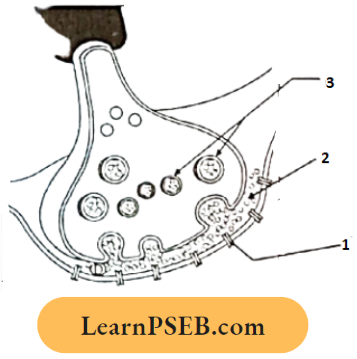
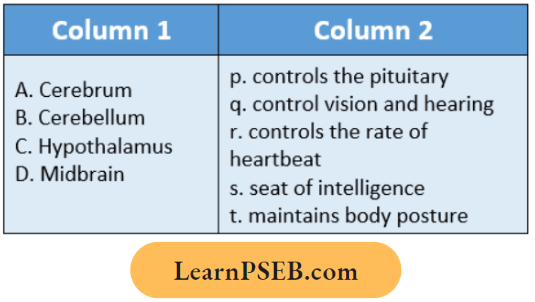
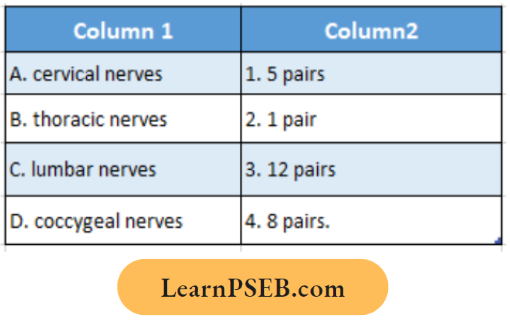
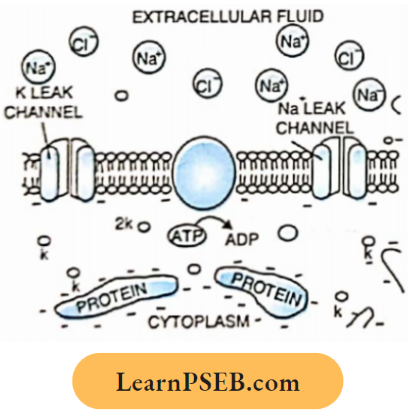
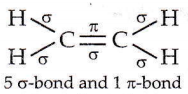Question 1. Among the following, which one is a wrong statement?
- PH5 and BiCl5 do not exist.
- pπ-dπ bonds are present in SO2.
- SeF4 and CH4 have the same shape.
- \(\mathrm{I}_3^{+}\) has bent geometry.
Answer: 3. SeF4 and CH4 have the same shape.
Question 2. The outer orbitals of C in an ethene molecule can be considered to be hybridized to give three equivalent sp² orbitals. The total number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in ethene molecule is
- 3 sigma (σ) and 2 pi (π) bonds
- 4 sigma (σ) and 1 pi (π) bonds
- 5 sigma (σ) and 1 pi (π) bonds
- 1 sigma (σ) and 2 pi (π) bonds.
Answer: 3. 5 sigma (σ) and 1 pi (π) bonds
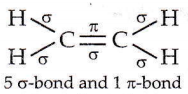
Question 3. In which of the following pairs both species have sp³ hybridization?
- \(\mathrm{SiF}_4, \mathrm{BeH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NF}_3, \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{NF}_3, \mathrm{BF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}, \mathrm{BF}_3\)
Read And Learn More Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{NF}_3, \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
NF3 and H2O are sp³-hybridised.
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs

Question 4. Which one of the following pairs is isostructural (i.e., having the same shape and hybridization)?
- \(\left[\mathrm{BCl}_3\right]\) and \(\left.\mathrm{BrCl}_3\right]\)
- \(\left[\mathrm{NH}_3\right]\) and \(\left.\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\right]\)
- \(\left[\mathrm{NF}_3\right]\) and \(\left.\mathrm{BF}_3\right]\)
- \(\left[\mathrm{BF}_4^{-}\right]\) and \(\left.\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\right]\)
Answer: 4. \(\left[\mathrm{BF}_4^{-}\right]\) and \(\left.\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\right]\)
- \(\mathrm{BCl}_3 \Rightarrow s p^2\), trigonal planar
- \(\mathrm{BrCl}_3 \Rightarrow s p^3 d\), T-shaped
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3 \Rightarrow s p^3\) pyramidal
- \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-} \Rightarrow s p^2\) trigonal planar
- \(\mathrm{NF}_3 \Rightarrow s p^3\), pyramidal
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3 \Rightarrow s p^2\), trigonal planar
- \(\mathrm{BF}_4^{-} \Rightarrow s p^3\), tetrahedral
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+} \Rightarrow s p^3\), tetrahedral
Question 5. Which of the two ions from the list given below that have the geometry that is explained by the same hybridization of orbitals, \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}, \mathrm{NO}_3^{-}, \mathrm{NH}_2^{-}, \mathrm{NH}_4^{+},\), SCN–?
