is negative.
Answer: 1. ΔG° is negative
For a cell reaction to be spontaneous, ΔG° should be negative. As ΔG° = -nFE°cell, the value will be -ve only when E°cell is +ve.
Question 31. Identify the correct statement regarding entropy.
- At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of all crystalline substances is taken to be zero.
- At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is +ve.
- At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero.
- At 0°C, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero.
Answer: 3. At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero.
The entropy of a substance increases with an increase in temperature. However, at absolute zero, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken as zero, which is also called as third law of thermodynamics.
Question 32. Following reaction occurring in an automobile \(2 \mathrm{C}_8 \mathrm{H}_{18(\mathrm{~g})}+25 \mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \rightarrow 16 \mathrm{CO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+18 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{g})}\) The sign of ΔH, ΔS and ΔG would be
- -,+,+
- +,+,-
- +,-,+
- -,+,-
Answer: 4. -,+,-
- The given reaction is a combustion reaction, therefore ΔH is less than 0. Hence, ΔH is negative.
- Since there is an increase in the number of moles of gaseous products, therefore ΔS is positive.
- Since the reaction is spontaneous, therefore ΔG is negative.