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SCN}^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{NH}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{NH}_2^{-}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
⇒ \(\begin{array}{cc}
\text { Ions } & \text { Hybridisation } \\
\mathrm{NO}_2^{-} & s p^2 \\
\mathrm{NO}_3^{-} & s p^2 \\
\mathrm{NH}_2^{-} & s p^3 \\
\mathrm{NH}_4^{+} & s p^3 \\
\mathrm{SCN}^{-} & s p
\end{array}\)
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs
Question 6. In which of the following pairs of molecules/ions, do the central atoms have sp² hybridization?
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_2\) and \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\) and \(\mathrm{NH}_2^{-}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{BF}_3\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
The hybridisation of calculated as
H = \(\frac{1}{2}\left[\begin{array}{r}
\left(\begin{array}{l}
\text { No. of electrons } \\
\text { in valence shell } \\
\text { of atom }
\end{array}\right)+\left(\begin{array}{l}
\text { No. of monovalent } \\
\text { atoms around } \\
\text { central atom }
\end{array}\right) \\
-\left(\begin{array}{l}
\text { Charge on } \\
\text { cation }
\end{array}\right)+\left(\begin{array}{l}
\text { Charge on } \\
\text { anion }
\end{array}\right)
\end{array}\right]\)
∴ For \(\mathrm{BF}_3, H=\frac{1}{2}[(3)+(3)-(0)+(0)]\)
= \(3 \Rightarrow s p^2\) hybridisation
For \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}, H=\frac{1}{2}[(5)+(0)-(0)+(1)]\)
= \(3 \Rightarrow s p^2\) hybridisation.
Question 7. In which one of the following species the central atom has the type of hybridization which is not the same as that present in the other three?
- \(\mathrm{SF}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{I}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{SbCl}_5^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{PCl}_5\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{SbCl}_5^{2-}\)
Hybridization of the central atom can be calculated as
H = \(\frac{1}{2}\left[\begin{array}{c}
\left(\begin{array}{l}
\text { No. of valence } \\
\text { electrons in the } \\
\text { central atom }
\end{array}\right)+\left(\begin{array}{l}
\text { No. of monovalent } \\
\text { atoms around } \\
\text { central atom }
\end{array}\right) \\
-\left(\begin{array}{l}
\text { Charge on } \\
\text { cation }
\end{array}\right)+\left(\begin{array}{l}
\text { Charge on } \\
\text { anion }
\end{array}\right)
\end{array}\right]\)
Applying this formula we find that all the given species except [SbCl5]2- have central atoms with sp³d (corresponding to H = 5) hybridization. In [SbCl5]2-, Sb is sp³d² hybridized.
Question 8. In which of the following molecules the central atom does not have sp³ hybridization?
- \(\mathrm{CH}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{SF}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{SF}_4\)
For neutral molecules,
No. of electron pairs = No. of atoms bonded to it + 1/2[Gp. number of the central atoms – Valency of the central atom]
∴ For \(\mathrm{CH}_4\), number of \(e^{-}\) pairs = \(4+\frac{1}{2}[4-4]=4\left(s p^3\right.\) hybridisation)
For \(\mathrm{SF}_4\), number of \(e^{-}\) pairs \(=4+\frac{1}{2}[6-4]=5\left(s p^3 d\right.\) hybridisation)
For ions,
No. of electron pairs = No. of atoms bonded to it +1/2 [Gp. no. of central atom – Valency of central atom ± No. of electrons equals to the units of charge]
∴ For \(\mathrm{BF}_4^{-}\), number of \(e^{-}\) pairs = \(4+\frac{1}{2}[3-4+1]\)
= \(4(s p^3\) hybridisation)
∴ For \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\), number of \(e^{-}\) pairs = \(4+\frac{1}{2}[5-4-1]\)
= \(4\left(s p^3 \text { hybridisation }\right)\)
Question 9. Some of the properties of the two species, NO3– and H3O+ are described below. Which one of them is correct?
- Dissimilar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures.
- Isostructural with the same hybridization for the central atom.
- Isostructural with different hybridization for the central atom.
- Similar in hybridization for the central gap atom with different structures.
Answer: 1. Dissimilar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures.
No. of electron pairs at the central atom = No. of atoms bonded to it + 1/2[Group number of the central atom – Valency of the central atom ± No. of electrons equals the units of charge]
No. of electron pairs at the central atom in \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\) = 3 + 1/2(5-6+1) = 3 (sp² hybridization).
No. of electron pairs at the central atom in \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{O}^{+}=3+\frac{1}{2}[6-3-1]=4\) (sp³ hybridization)
Question 10. In which of the following molecules/ions BF3, NO–2, NH–2, and H2O, the central atom is sp² hybridized?
- \(\mathrm{NH}_2^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{NH}_2^{-}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{BF}_3\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
∴ \(\mathrm{BF}_3 \rightarrow s p^2, \mathrm{NO}_2^{-} \rightarrow s p^2, \mathrm{NH}_2^{-} \rightarrow s p^3, \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow s p^3\)
Question 11. Among the following, the pair in which the two species are not isostructural is
- \(\mathrm{SiF}_4\) and \(\mathrm{SF}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{IO}_3^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{XeO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{BH}_4^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{PF}_6^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{SF}_6\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{SiF}_4\) and \(\mathrm{SF}_4\)
SiF4 has a symmetrical tetrahedral shape which is due to sp³ hybridisation of the centrai silicon atom. SF4 has distorted tetrahedral or see-saw geometry which arises due to sp³d hybridisation of a central sulfur atom and due to the presence of one lone pair of electrons in one of the equatorial hybrid orbitals.
Question 12. Which of the following two are isostructural?
- \(\mathrm{XeF}_2, \mathrm{IF}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3, \mathrm{BF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}, \mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{PCl}_5, \mathrm{ICl}_5\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{XeF}_2, \mathrm{IF}_2^{-}\)
Compounds having the same shape with the same hybridization are known as isostructural.
∴ \(\mathrm{XeF}_2, \mathrm{IF}_2^{-}\) + both are sp³d hybridised linear molecules
Question 13. The bond length between hybridized carbon atoms and other carbon atoms is minimal in
- Propene
- Propyne
- Propane
- Butane.
Answer: 2. Propyne
The C-C bond length = 1.54 Å, C = C bond length = 1.34 Å, and C: C bond length = 1.20 Å.
Since propyne has a triple bond, therefore it has a minimum bond length.
Question 14. Which of the following has sp²-hybridisation?
- \(\mathrm{BeCl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_6\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_4\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_4\)
BeCl2 and C2H2 have sp-hybridisation and C2H6 has sp³-hybridisation. C2H4 has sp² hybridisation.
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs PSEB Class 11
Question 15. When the hybridization state of the carbon atom changes from sp³ to sp² and finally to sp, the angle between the hybridized orbitals
- Decreases gradually
- Decreases considerably
- Is not affected
- Increases progressively.
Answer: 4. Increases progressively.
The angle increases progressively, sp³ (109° 28′), sp² (120°), sp (180°).
Question 16. Which one of the following has the shortest carbon-carbon bond length?
- Benzene
- Ethene
- Ethyne
- Ethane
Answer: 3. Ethyne
There is a triple bond in the ethyne molecule (H – C ≡ C – H) and due to this triple bond, the carbon-carbon bond distance is the shortest in ethyne.
Question 17. Which structure is linear?
- \(\mathrm{SO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{CO}_2\)
The CO2 molecule is sp-hybridized and thus, it is linear while \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}\) is planar (sp² -hybridized), SO2 is an angular molecule with sp² hybridization and \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\) is tetrahedral (sp³-hybridised).
Question 18. A sp³ hybrid orbital contains
- 1/4 s-character
- 1/2 s-character
- 1/3 s-character
- 2/3 s-character.
Answer: 1. 1/4 s-character
sp³ orbital has 1/4(25%) s-character.
Question 19. The complex ion [Co(NH3)6]3+ is formed by sp³d² hybridization. Hence the ion should possess
- Octahedral geometry
- Tetrahedral geometry
- Square planar geometry
- Tetragonal geometry.
Answer: 1. Octahedral geometry
According to VSEPR theory, a molecule with 6 bond pairs must be octahedral.
Question 20. Which of the following molecules does not have a linear arrangement of atoms?
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{BeH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_2\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\)
For the linear arrangement of atoms, the hybridization is sp (bond angle = 180°).
Only H2S has sp³-hybridisation and hence it has an angular shape while C2H2, BeH2, and CO2 all involve sp-hybridization and hence, have a linear arrangement of atoms.
Question 21. In which one of the following molecules the central atom can be said to adopt sp² hybridization?
- \(\mathrm{BeF}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{BF}_3\)
BF3 involves sp²-hybridisation.
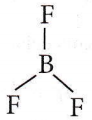
Question 22. Equilateral shape has
- sp hybridization
- sp² hybridisation
- sp³ hybridisation
- dsp³ hybridisation
Answer: 2. sp² hybridization
Equilateral or triangular planar shape involves sp² hybridization, for example, BCl3.
Question 23. The correct order of energies of molecular orbitals of N2 molecules is
- \(\sigma 1 s<\sigma^* 1 s< \sigma 2 s<\sigma^* 2 s<\sigma 2 p_z<\sigma^* 2 p_z\) \(<\left(\pi 2 p_x=\pi 2 p_y\right) <\left(\pi^* 2 p_x=\pi^* 2 p_y\right)\)
- \(\sigma 1 s<\sigma^* 1 s<\sigma 2 s<\sigma^* 2 s<\left(\pi 2 p_x\right.\left.=\pi 2 p_y\right)\) \(<\left(\pi^* 2 p_x=\pi^* 2 p_y\right)<\sigma 2 p_z<\sigma^* 2 p_z\)
- \(\sigma 1 s<\sigma^* 1 s<\sigma 2 s<\sigma^* 2 s<\left(\pi 2 p_x=\pi 2 p_y\right)\) \(<\sigma 2 p_z<\left(\pi^* 2 p_x=\pi^* 2 p_y\right)<\sigma^* 2 p_z\)
- \(\sigma 1 s<\sigma^* 1 s<\sigma 2 s<\sigma^* 2 s<\sigma 2 p_z<\left(\pi 2 p_x=\pi 2 p_y\right)\) \(<\left(\pi^* 2 p_x=\pi^* 2 p_y\right)<\sigma^* 2 p_z\)
Answer: 3. \(\sigma 1 s<\sigma^* 1 s<\sigma 2 s<\sigma^* 2 s<\left(\pi 2 p_x=\pi 2 p_y\right)\) \(<\sigma 2 p_z<\left(\pi^* 2 p_x=\pi^* 2 p_y\right)<\sigma^* 2 p_z\)
For molecules Li2, Be2, Br2, C2, and N2 the order of energies of various molecular orbitals is \(\sigma 1 s<\sigma^* 1 s<\sigma 2 s<\sigma^* 2 s<\left(\pi 2 p_x=\pi 2 p_y\right)<\sigma 2 p_z<\left(\pi^* 2 p_x\right. \left.=\pi^* 2 p_y\right) <\sigma^* 2 p_z\)
Question 24. Consider the following species: CN+, CN–, NO and CN. Which one of these will have the highest bond order?
- NO
- CN–
- CN+
- CN
Answer: 2. CN–
NO(15): \((\sigma 1 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2,(\sigma 2 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2,\left(\sigma 2 p_z\right)^2, \left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2=\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2,\left(\pi^* 2 p_x\right)^1=\left(\pi^* 2 p_y\right)^0\)
B.O. = \(\frac{10-5}{2}=2.5\)
∴ \(\mathrm{CN}^{-}(14):(\sigma 1 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2,(\sigma 2 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2,\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2=\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2,\left(\sigma 2 p_z\right)^2\)
B.O. = \(\frac{10-4}{2}=3\)
CN(13): \((\sigma 1 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2,(\sigma 2 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2,\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2=\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2,\left(\sigma 2 p_z\right)^1\)
B.O. = \(\frac{9-4}{2}=2.5\)
∴ \(\mathrm{CN}^{+}(12):(\sigma 1 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2,(\sigma 2 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2,\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2=\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2\)
B.O. \(=\frac{8-4}{2}=2\)
Hence, CN– has the highest bond order.
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs PSEB Class 11
Question 25. Which one of the following pairs of species have the same bond order?
- \(\mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{NO}^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{CN}^{-}, \mathrm{CO}\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2, \mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}, \mathrm{NO}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{CN}^{-}, \mathrm{CO}\)
Molecular orbital electronic configurations and bond order values are \(\mathrm{O}_2(16): \sigma 1 s^2, \sigma^* 1 s^2, \sigma 2 s^2, \sigma^* 2 s^2, \sigma 2 p_z^2, \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2,\pi^* 2 p_x^1=\pi^* 2 p_y^1\)
B.O. = \(\frac{1}{2}\left(N_b-N_a\right)=\frac{1}{2}(10-6)=2\)
∴ \(\mathrm{NO}^{+}(14): \sigma 1 s^2, \sigma^* 1 s^2, \sigma 2 s^2, \sigma^* 2 s^2, \sigma 2 p_z^2, \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2\)
B.O. = \(\frac{1}{2}(10-4)=3\)
∴ \(\mathrm{CN}^{-}(14): \sigma 1 s^2, \sigma^* 1 s^2, \sigma 2 s^2, \sigma^* 2 s^2, \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2, \sigma 2 p_z^2\)
B.O. = \(\frac{1}{2}(10-4)=3\)
CO(14): \(1 s^2, \sigma^* 1 s^2, \sigma 2 s^2, \sigma^* 2 s^2, \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2, \sigma 2 p_z^2\)
B.O. = \(\frac{1}{2}(10-4)=3\)
∴ \(N_2\) (14): \(\sigma 1 s^2, \sigma^* 1 s^2, \sigma 2 s^2, \sigma^* 2 s^2, \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2, \sigma 2 p_z^2\)
B.O. = \(\frac{1}{2}(10-4)=3\)
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}(17)=\sigma 1 s^2, \sigma^* 1 s^2, \sigma 2 s^2, \sigma^* 2 s^2, \sigma 2 p_z^2, \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2,\pi^* 2 p_x^2=\pi^* 2 p_y^1\)
B.O. = \(\frac{1}{2}(10-7)=1.5\)
NO(15): \(\sigma 1 s^2, \sigma^* 1 s^2, \sigma 2 s^2, \sigma^* 2 s^2, \sigma 2 p_z^2, \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2, \pi^* 2 p_x^1\)
B.O. = \(\frac{1}{2}(10-5)=2.5\)
Question 26. Which of the following is paramagnetic?
- \(\mathrm{CN}^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2{ }^{-}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{O}_2{ }^{-}\)
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}(17)\) superoxide has one unpaired electron. \(\sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^2=\pi^* 2 p_y^1\)
Question 27. The pair of species that has the same bond order in the following is
- \(\mathrm{CO}, \mathrm{NO}^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}^{-}, \mathrm{CN}^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{~N}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{~B}_2\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{CO}, \mathrm{NO}^{+}\)
CO = 6 + 8 = 14electrons
NO+ = 7 + B – 1 = 14 electrons
Electronic configuration of \(\mathrm{NO}^{+}:\sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2\)
Electronic configuration of \(\mathrm{CO}:\sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2\)
So, both have bond order = \(\frac{10-4}{2}=3\)
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 MCQs with Answers
Question 28. In which of the following ionization processes does the bond energy increase and the magnetic behavior change from paramagnetic to diamagnetic?
- \(\mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{O}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO} \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{N}_2^{+}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{NO} \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}^{+}\)
Molecular orbital configuration of \(\mathrm{O}_2(16): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^1 \pi^* 2 p_y{ }^1\)
⇒ Paramagnetic-Bond order =\(\frac{10-6}{2}=2\)
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}(15): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^1\)
⇒ Paramagnetic- Bond order = \(\frac{10-5}{2}=2.5\)
∴ \(\mathrm{C}_2(12): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2\)
⇒ Diamagnetic ; Bond order \(=\frac{8-4}{2}=2\)
∴ \(\mathrm{C}_2^{+}(11): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y{ }^1\)
⇒ Paramagnetic; Bond order = \(\frac{7-4}{2}=1.5\)
∴ \(\mathrm{NO}(15): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^{\star} 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^{\star} 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^1\)
⇒ Paramagnetic;Bond order \(=\frac{10-5}{2}=2.5\)
∴ \(\mathrm{NO}^{+}(14): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2\)
⇒ Diamagnetic; Bond order = \(\frac{10-4}{2}=3\)
∴ \(\mathrm{~N}_2(14): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \)
⇒ Diamagnetic; Bond order = \(\frac{10-4}{2}=3\)
∴ \(\mathrm{~N}_2^{+}(13): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2 \sigma 2 p_z^1\)
⇒ Paramagnetic Bond order = \(\frac{9-4}{2.5}=2.5\)
Thus from NO → NO+, bond order increases i.e., bond energy increases, and magnetic behaviour changes from paramagnetic to diamagnetic
Question 29. The pair of species with the same bond order is
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}, \mathrm{B}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}, \mathrm{NO}^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}, \mathrm{CO}\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2, \mathrm{O}_2\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}, \mathrm{B}_2\)
⇒ \(\begin{array}{ll}
\mathrm{O}_2^{2-} \rightarrow 1.0 & \mathrm{~B}_2 \rightarrow 1.0 \\
\mathrm{O}_2^{+} \rightarrow 2.5 & \mathrm{NO}^{+} \rightarrow 3.0 \\
\mathrm{NO} \rightarrow 2.5 & \mathrm{CO} \rightarrow 3.0 \\
\mathrm{~N}_2 \rightarrow 3.0 & \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow 2.0
\end{array}\)
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 MCQs with Answers
Question 30. During the change of O2 to O–2 ion, the electron adds on which one of the following orbitals?
- π* orbital
- π orbital
- σ* orbital
- σ orbital
Answer: 1. π* orbital
Electronic configuration of O2(16) \(\sigma(1 s)^2 \sigma^*(1 s)^2 \sigma(2 s)^2 \sigma^*(2 s)^2 \sigma\left(2 p_z\right)^2 \pi\left(2 p_x\right)^2=\pi\left(2 p_y\right)^2 \pi^*\left(2 p_x\right)^1=\pi^*\left(2 p_y\right)^1\)
Question 31. Which of the following is isoelectronic?
- \(\mathrm{CO}_2, \mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}, \mathrm{CO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CN}^{-}, \mathrm{CO}\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_2, \mathrm{CO}_2\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{CN}^{-}, \mathrm{CO}\)
In CO, the number of electrons = 6 + 8 = 14 Molecular orbital electronic configuration of
CO: \((\sigma 1 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2(\sigma 2 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2\left(\sigma 2 p_z\right)^2\)
CN– have also gets (6 + 7 + 1) 14 electrons and the configuration is similar to that of CO.
CN– and CO are isoelectronic species.
Question 32. Which species does not exhibit paramagnetism?
- \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{CO}\)
In ‘CO’ (14 electrons), there is no unpaired electron in its molecular orbital. Therefore, this does not exhibit paramagnetism.
Question 33. The number of anti-bonding electron pairs in O22- molecular ion on the basis of the molecular orbital theory is (Atomic number of O is 8.)
- 3
- 2
- 5
- 4
Answer: 4. 4
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}(18):(\sigma 1 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2,(\sigma 2 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2,\left(\sigma 2 p_z\right)^2,\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2, \left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2,\left(\pi^{\star} 2 p_x\right)^2,\left(\pi^{\star} 2 p_y\right)^2\)
Thus the number of electrons in O22- ion is 8(4 pairs).
Question 34. Which of the following species is paramagnetic?
- \(\mathrm{CO}\)
- \(\mathrm{CN}^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{NO}\)
As per their molecular orbital electronic configurations \(\mathrm{CO}, \mathrm{CN}^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\) are diamagnetic and NO is paramagnetic.
Question 35. Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
- The bond orders of \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}, \mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{O}_2^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\) are 2.5, 2, 1.5 and 1, respectively.
- C2 molecule has four electrons in its two degenerate Tt molecular orbitals
- \(\mathrm{H}_2^{+}\) ion has one electron.
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\) ion is diamagnetic.
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\) ion is diamagnetic.
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}: \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^1\)
Due to the presence of one unpaired electron, \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\) is paramagnetic in nature.
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 MCQs
Question 36. Identify a molecule that does not exist.
- \(\mathrm{He}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Li}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{He}_2\)
He2 does not exist as it has zero bond order \(\mathrm{He}_2: \sigma 1 s^2, \sigma^* 1 s^2\)
Bond order = \(\frac{1}{2}\left(N_b-N_a\right)=\frac{1}{2}(2-2)=0\)
Question 37. Which of the following diatomic molecular species has only π bonds according to Molecular Orbital Theory?
- Be2
- O2
- N2
- C2
Answer: 4. C2
∴ \(\mathrm{Be}_2(8): K K \sigma(2 s)^2 \sigma^*(2 s)^2\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2(16): K K \sigma(2 s)^2 \sigma^*(2 s)^2 \sigma\left(2 p_z\right)^2 \pi\left(2 p_x\right)^2 \pi\left(2 p_y\right)^2 \pi^*\left(2 p_x\right)^1 \pi^*\left(2 p_y\right)^1\)
- \(\mathrm{~N}_2(14): K K \sigma(2 s)^2 \sigma^*(2 s)^2 \pi\left(2 p_x\right)^2 \pi\left(2 p_y\right)^2 \sigma\left(2 p_z\right)^2\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2(12): K K \sigma(2 s)^2 \sigma^*(2 s)^2 \pi\left(2 p_x\right)^2 \pi\left(2 p_y\right)^2\)
Therefore, C2 contains 2 π bonds as, it has 4 electrons in two pi-molecular orbitals.
Question 38. Which of the following is paramagnetic?
- N2
- H2
- Li2
- O2
Answer: 4. O2
∴ \(\mathrm{N}_2(14): K K \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2\); Diamagnetic
- \(\mathrm{H}_2(2): \sigma l s^2\); Diamagnetic
- \(\mathrm{Li}_2(6): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2\); Diamagnetic
- \(\mathrm{O}_2(16): \sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^{\star} 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^{\star} 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2\)
- \(\pi^* 2 p_x^1=\pi^* 2 p_y^1 ;\) Paramagnetic
Question 39. Decreasing order of stability of \(\mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{O}_2^{-}, \mathrm{O}_2^{+}\) and \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}>\mathrm{O}_2^{-}>\mathrm{O}_2>\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2>\mathrm{O}_2^{+}>\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}>\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}>\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}>\mathrm{O}_2^{+}>\mathrm{O}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}>\mathrm{O}_2>\mathrm{O}_2^{-}>\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}>\mathrm{O}_2>\mathrm{O}_2^{-}>\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\)
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2(16): K K \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^1=\pi^* 2 p_y^1\)
Bond order \(=\frac{1}{2}(8-4)=2\)
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}(18): K K \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^2=\pi^* 2 p_y^2\)
Bond order = \(\frac{1}{2}(8-6)=1\)
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}(17): K K \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^2=\pi^* 2 p_y{ }^1\)
Bond order \(=\frac{1}{2}(8-5)=1.5\)
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}(15): K K \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^1\)
Bond order \(=\frac{1}{2}(8-3)=2.5\)
As, bond order ∝ stability
The decreasing order of stability is \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}>\mathrm{O}_2>\mathrm{O}_2^{-}>\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\)
PSEB Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 MCQs
Question 40. The correct bond order in the following species is
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{O}_2^{2+}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{O}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{2+}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{O}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{2+}\)
∴ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{O}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{2+}\)
B.O.: 1.5 = 2.5 3.0
Question 41. Bond order of 1.5 is shown by
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
Configuration of \(\mathrm{O}_2(16)\): \(\sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2 \sigma 2 p_z^2 \pi 2 p_x^2 \pi 2 p_y^2 \pi^* 2 p_x^1 \pi^* 2 p_y^1\)
Bond order \(=\frac{\begin{array}{l}\text { No. of } e^{-} \text {in } \\ \text { bonding M.O. }-\end{array} \begin{array}{c}\text { No. of } e^{–} \text {in } \\ \text { antibonding M.O. }\end{array}}{2}\)
Bond order of \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}=\frac{10-5}{2}=2.5\)
Bond order of \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}=\frac{10-7}{2}=1.5\)
Bond order of \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}=\frac{10-8}{2}=1.0\)
Bond order of \(\mathrm{O}_2=\frac{10-6}{2}=2\)
Question 42. Which of the following has the minimum bond length?
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\)
Electronic configuration \(\mathrm{O}_2: \mathrm{KK}(\sigma 2 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2\left(\sigma 2 p_y\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2\left(\pi^* 2 p_x\right)^1\left(\pi^* 2 p_y\right)^1\)
Bond order = \(\frac{1}{2}(8-4)=2\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\): Bond order = \(\frac{1}{2}(8-3)=2 \frac{1}{2}\)
⇒\(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\): Bond order = \(\frac{1}{2}(8-5)=1 \frac{1}{2}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}: \text { Bond order }=\frac{1}{2}(8-6)=1\)
As bond order increases, bond length decreases
Question 43. The pairs of species of oxygen and their magnetic behavior are noted below. Which of the following presents the correct description?
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}, \mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\) – Both diamagnetic
- \(\mathrm{O}^{+}, \mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\) – Both paramagnetic
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}, \mathrm{O}_2\) – Both paramagnetic
- \(\mathrm{O}, \mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\) – Both paramagnetic
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}, \mathrm{O}_2\) – Both paramagnetic
O+2 and O2 are paramagnetic in nature as they contain one and two unpaired electrons respectively.
Question 44. Which one of the following species does not exist under normal conditions?
- \(\mathrm{Be}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{Be}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{B}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Li}_2\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{Be}_2\)
Be2 does not exist.
Be2 has an electronic configuration of: \(\sigma 1 s^2 \sigma^* 1 s^2 \sigma 2 s^2 \sigma^* 2 s^2\)
∴ Bond order = \(\frac{4-4}{2}=0\) Thus, \(\mathrm{Be}_2\) does not exist.
Question 45. According to MO theory which of the lists ranks the nitrogen species in terms of increasing bond order?
- \(\mathrm{N}_2^{2-}<\mathrm{N}_2^{-}<\mathrm{N}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2<\mathrm{N}_2^{2-}<\mathrm{N}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2^{-}<\mathrm{N}_2^{2-}<\mathrm{N}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2^{-}<\mathrm{N}_2<\mathrm{N}_2^{2-}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{N}_2^{2-}<\mathrm{N}_2^{-}<\mathrm{N}_2\)
According to MOT, the molecular orbital electronic configuration of
∴ \(\mathrm{N}_2(14):(\sigma 1 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2(\sigma 2 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2\left(\sigma 2 p_z\right)^2\)
B.O = \(\frac{10-4}{2}=3\)
∴ \(\mathrm{~N}_2^{-}(15):(\sigma 1 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2(\sigma 2 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2\)
∴ \(\left(\sigma 2 p_z\right)^2\left(\pi^* 2 p_x\right)^1\)
B.O = \(\frac{10-5}{2}=2.5\)
∴ \(\mathrm{~N}_2^{2-}(16):(\sigma 1 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2(\sigma 2 s)^2\left(\sigma^* 2 s\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2\)
B.O. = \(\frac{10-6}{2}=2\)
Hence, bond order increases as: \(\mathrm{N}_2^{2-}<\mathrm{N}_2^{-}<\mathrm{N}_2\)
Question 46. Right order of dissociation energy N2 and \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\) is
- \(\mathrm{N}_2>\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2=\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}>\mathrm{N}_2\)
- None.
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{N}_2>\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\)
∴ \(\mathrm{N}_2(14):(\sigma 1 s)^2,\left(\sigma^* 1 s\right)^2,(\sigma 2 s)^2,\left(\sigma^{\star} 2 s\right)^2\) \(\left(\pi 2 p_x\right)^2,\left(\pi 2 p_y\right)^2,\left(\sigma 2 p_z\right)^2\)
In \(N_2\), bond order \(=\frac{N_b-N_a}{2}=\frac{10-4}{2}=3\)
In \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\), bond order \(=\frac{9-4}{2}=2 \cdot 5\)
As the bond order in \(\mathrm{N}_2\) is more than \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\) so the dissociation energy of \(\mathrm{N}_2\) is higher than \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\)
Question 47. N2 and O2 are converted into monocations, \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\) and \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\) respectively. Which is wrong?
- In \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\), paramagnetism decreases.
- \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\) becomes diamagnetic.
- In \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\), the N-N bond weakens.
- In \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\), the O-O bond order increases.
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\) becomes diamagnetic.
Diamagnetism is caused due to the absence of unpaired electrons. But in \(\mathrm{N}_2^{+}\) there is an unpaired electron So, it is paramagnetic.
Question 48. N2 and O2 are converted into monoanionic N–2 and O–2 respectively, which of the following statements is wrong?
- In \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\) bond length increases.
- \(\mathrm{N}_2^{-}\) becomes diamagnetic.
- In \(\mathrm{N}_2^{-}\), N-N bond weakens.
- In \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\), the O-O bond order decreases.
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{N}_2^{-}\) becomes diamagnetic.
∴ \(\mathrm{N}_2^{-}\) becomes paramagnetic due to one unpaired electron in \(\pi^* 2 p_x\), orbital.
Question 49. The ground state electronic configuration of valence shell electrons in nitrogen molecule (N2) is written as \(K K, \sigma 2 s^2, \sigma^* 2 s^2, \pi 2 p_x^2=\pi 2 p_y^2, \sigma 2 p_z^2\). Hence the bond order in nitrogen molecules is
- 2
- 3
- 0
- 1
Answer: 2. 3
Number of electrons in bonding orbitals, \(\mathrm{N}_b\) = 10 and number of electrons in antibonding orbitals, \(\mathrm{N}_a\) = 4
Therefore bond order = 1/2(\(\mathrm{N}_b\) – \(\mathrm{N}_a\)) = 1/2(10 – 4) = 3
Question 50. Which of the following molecules has the highest bond order?
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{2-}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}\)
The bond order of \(\mathrm{O}_2^{+}=2.5, \mathrm{O}_2^{2-}=1\), \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\) = 1 .5 and that of O2 = 2
Question 51. Which one of the following compounds shows the presence of an intramolecular hydrogen bond?
- H2O2
- HCN
- Cellulose
- Concentrated acetic acid
Answer: 3. Cellulose
H2O2, HCN and cons. CH3COOH forms intermolecular hydrogen bonding while cellulose has intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Question 51. In X – H….Y, X, and Y both are electronegative elements. Then
- Electron density on X will increase and on H will decrease
- In both electron density will increase
- In both electron density will decrease
- On X electron density will decrease and on H increases.
Answer: 1. Electron density on X will increase and on H will decrease
∴ \({ }^{\delta-} X-\mathrm{H}^{\delta+} \ldots . . . Y\), the electrons of the covalent bon<l are shifted towards the more electronegative atom’ This partially positively charged H-atom forms hydrogen bond with the other more electronegative atom.
Question 52. Strongest hydrogen bond is shown by
- Water
- Ammonia
- Hydrogen fluoride
- Hydrogen sulfide.
Answer: 3. Hydrogen fluoride
H – F shows the strongest H-bonds because fluorine is the most electronegative.
Question 53. Which one shows maximum hydrogen bonding?
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{Se}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\)
- \(\mathrm{HF}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
H2O shelves maximum H-bonding because each H2O molecule is linked to four H2O molecules through H-bonds.